Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times




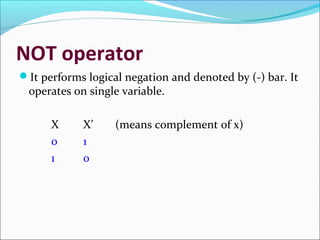

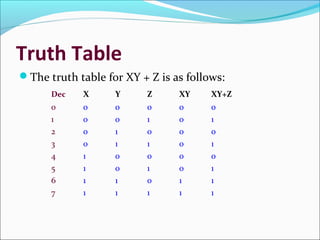
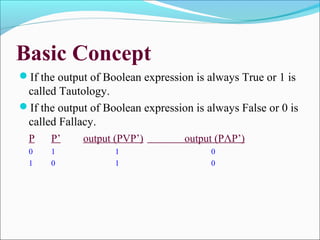
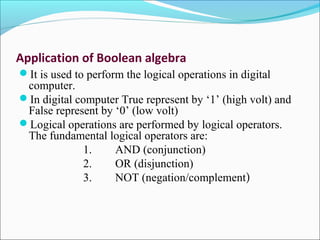

This document provides an introduction to logic gates and Boolean algebra. It defines logic as statements with binary true/false outcomes. It describes the AND, OR, and NOT logic gates and provides their truth tables. It also discusses truth tables in general and provides an example truth table. The document notes that a tautology is an expression that is always true, while a fallacy is always false. It concludes by discussing applications of Boolean algebra in digital computers and common logical operators.









