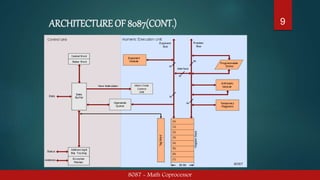
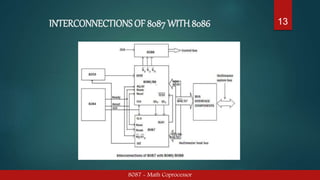
The 8087 was the first math coprocessor designed by Intel to pair with the 8086 and 8088 processors. It was built to speed up floating point calculations by freeing up the CPU's time and resources. The 8087 introduced 60 new instructions beginning with "F" and contained an control unit and numerical execution unit. It connected to the 8086 via address-data bus lines, status lines, and interrupt/request signals to process floating point operations simultaneously while allowing the CPU to focus on other tasks.