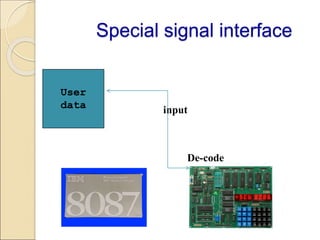
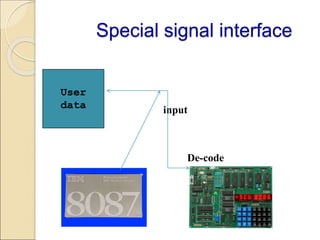
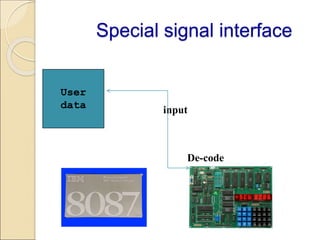
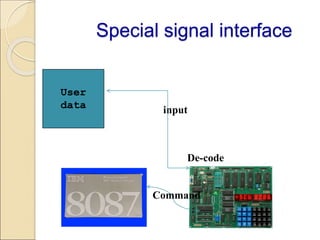
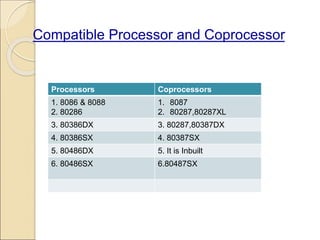
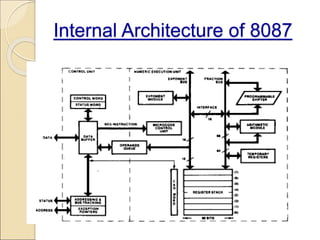
Coprocessors were introduced in the 1970s to offload floating-point arithmetic operations from main processors. A coprocessor is a specialized circuit that performs tasks like floating-point operations faster than the main processor. Coprocessors extend capabilities and increase processing speed. They are used for tasks the main processor cannot perform directly, like trigonometric or logarithmic functions. Coprocessors interface with the main processor via instruction monitoring or command registers, and perform calculations to aid the main processor. Common coprocessors include the 8087, 80287, and 80387 which added floating-point support to processors like the 8086, 80286, and 80386 respectively.