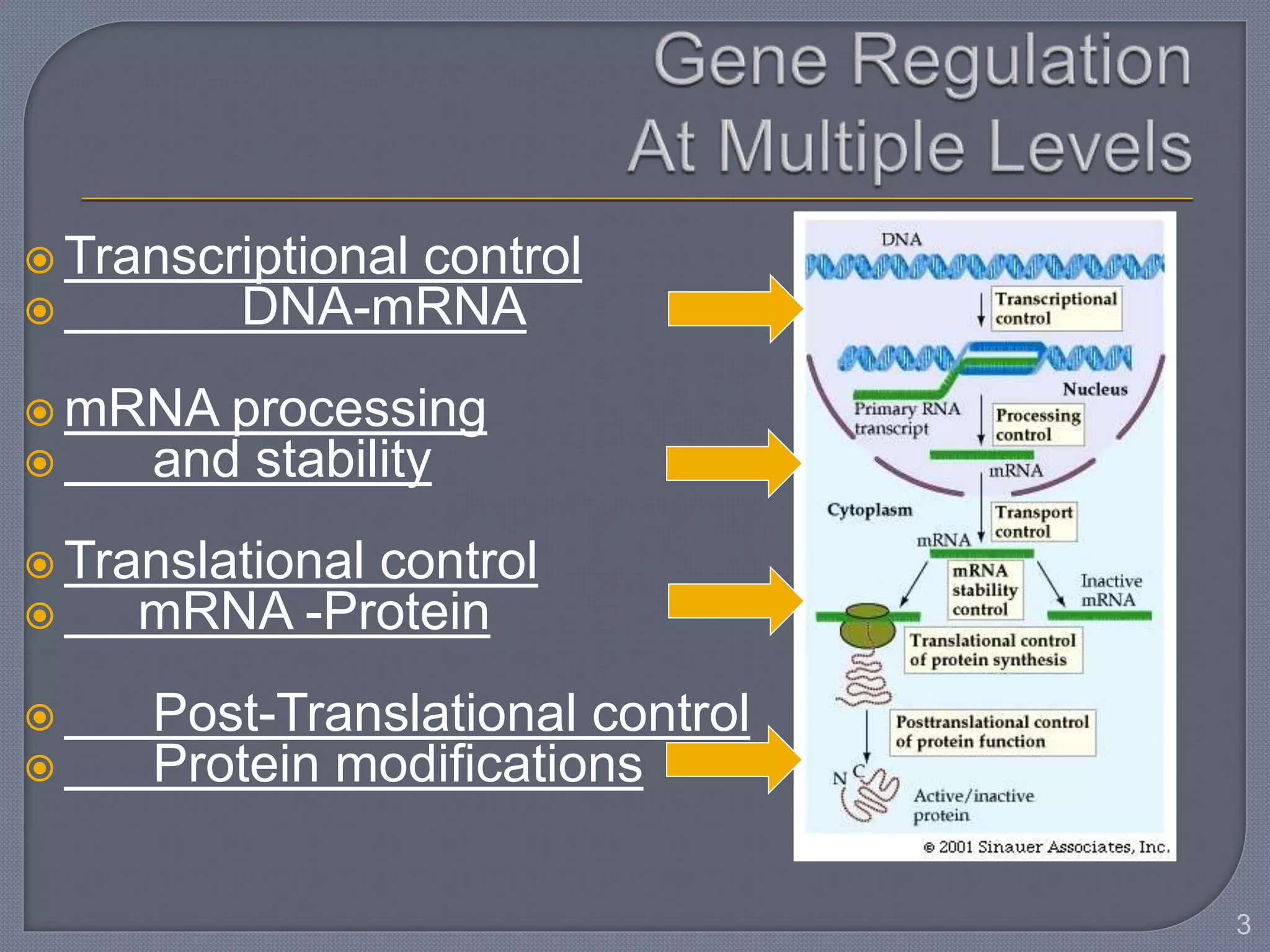
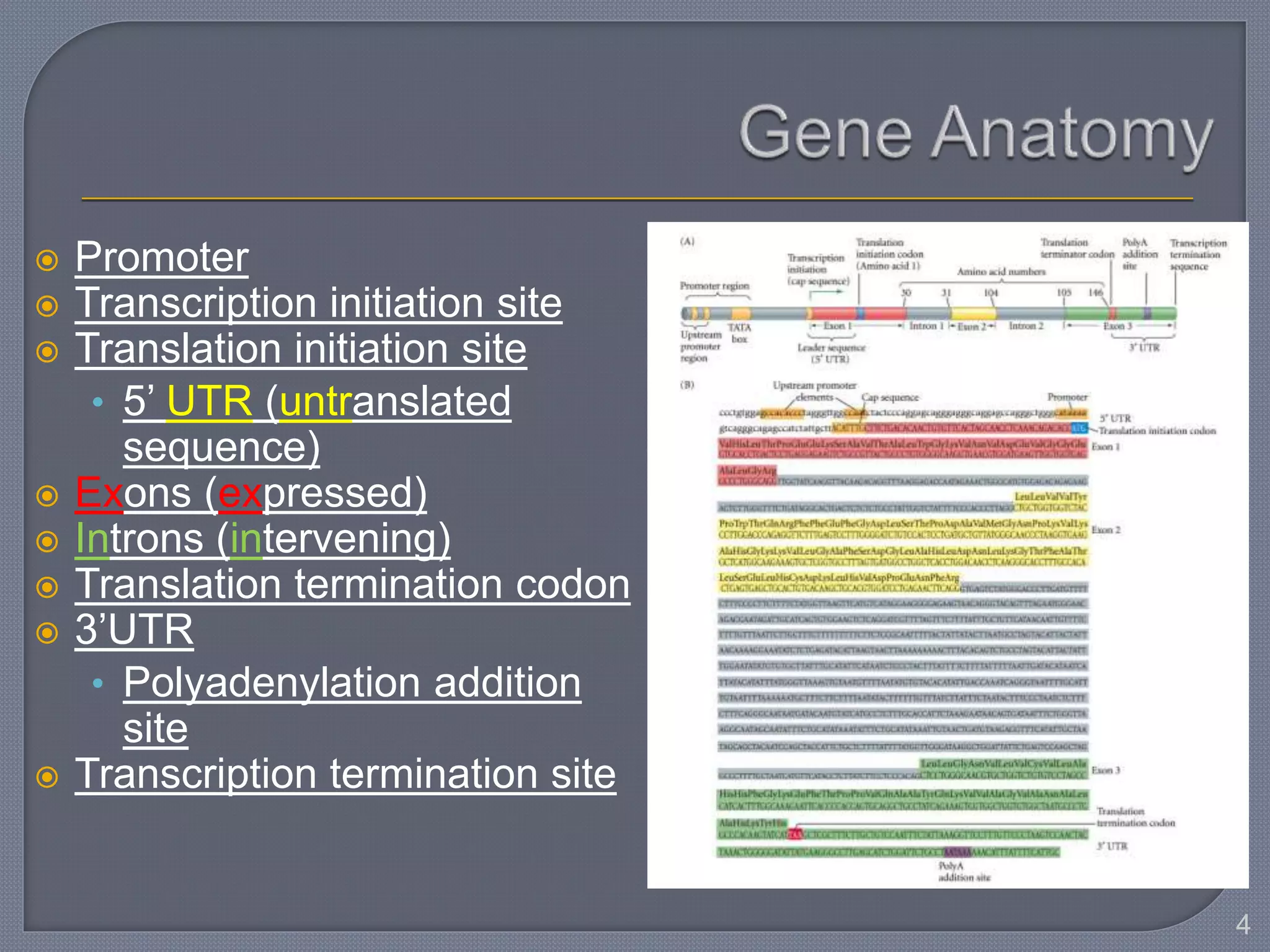
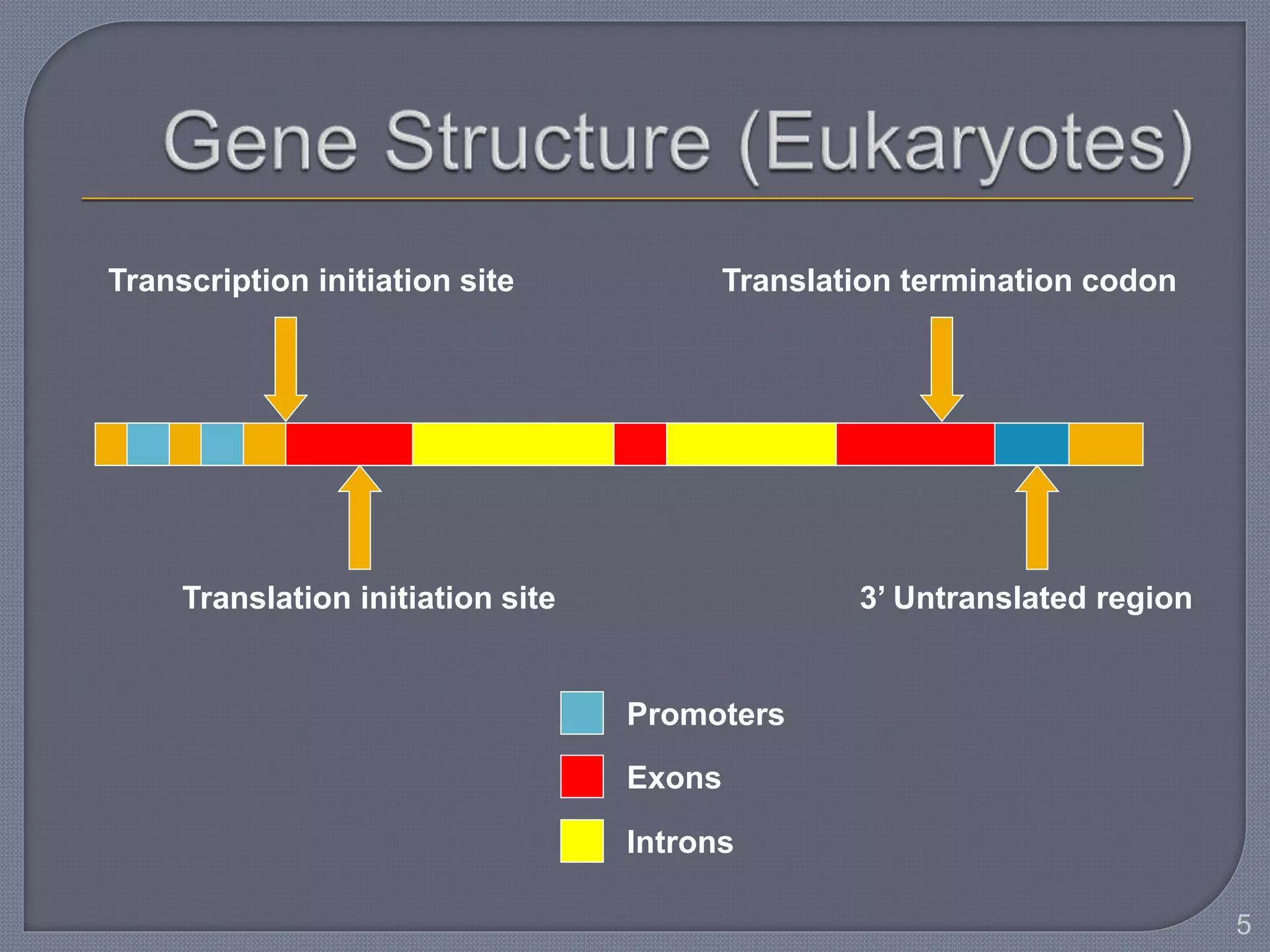
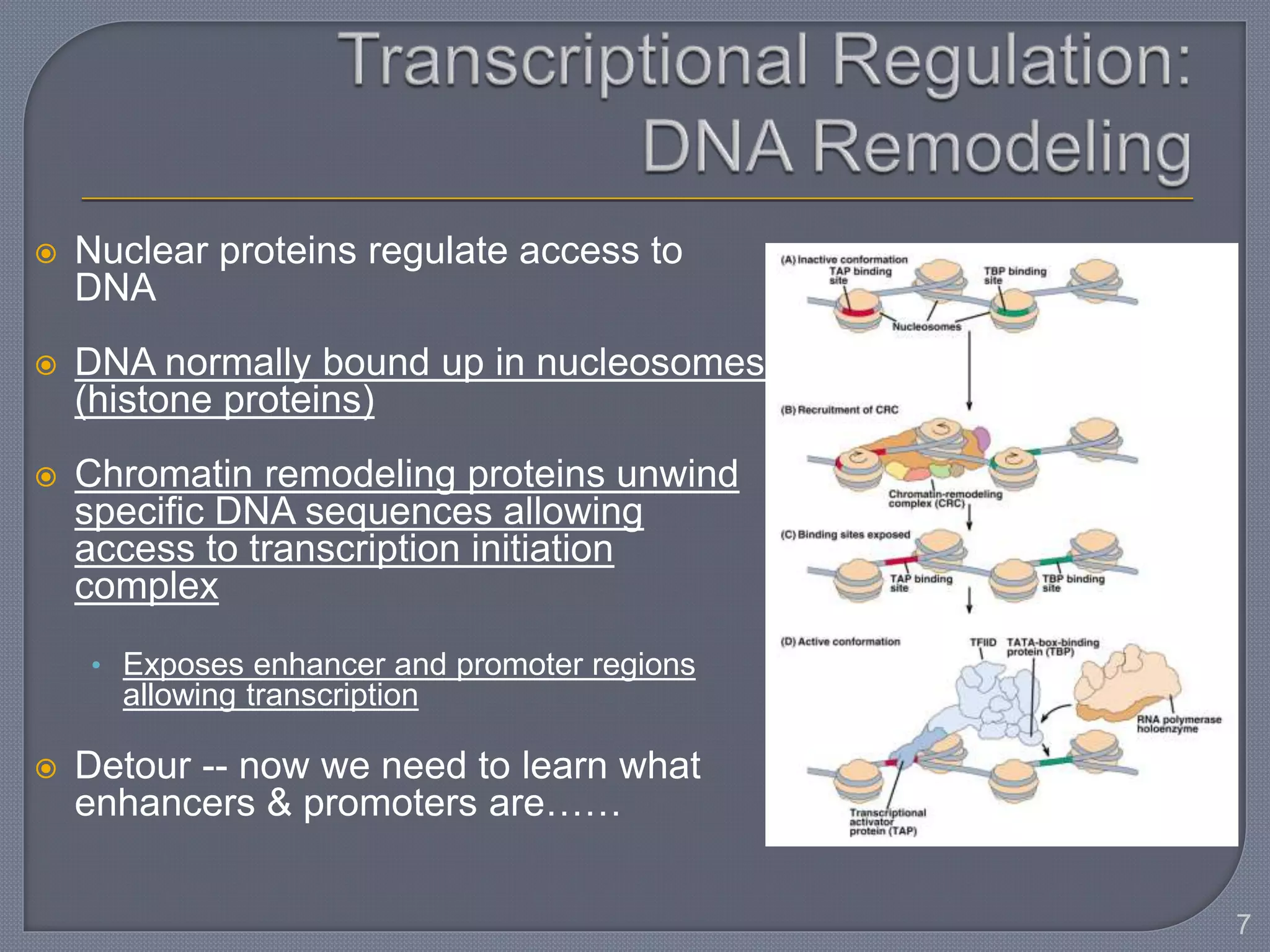
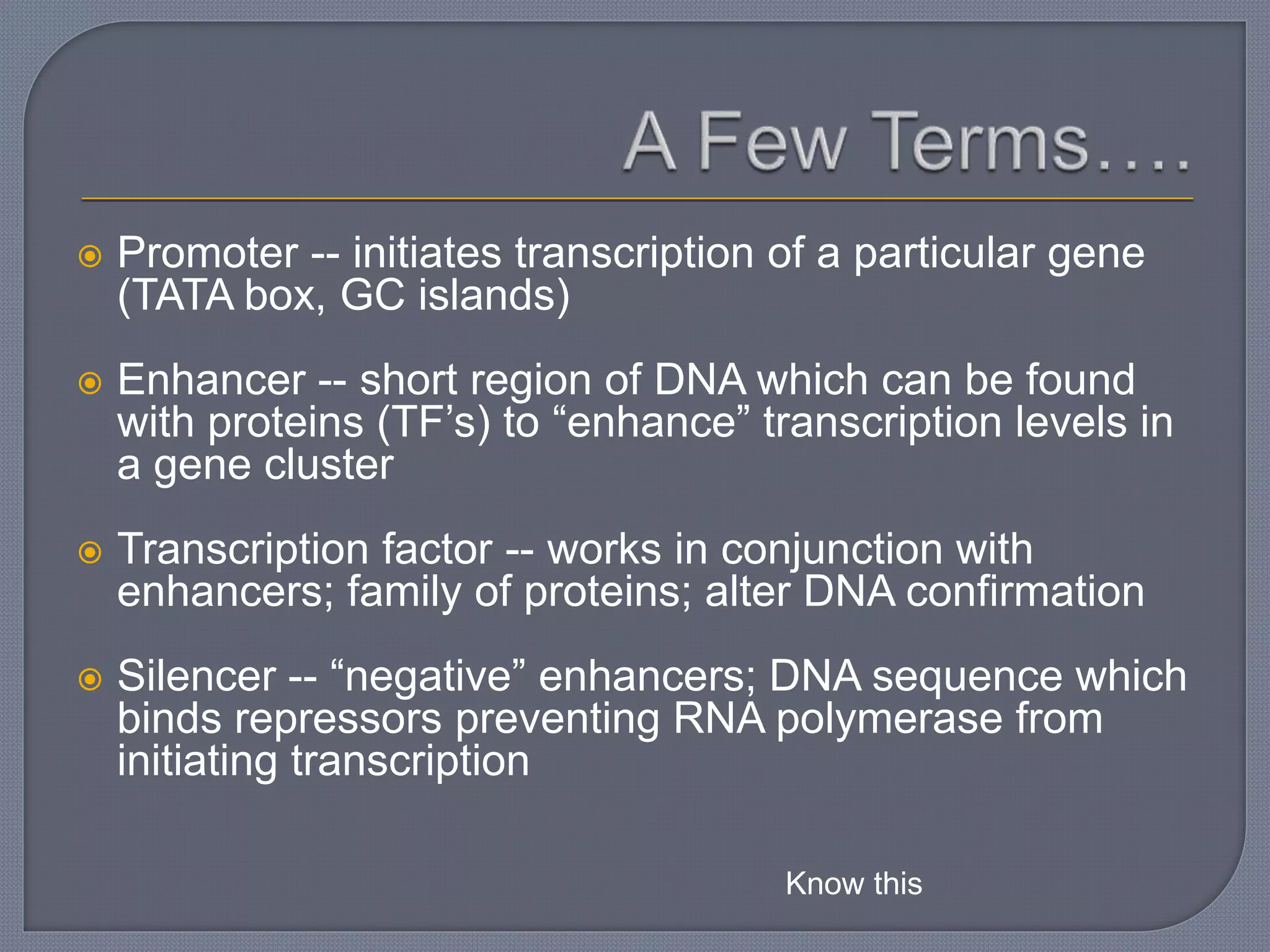
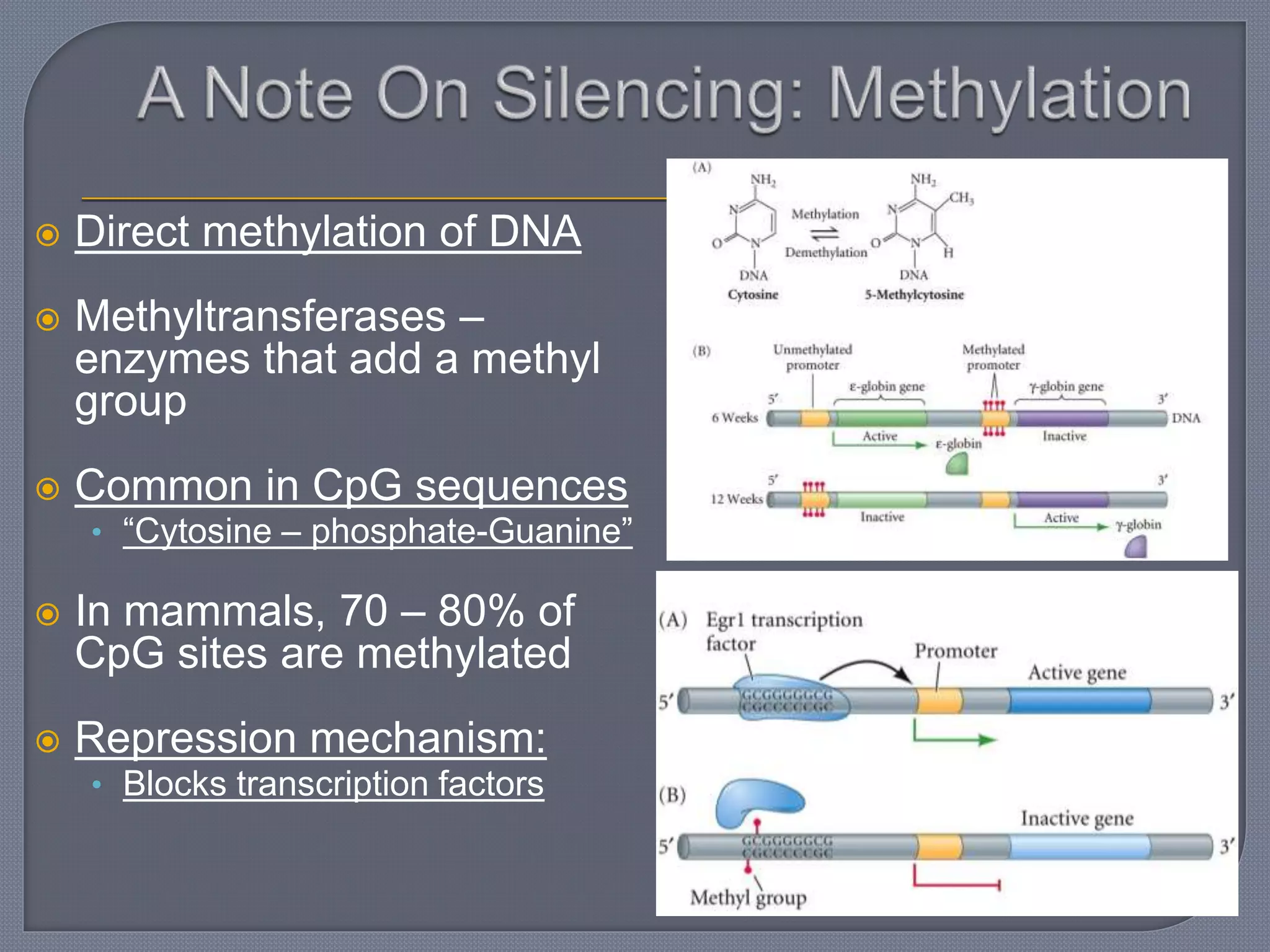
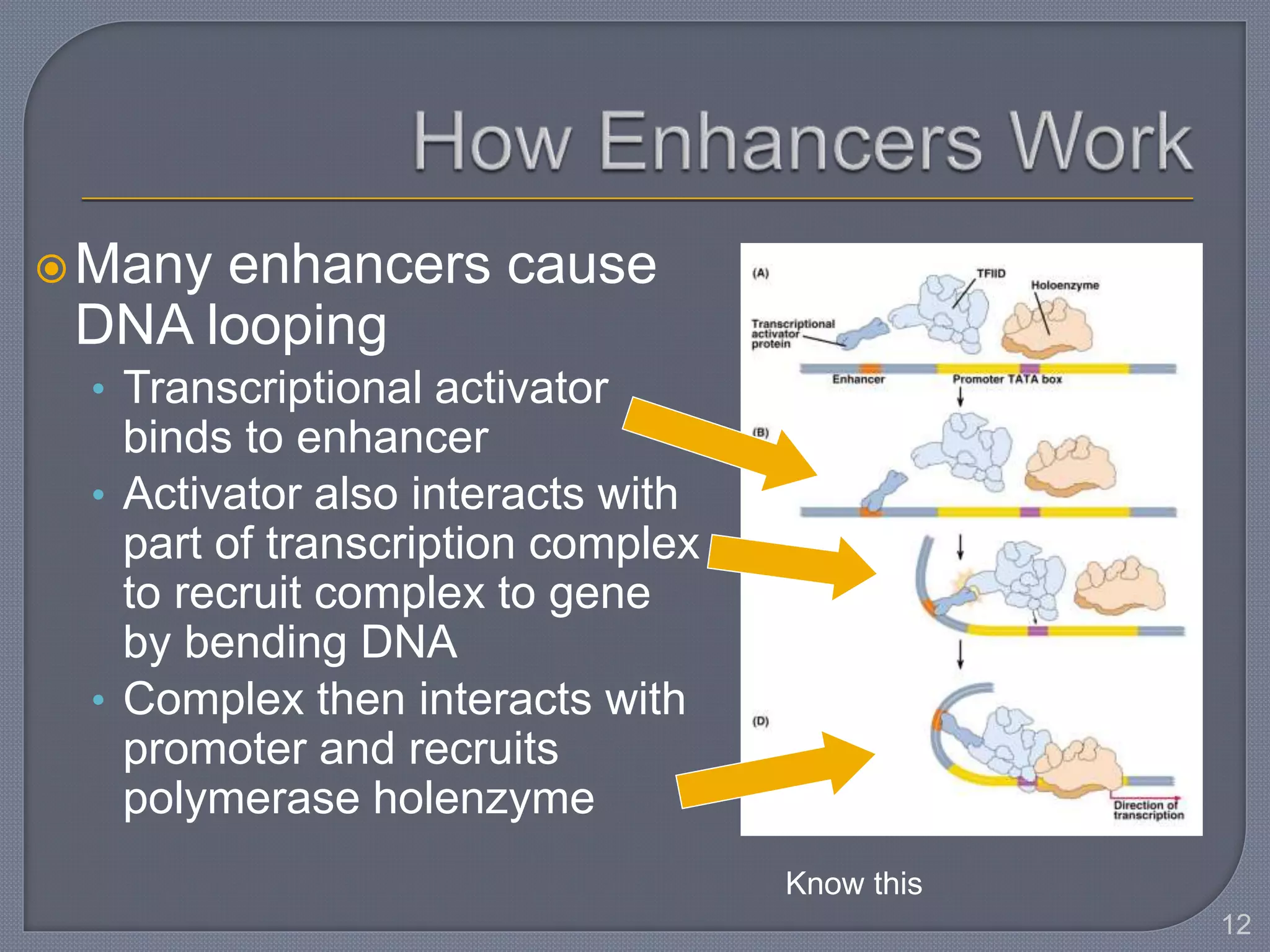
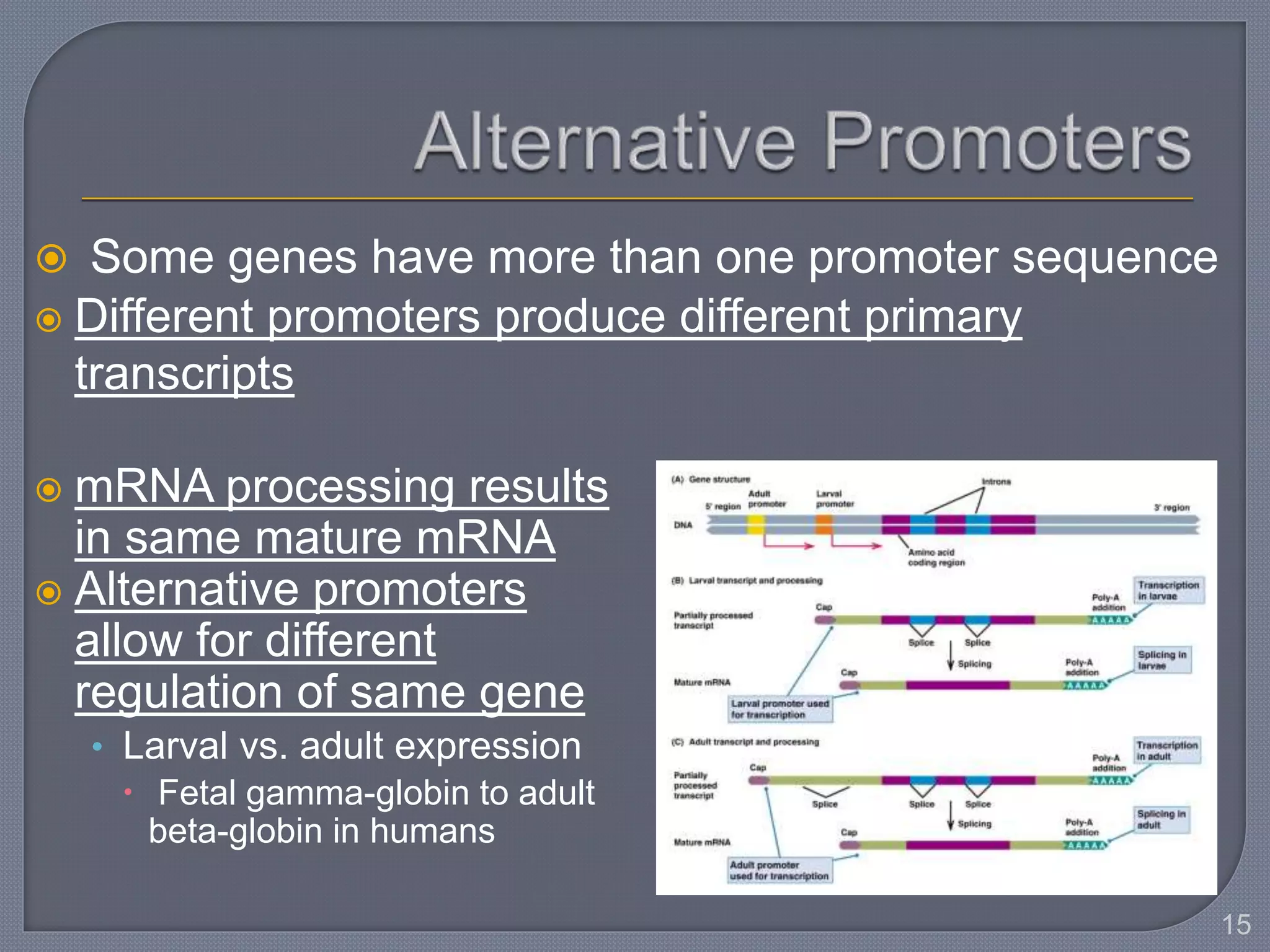
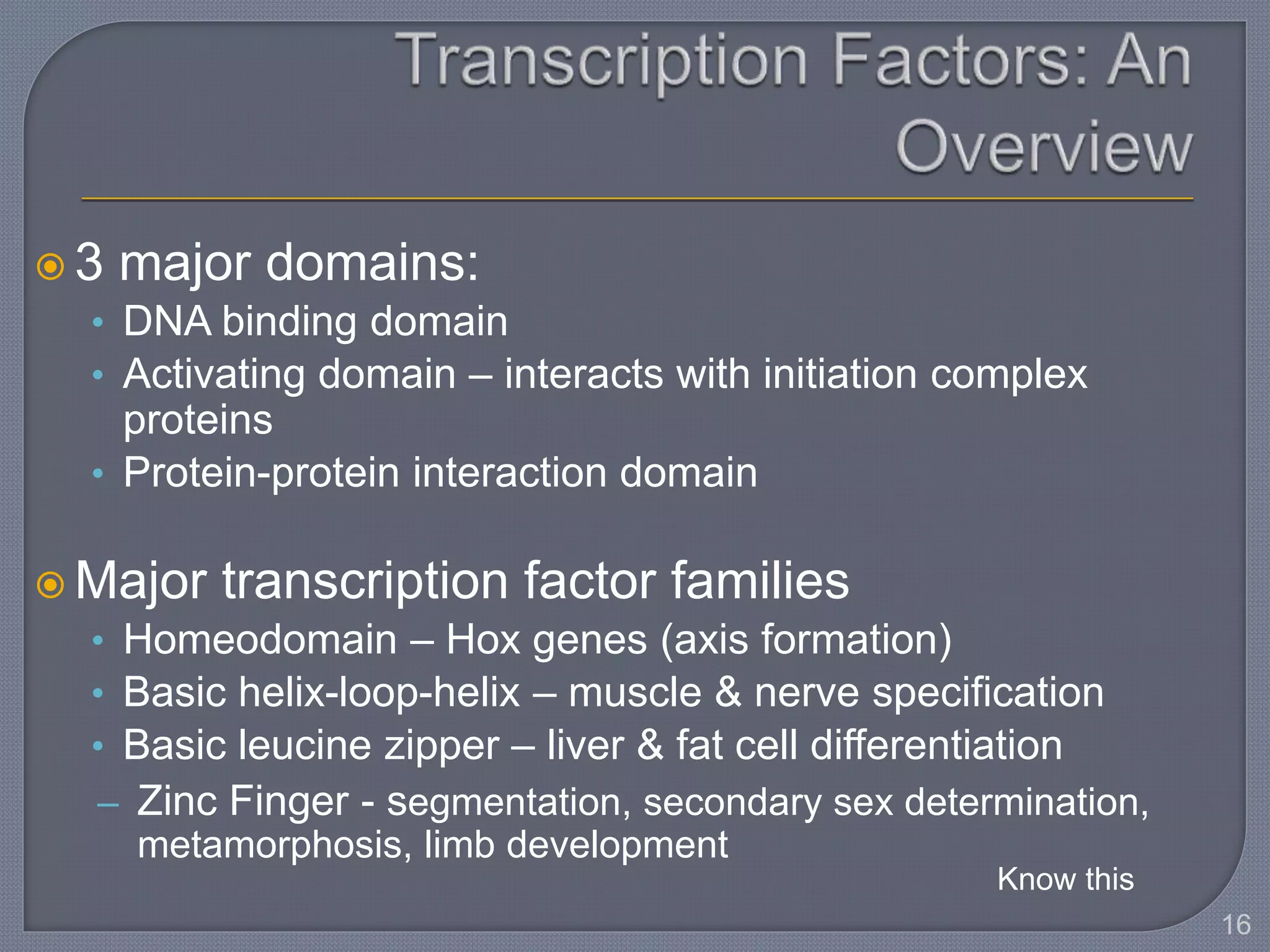
The document discusses four main levels of gene expression control: transcriptional, RNA processing, translational, and post-translational. It provides details on the mechanisms of transcriptional control, including promoters, enhancers, transcription factors, silencers, and chromatin remodeling. Alternative promoters allow for different regulation of the same gene, producing different primary transcripts and mRNA processing results in the same mature mRNA.