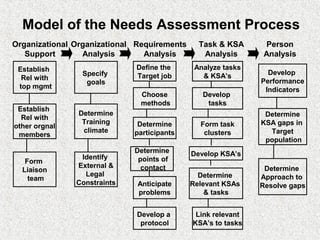
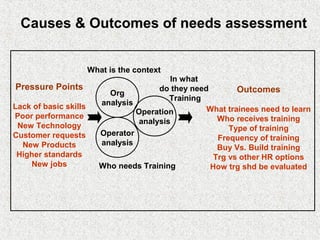
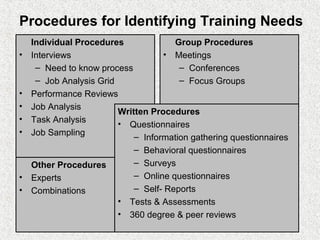
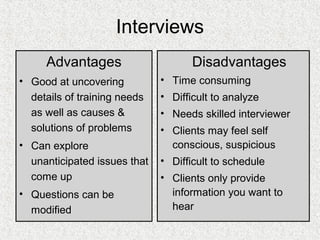
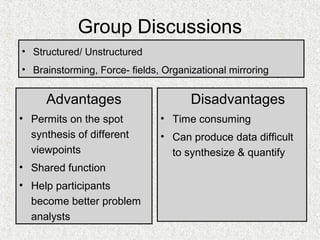
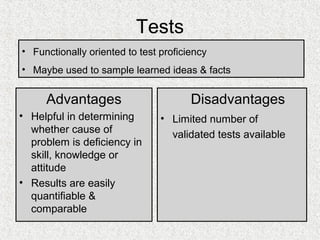
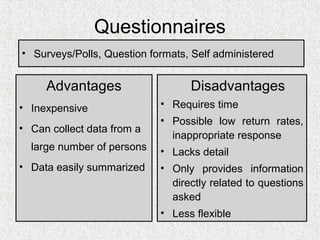
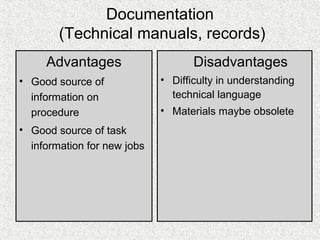
The document discusses needs assessment and analysis for determining training needs. It outlines the needs assessment process, including analyzing organizational, task, person, and KSA requirements. Common causes of needs assessment are discussed such as performance issues, incorrect training solutions, lack of prerequisites. Methods for identifying training needs include interviews, surveys, documentation review, and focus groups. The outcomes of needs assessment should identify training subjects, importance, population, and required results.