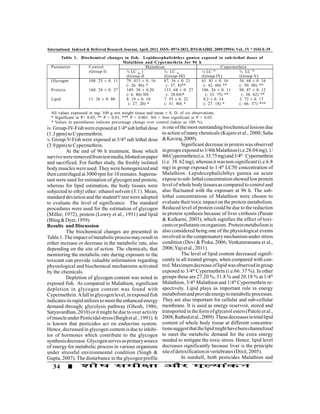
This document summarizes a research study on the effects of the pesticides malathion and cypermethrin on biochemical constituents in the freshwater fish Lepidocephalichthys guntea. The study found that exposing the fish to sub-lethal concentrations of both pesticides for 96 hours resulted in significant decreases in glycogen, protein, and lipid levels compared to the control group. The decreases indicated that the pesticides affected the fish's metabolism and energy utilization. Both malathion and cypermethrin were shown to be highly toxic to L. guntea and cause harmful biochemical changes.