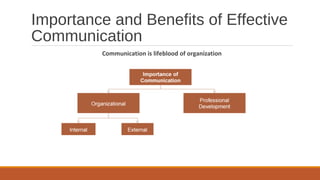
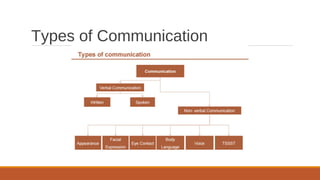
This lecture discusses effective communication in business. It defines communication and notes that it is a two-way process of exchanging information. Business communication facilitates both internal and external business dealings. Effective communication achieves the desired results and influences others as intended. The key components of communication are context, sender, message, medium, receiver, and feedback. Non-verbal cues like appearance, facial expressions, eye contact and body language convey important messages. Factors like voice, time, space, silence, smell and touch also impact communication effectiveness.