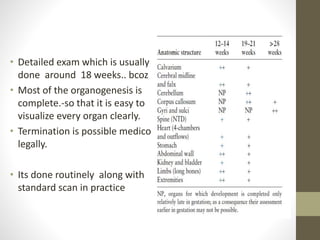
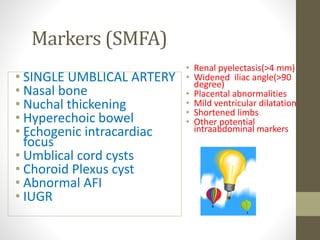
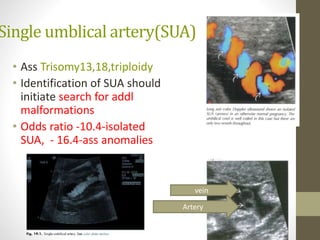
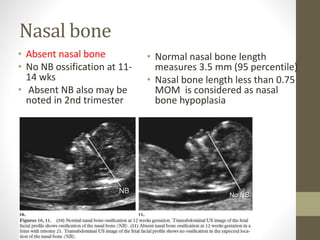
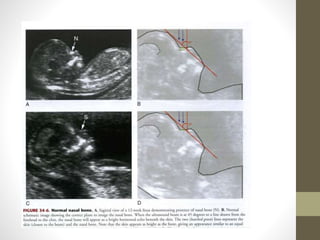
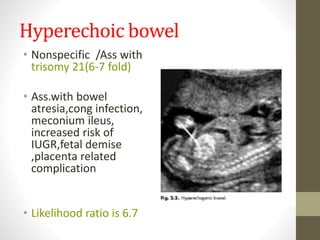
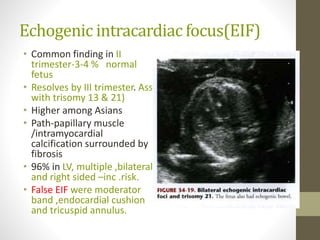
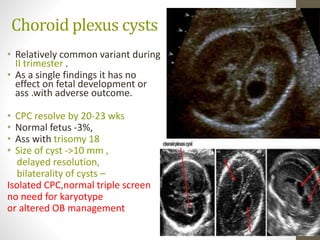
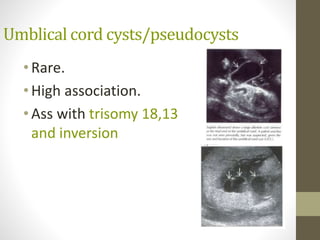
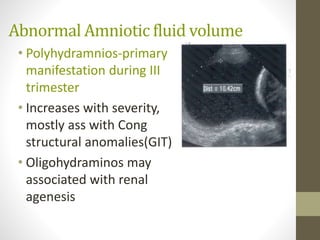
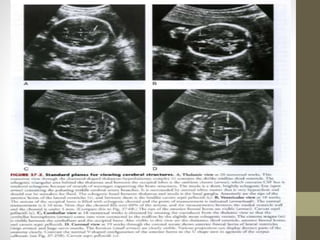
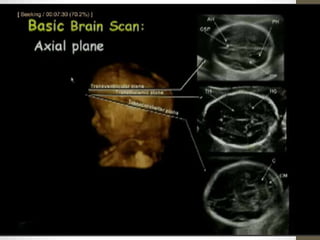
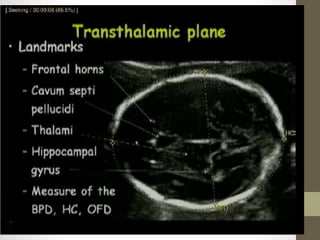
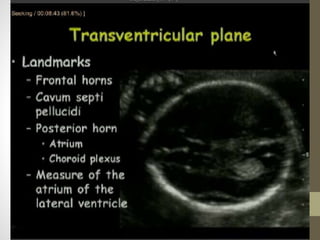
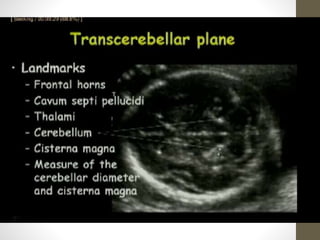
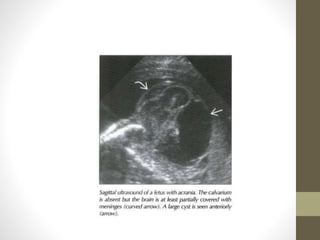
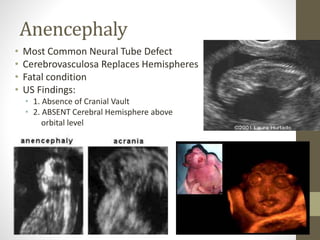
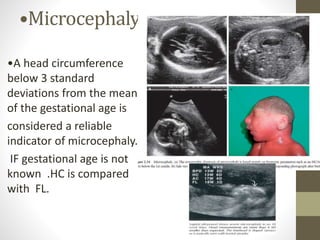
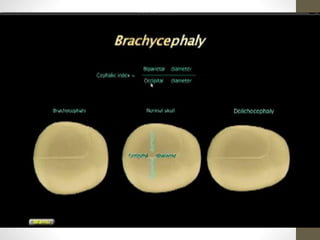
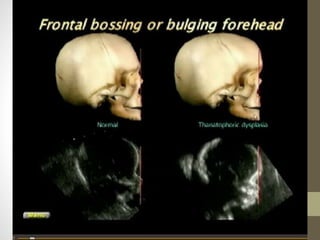
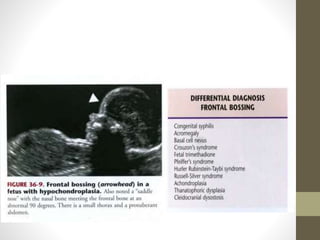
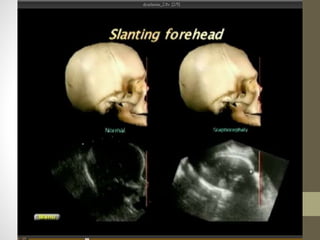
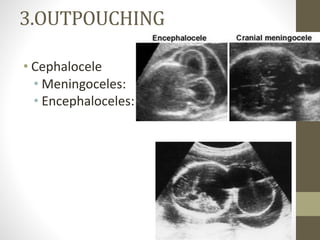
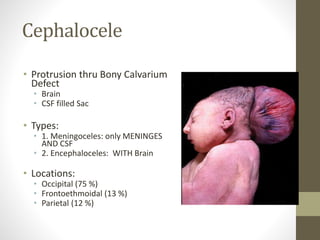
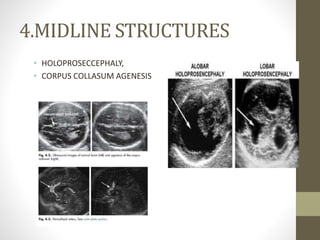
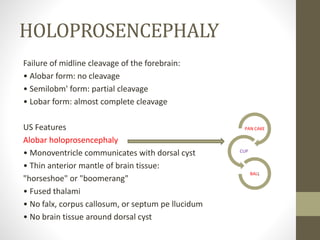
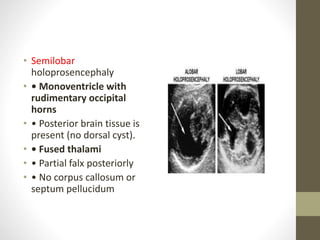
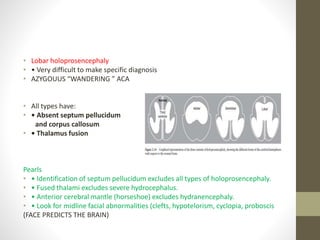
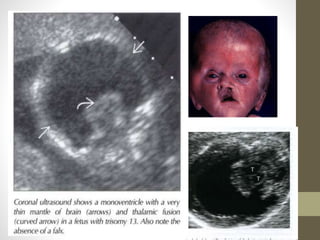
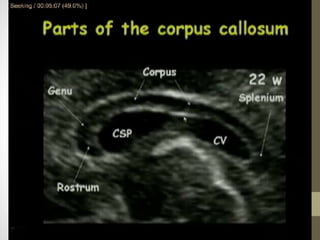
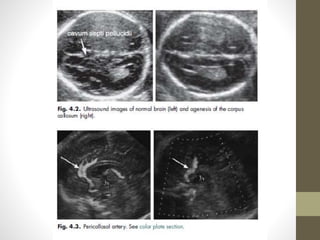
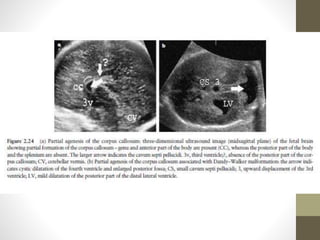
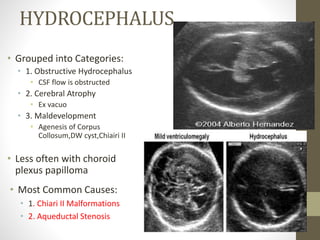
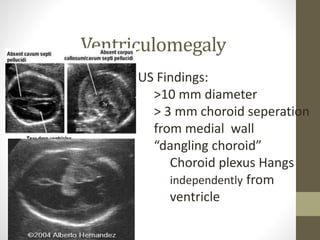
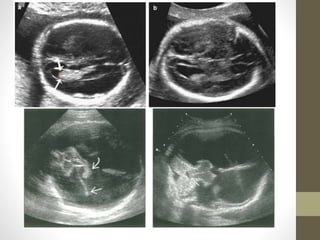
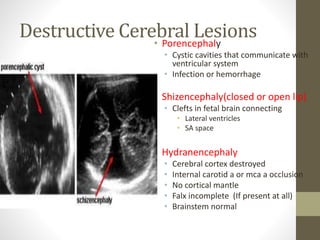
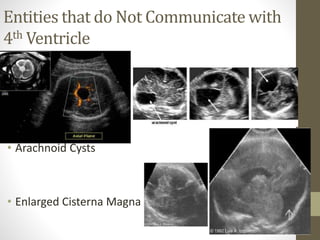
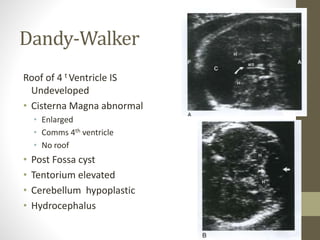
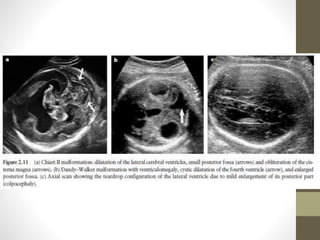
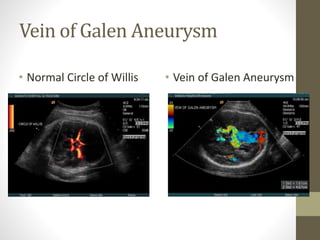
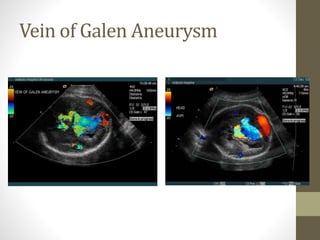
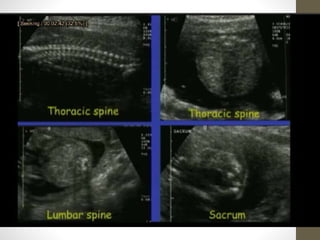
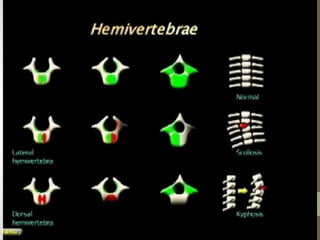
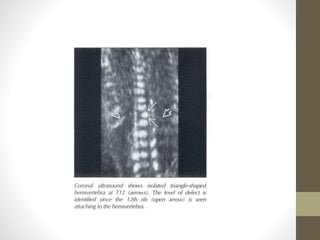
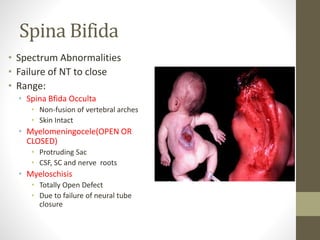
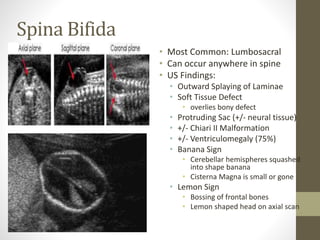
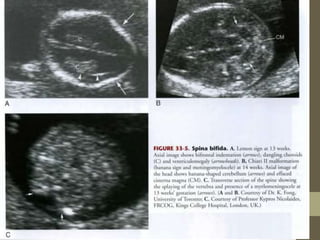
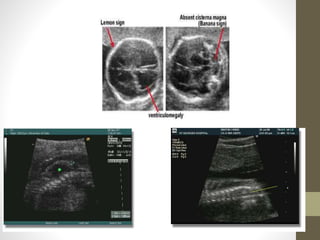
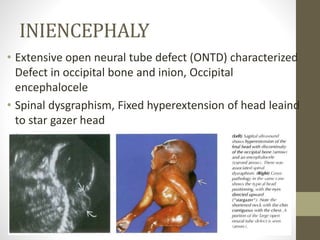
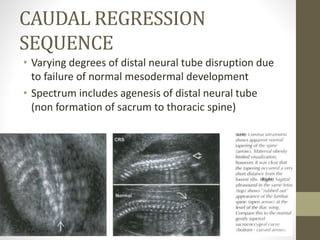
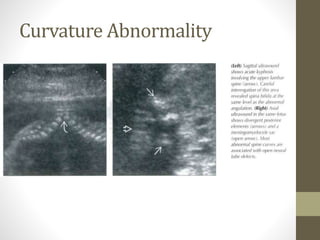
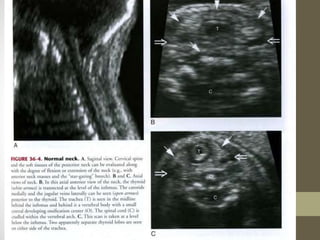
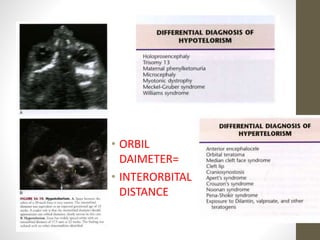
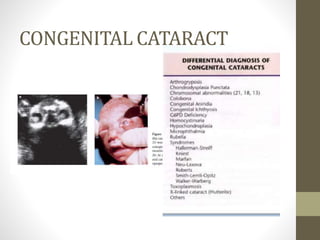
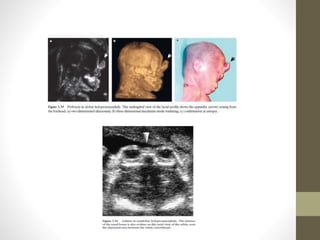
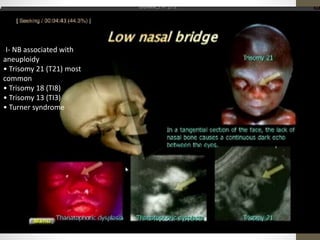
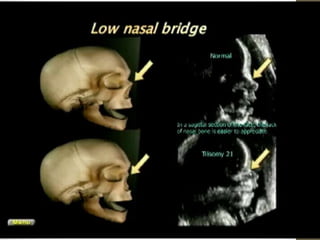
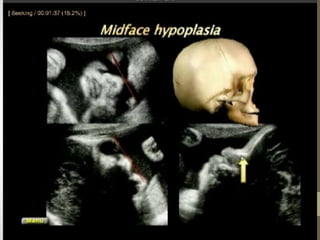
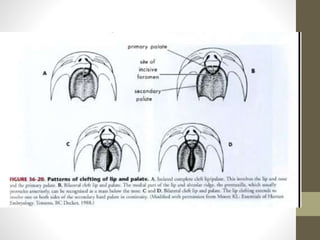
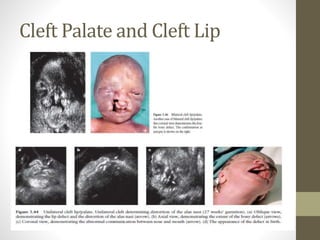
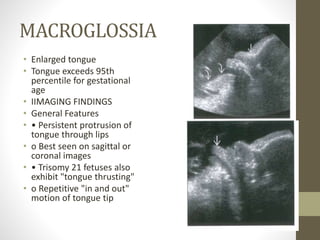
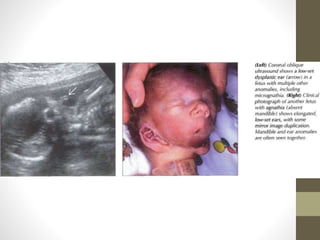
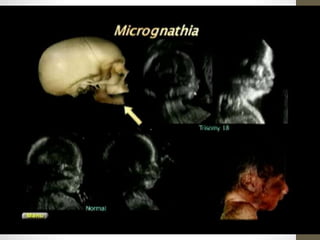
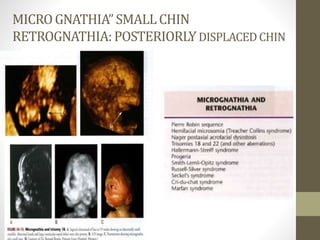
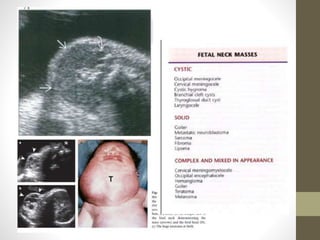
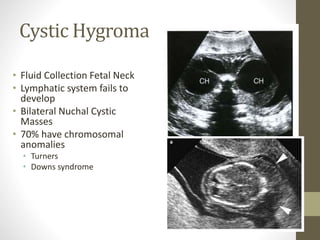
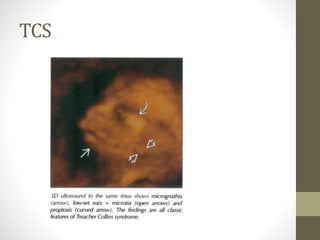
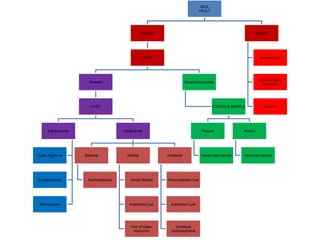
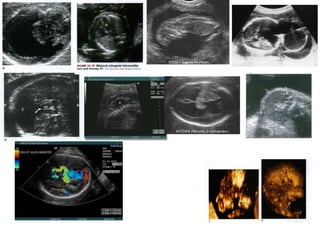
The document discusses a targeted ultrasound scan done to examine a fetus for potential anomalies. A targeted scan is recommended when an initial scan detects suspicious results, abnormalities are suspected based on history or tests, or the mother is considered high risk. It describes scanning various parts of the fetus including the head, brain, spine and abdomen to check for markers that may indicate chromosomal issues like Down syndrome. Specific structures and features that are evaluated are discussed in detail, along with their significance and potential associations with genetic conditions.