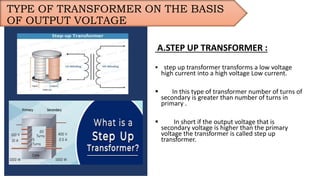
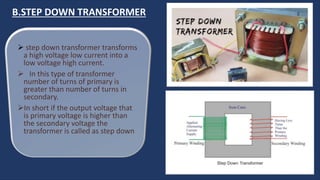
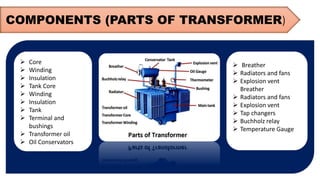
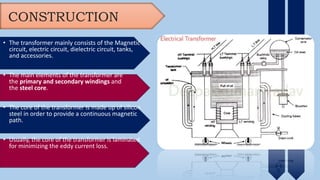
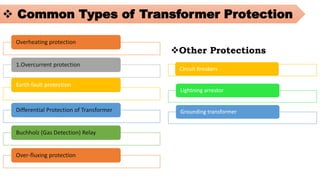
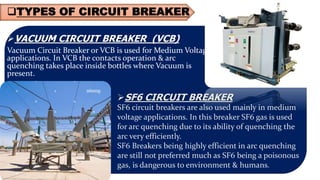
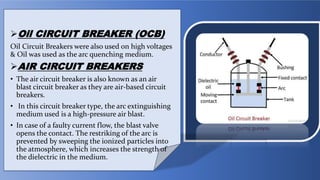
The document provides an overview of transformers, including their types, components, construction, and protection mechanisms. It details step-up and step-down transformers, their main parts, and the importance of transformer oil and insulation. Additionally, it outlines various transformer protection strategies such as overheating, overcurrent, and earth fault protections, along with the role of circuit breakers and lightning arresters.