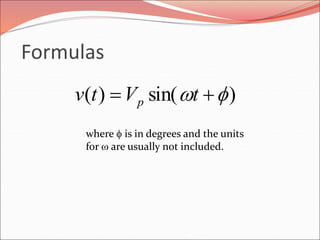
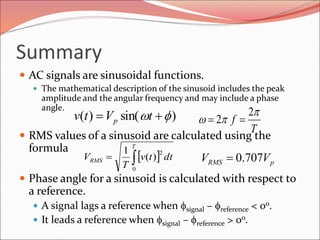
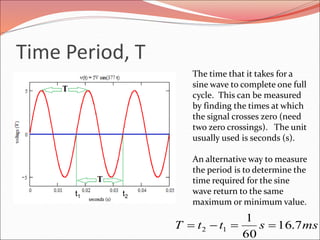
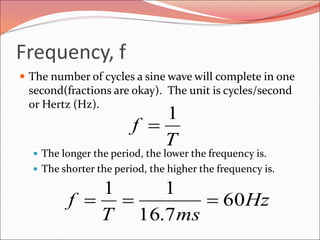
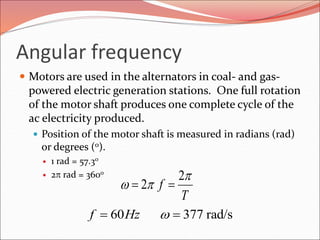
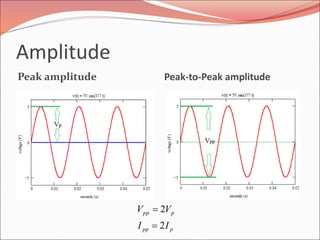
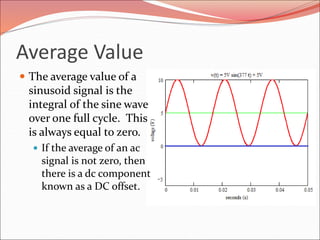
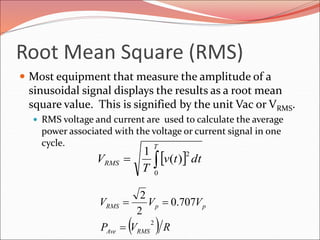
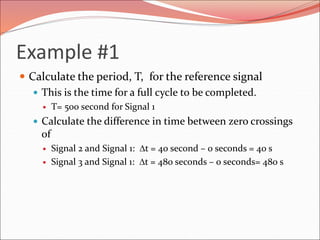
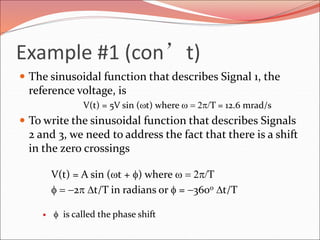
This document discusses sinusoidal waves and their characteristics. It defines key terms like period, frequency, amplitude, phase angle, and explains how to calculate these values. Period is the time for one full cycle, frequency is the number of cycles per second. Amplitude refers to the maximum voltage or current values. Phase angle describes the shift between two sinusoidal waves with the same frequency. A lagging signal has a negative phase angle compared to the reference, while a leading signal has a positive phase angle.



![Instantaneous Value
Instantaneous value or amplitude is the magnitude of
the sinusoid at a point in time.
VssradVtvmst
VssradVtvst
tsradVtv
94.2)]01.0)(/377sin[(5)(10
0)]0)(/377sin[(5)(0
])/377sin[(5)(
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alternatingcurrentvoltages1-170302013318/85/Alternating-current-voltages-10-320.jpg)

![Lagging and Leading
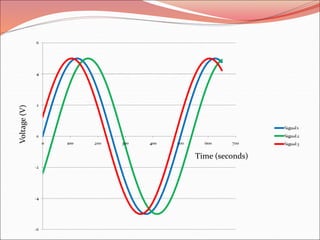
Don’t get fooled by the positions of the curves on the
graph!
Signal 2: V(t) = 5V sin [12.6 mrad/s)t – 28.8o]
f is -0.502 radians or -28.8 degrees
Signal 2 lags Signal 1 as it reaches zero at a later time than Signal 1
Signal 3: V(t) = 5V sin [12.6 mrad/s)t + 14.4o]
f is 0.251 radians or 14.4 degrees
Signal 3 leads Signal 1 as it reaches zero at an earlier time than
Signal 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alternatingcurrentvoltages1-170302013318/85/Alternating-current-voltages-18-320.jpg)