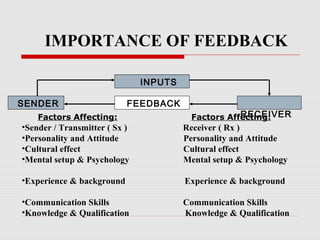
The document discusses various aspects of oral communication including face-to-face conversations, telephonic conversations, lectures, speeches and other forms of oral communication. It outlines the PRIDE model for effective communication and describes merits like the use of facial expressions and gestures as well as limitations such as the inability to reach a large group. Various principles of successful oral communication are provided along with the importance of feedback. Different modes of nonverbal communication such as pictures, posters and films are also examined.