This document discusses Boolean algebra concepts including logic gates, Boolean expressions, truth tables, and logic circuit design. It covers:
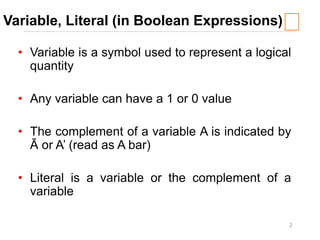
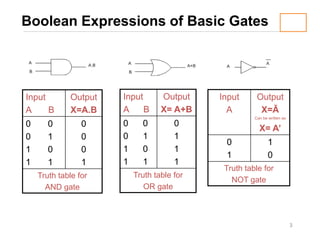
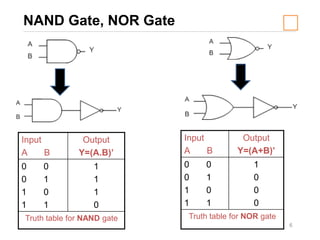
1) The definitions and truth tables of common logic gates like AND, OR, NAND, and NOR.
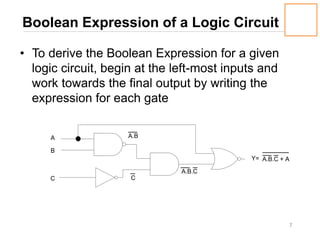
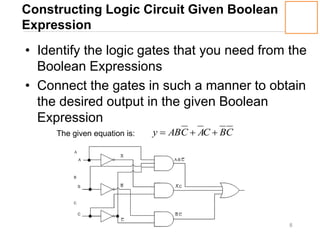
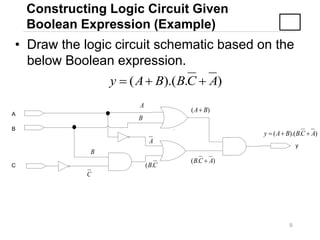
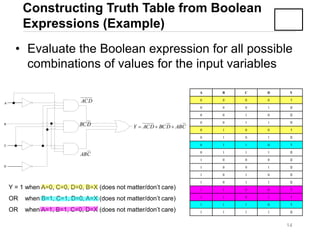
2) How to derive the Boolean expression of a logic circuit and construct a circuit from a given Boolean expression.
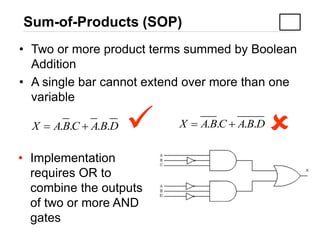
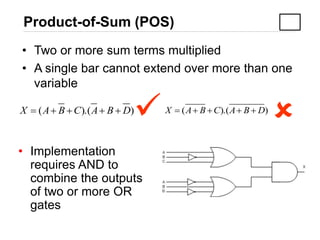
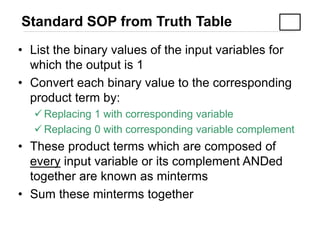
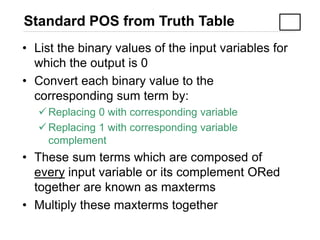
3) Converting between Sum of Products (SOP) and Product of Sums (POS) forms using techniques like standard SOP from a truth table.