This document provides an introduction and overview of JSP (JavaServer Pages) technology. Key points include:
- JSP pages allow for mixing HTML and Java code to create dynamic web applications more easily than servlets alone.
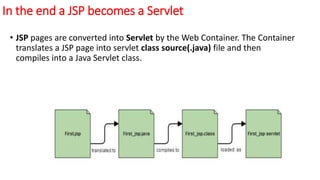
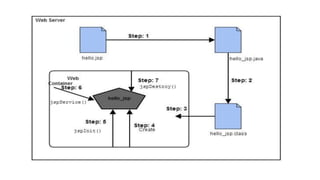
- JSP pages are translated into servlets by the web container before execution.
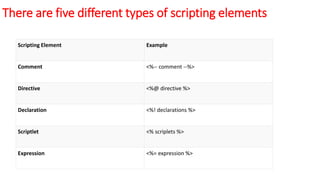
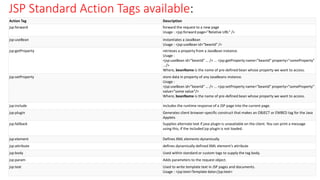
- JSP offers implicit objects, standard actions, tags and directives to simplify coding dynamic content.
- Exception handling and lifecycle management are similar to servlets in JSP.
- Java beans can be used to encapsulate reusable data and logic in JSP applications.