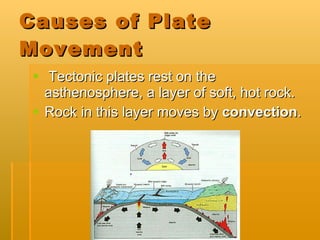
Continental drift theory developed by Alfred Wegener in 1912 proposes that the Earth's continents were once joined together and have been slowly moving apart over geologic time. Evidence for this includes matching fossil and rock formations found on different continents, as well as evidence that climates have changed in certain areas. The theory of plate tectonics expanded on this, stating that the Earth's lithosphere is made up of plates that move over Earth's surface, causing geologic events where they meet.