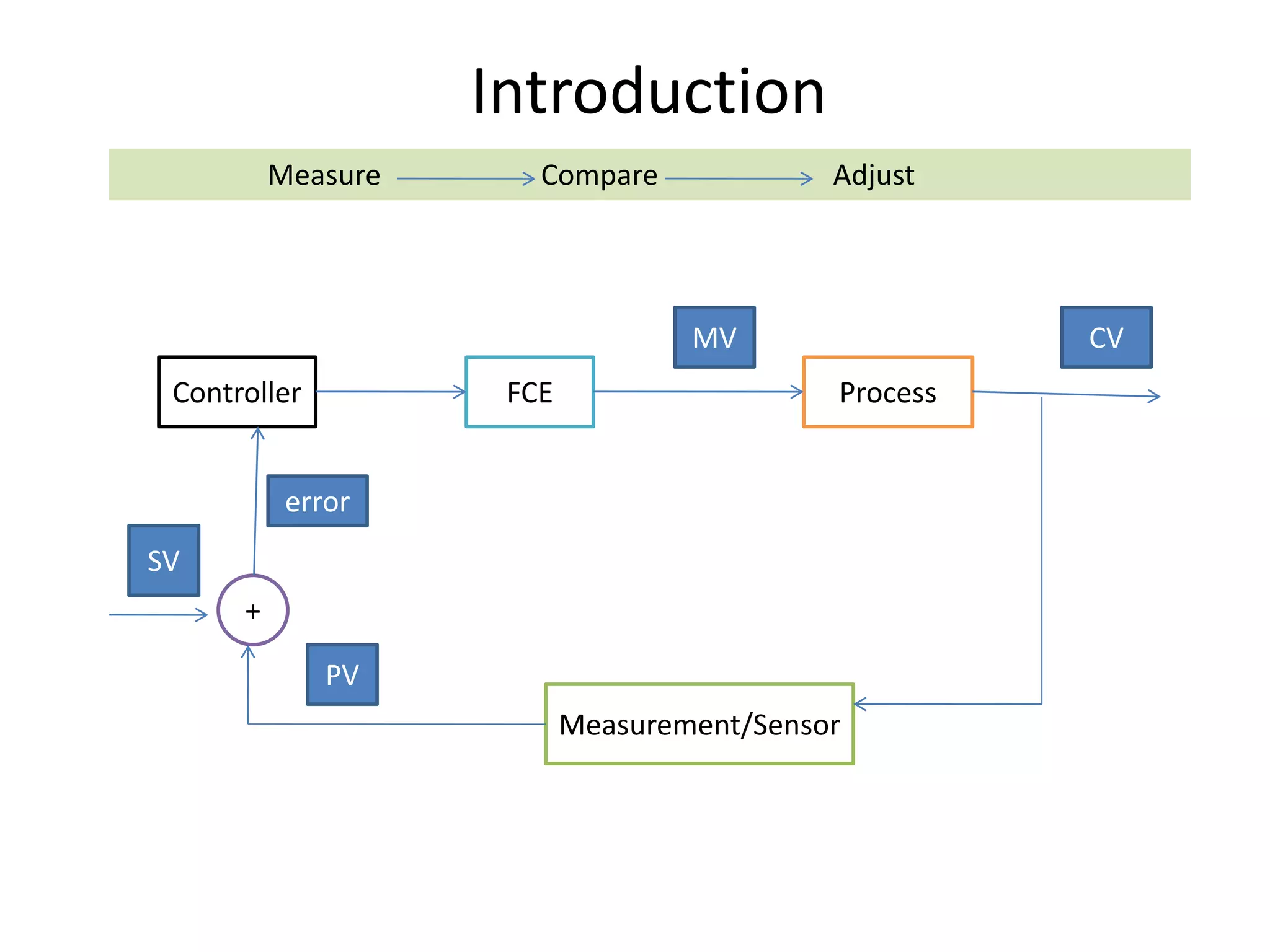
This document provides an introduction to process control and dynamics laboratory experiments. It discusses key process control concepts like feedback control loops, controllers, sensors, setpoints, process values, and manipulated variables. The laboratory experiments will focus on controlling processes like gas pressure, level and flow, temperature, and pH using different control methods including open loop, P-control, PI control, and PID control. Students will learn to understand control systems, illustrate instrumentation, analyze controller responses, tune controllers to find optimal PID settings, and use the Ziegler-Nichols method to determine PID values from open loop tests. System behaviors like underdamped, critically damped, and overdamped responses will also be explored.