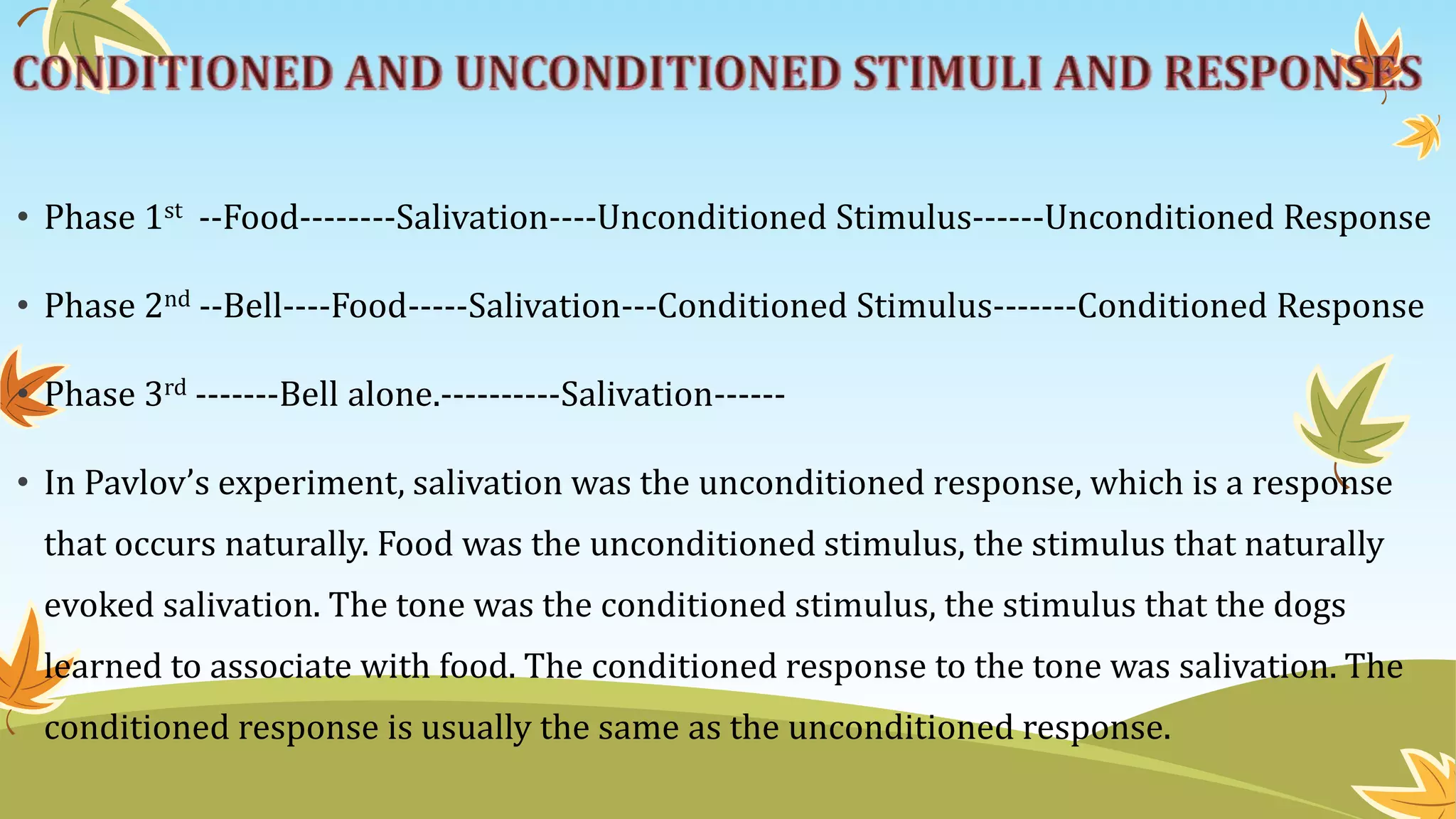
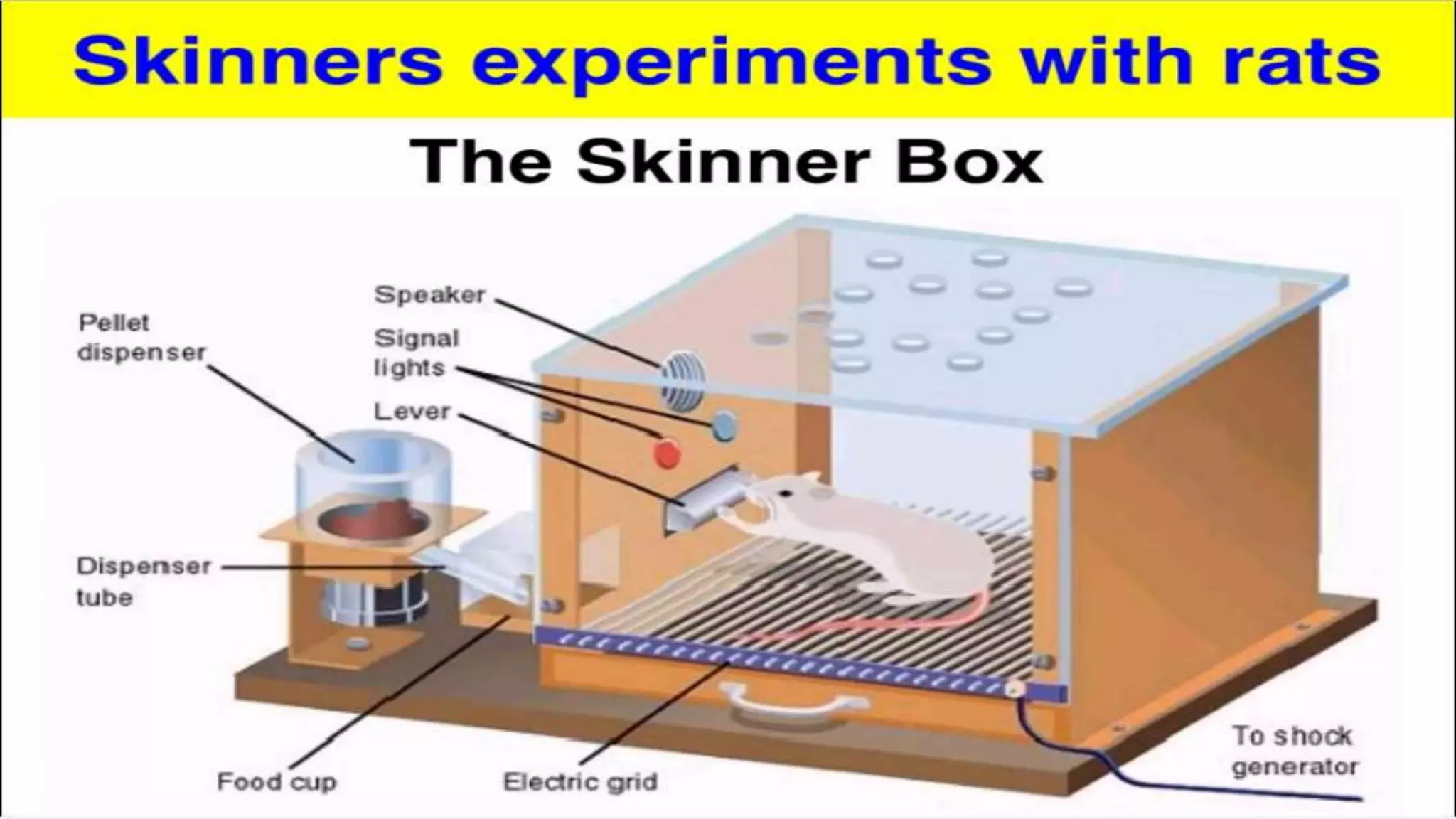
Classical conditioning involves learning through association. Ivan Pavlov's dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with food. They began to salivate in response to the bell alone. Operant conditioning is learning through consequences. B.F. Skinner studied how responses are controlled by their outcomes using devices like the Skinner box. Reinforcement increases behaviors by adding or removing stimuli, while punishment decreases behaviors through similar means.