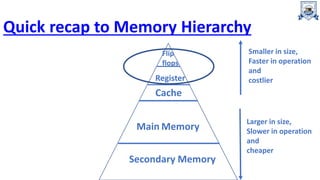
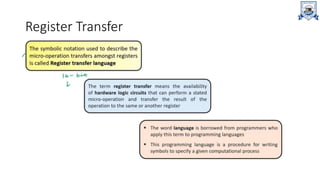
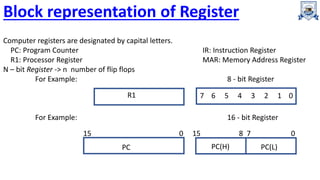
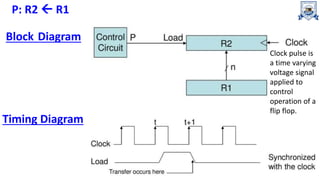
Registers are the fastest type of memory in a computer and are made up of flip-flops. There are two types of registers: special purpose registers that are used internally by the processor, and general purpose registers that can be accessed by programming to store intermediate results. Important special purpose registers include the program counter, memory address register, and instruction register. Register transfer language describes the transfer of data between registers using microoperations, and memory transfer operations describe transferring data between registers and memory.











![Memory Transfer
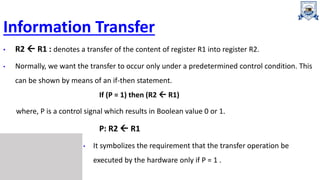
The transfer of information from a memory word to the outside environment is called a
READ
operation.
Read: DR M[AR]
The transfer of new information to be stored into the memory is called a WRITE operation.
Write: M[AR] DR
A memory word will be symbolized by the letter M.
M[AR]: to specify the address of M when writing memory transfer
operations, address is enclosed in square brackets.(here, AR is
address register)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3registerincoa-230209030112-29292860/85/3_Register-in-COA-ppt-17-320.jpg)



