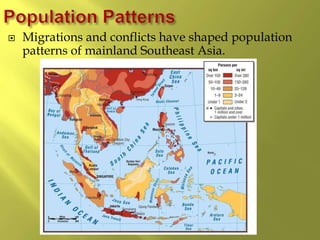
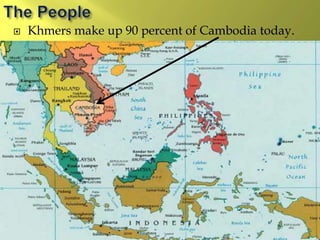
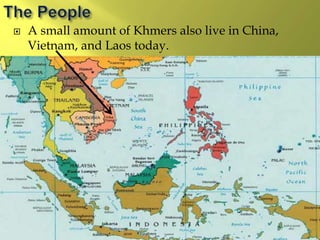
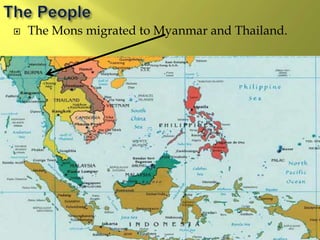
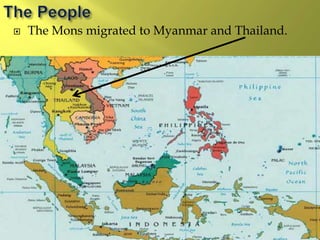
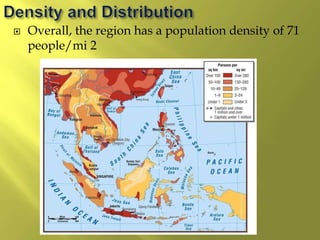
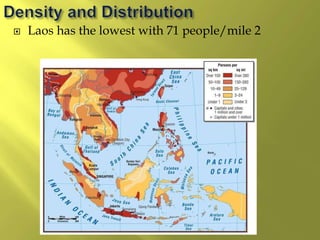
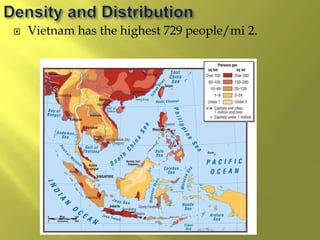
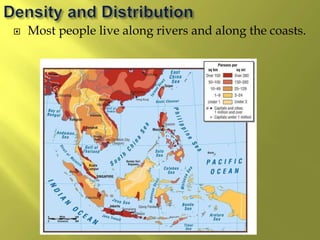
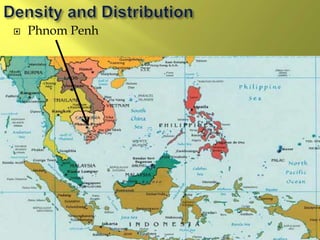
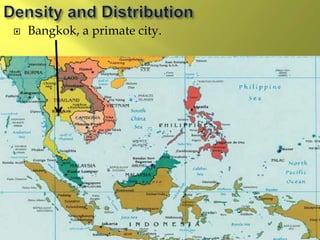
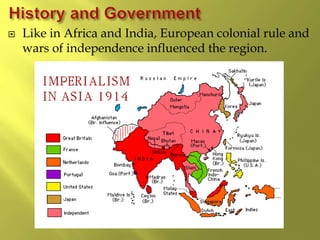
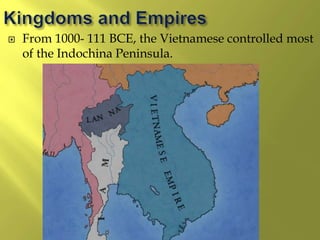
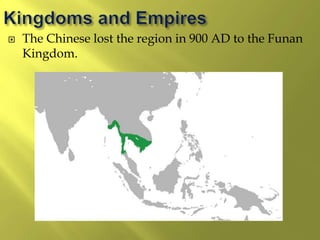
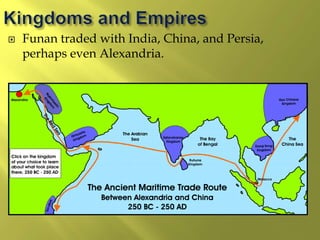
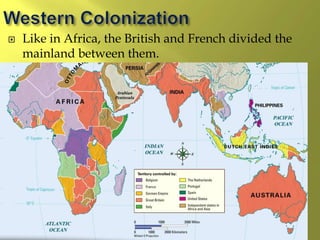
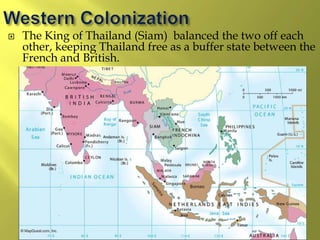
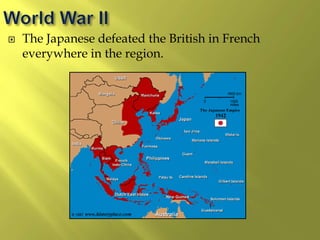
The document summarizes the history and cultures of mainland Southeast Asia. It describes how ancient migrations over thousands of years have shaped populations in the region. Major groups include the Khmers of Cambodia, Mons of Myanmar and Thailand, and Thai people of Thailand. European colonialism in the 1500s was followed by British and French rule until independence movements in the mid-1900s. Countries have diverse cultures but most practice Theravada Buddhism and have been influenced by ancient trade with India and China.