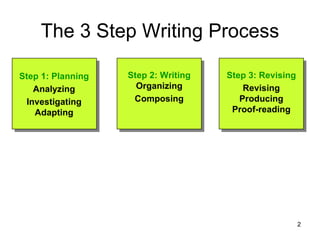
The document outlines a 3-step process for business writing:
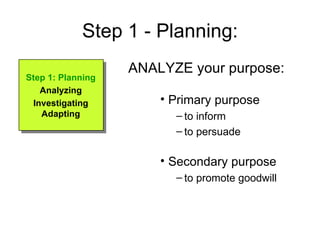
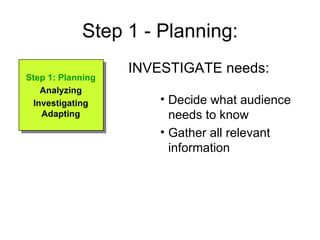
1. Planning - Analyze your purpose, audience, and their needs then adapt your message accordingly
2. Writing - Organize your message using either a direct or indirect method and select an appropriate channel of communication
3. Revising - Revise, edit, and proofread your written content
It provides examples and factors to consider for each step, such as directly stating the main point first or providing explanation/justification first depending on your audience and purpose.