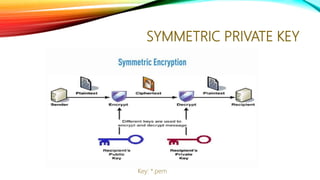
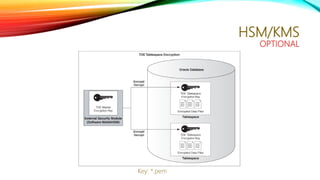
The document is a summary of a technology catch-up session led by Amr Salah, a middleware and cloud expert with over eight years of experience. It covers topics such as software engineering processes, data and program security, data protection methods, security policies, and role definitions within cybersecurity. It also includes a call to action for further engagement through a Slack channel and a registration link.