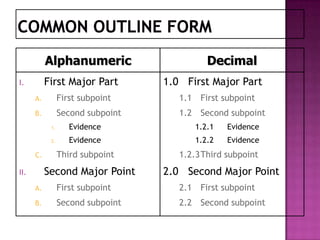
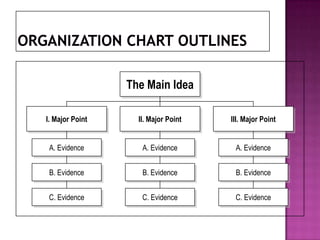
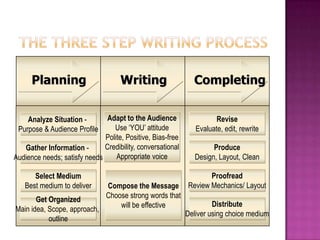
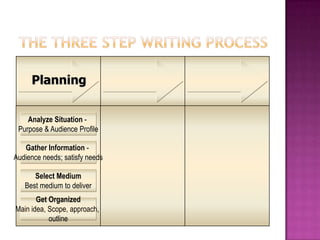
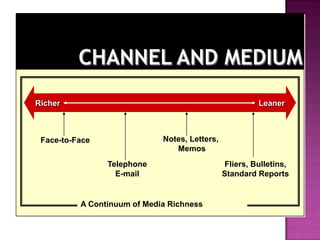
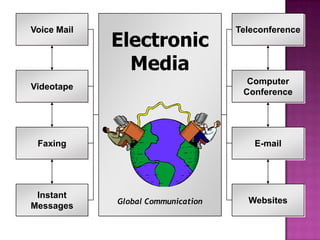
The document discusses the importance of planning business messages by analyzing the situation, gathering information, selecting the right medium, and organizing the information. It provides guidance on analyzing the purpose and audience, gathering stakeholder input, and choosing oral, written, visual, or electronic channels based on factors like feedback needs and message complexity. The document also outlines how to define the main idea, limit the scope, choose a direct or indirect structure, and create an outline to organize the message content in a logical way for the audience.











![WRITTEN
Memo
Letters
Proposals
Reports
ELECTRONIC
Oral – phone calls,
teleconferencing, internet
telephony, VoIP [skype, Tango]
Written – IM, email, hangout, blogs,
websites, wikis
Visual - PPT, computer animation,
video [vidcasts, vblogs],
multimedia
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmd225-3-140205232719-phpapp02/85/Cmd-225-3-15-320.jpg)




![ Choose
between direct/indirect approaches
Use direct when audience is positive,
receptive; start with main idea
[recommendation, conclusion, request] and
follow with supporting facts]; deductive.
Use indirect when audience is skeptical,
resistant, negative; start with supporting
evidences first and build up to your main
idea; inductive.
Choices is dependent on purpose and
message and medium.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmd225-3-140205232719-phpapp02/85/Cmd-225-3-21-320.jpg)