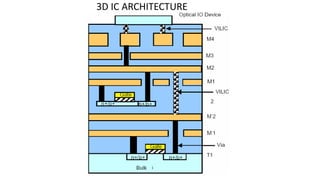
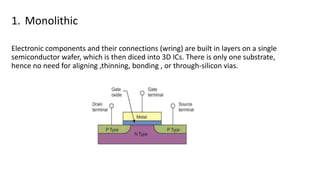
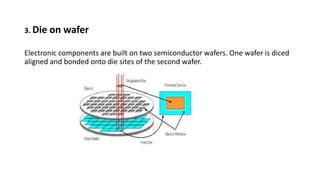
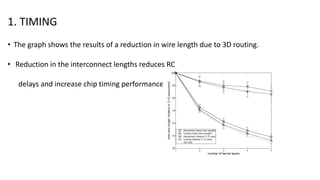
3D integrated circuits can alleviate problems associated with increasing chip complexity by integrating multiple layers of active components vertically. This reduces interconnect length and delays, lowers power dissipation, and facilitates heterogeneous integration. 3D ICs can be constructed using different techniques like monolithic, wafer-on-wafer, die-on-wafer, and die-on-die approaches. The technology offers advantages like improved performance, reduced chip area and costs, and better noise isolation of digital and analog circuits. While thermal and reliability issues require attention, 3D ICs are expected to replace conventional chips in applications like mobile devices due to their reduced size, cost and power consumption.