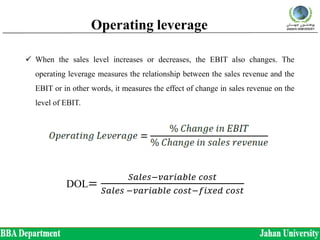
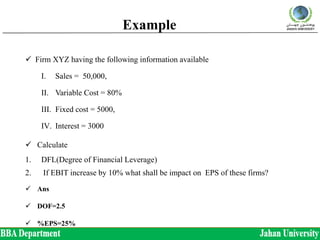
The document discusses three types of leverage: operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage. Operating leverage measures the relationship between sales and earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). Financial leverage measures the relationship between EBIT and earnings per share (EPS). Combined leverage can be defined as the percentage change in EPS given a certain percentage change in sales. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate the degree of each type of leverage.