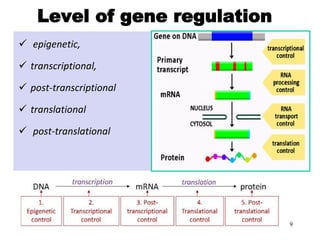
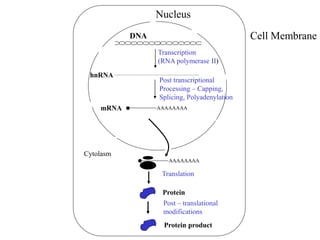
Gene regulation allows eukaryotic cells to control which genes are expressed and when. It occurs at multiple levels, including epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational control. Epigenetic gene regulation involves DNA methylation and histone modification, which influence chromatin structure and accessibility. Transcriptional control involves transcription factors binding to promoters and enhancers to regulate RNA polymerase recruitment and transcription initiation. Post-transcriptional mechanisms include alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and regulation by microRNAs. Gene regulation enables cellular differentiation and response to environmental changes.