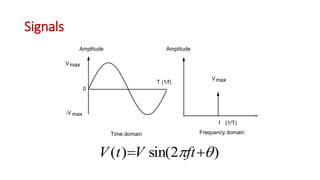
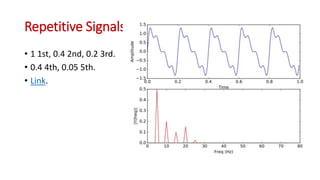
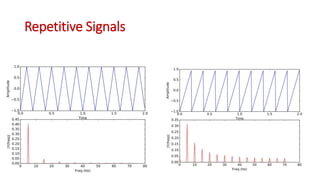
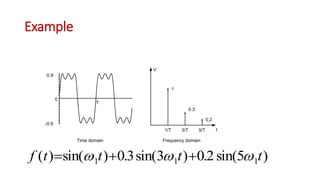
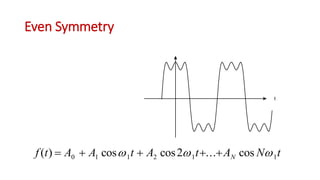
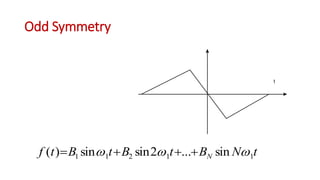
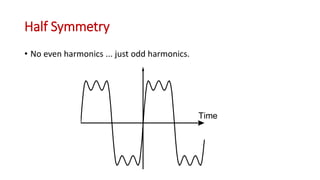
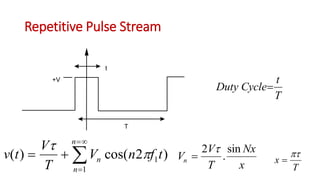
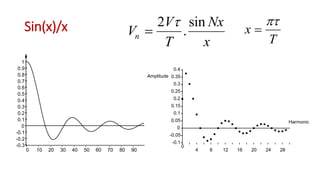
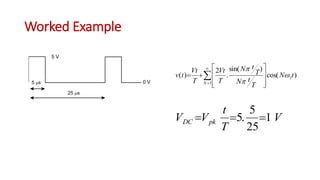
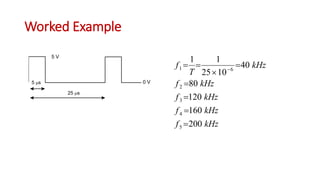
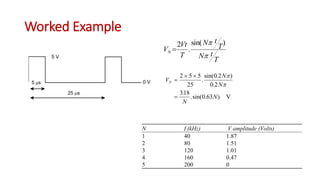
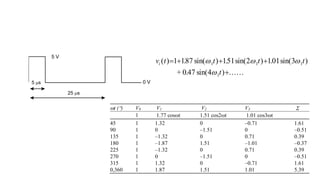
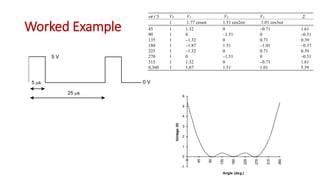
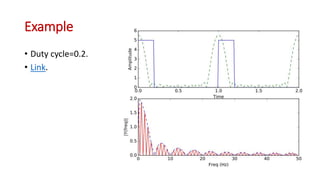
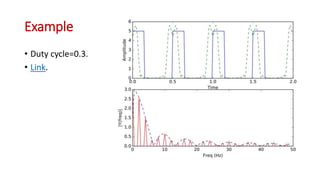
This document discusses the analysis of digital pulses in both the time and frequency domains. It begins by introducing signals and repetitive signals, describing their representations in both domains. It then discusses repetitive pulse streams and their Fourier series representations. Specific topics covered include duty cycle, the sine function divided by x, even symmetry, odd symmetry, and half symmetry. Worked examples are provided to demonstrate analyzing a pulse stream and calculating its harmonic amplitudes. The document concludes with examples of different duty cycle pulse streams.