This document provides information on Java applets including:
- An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser context
- It must extend the Applet class or JApplet class
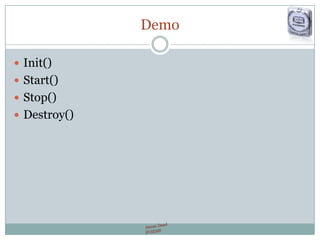
- Includes the applet lifecycle of loading, creating, initializing, starting, stopping, and destroying
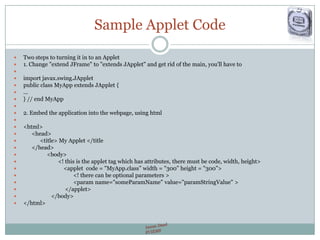
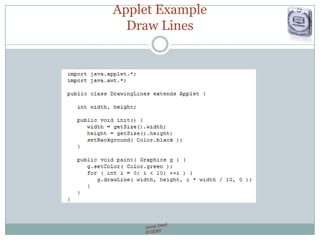
- Provides sample code for creating a basic "MyApp" applet class and embedding it in an HTML page
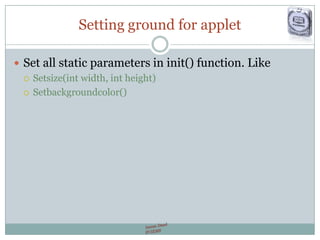
- Discusses restrictions on applets and demonstrates creating an applet project in NetBeans