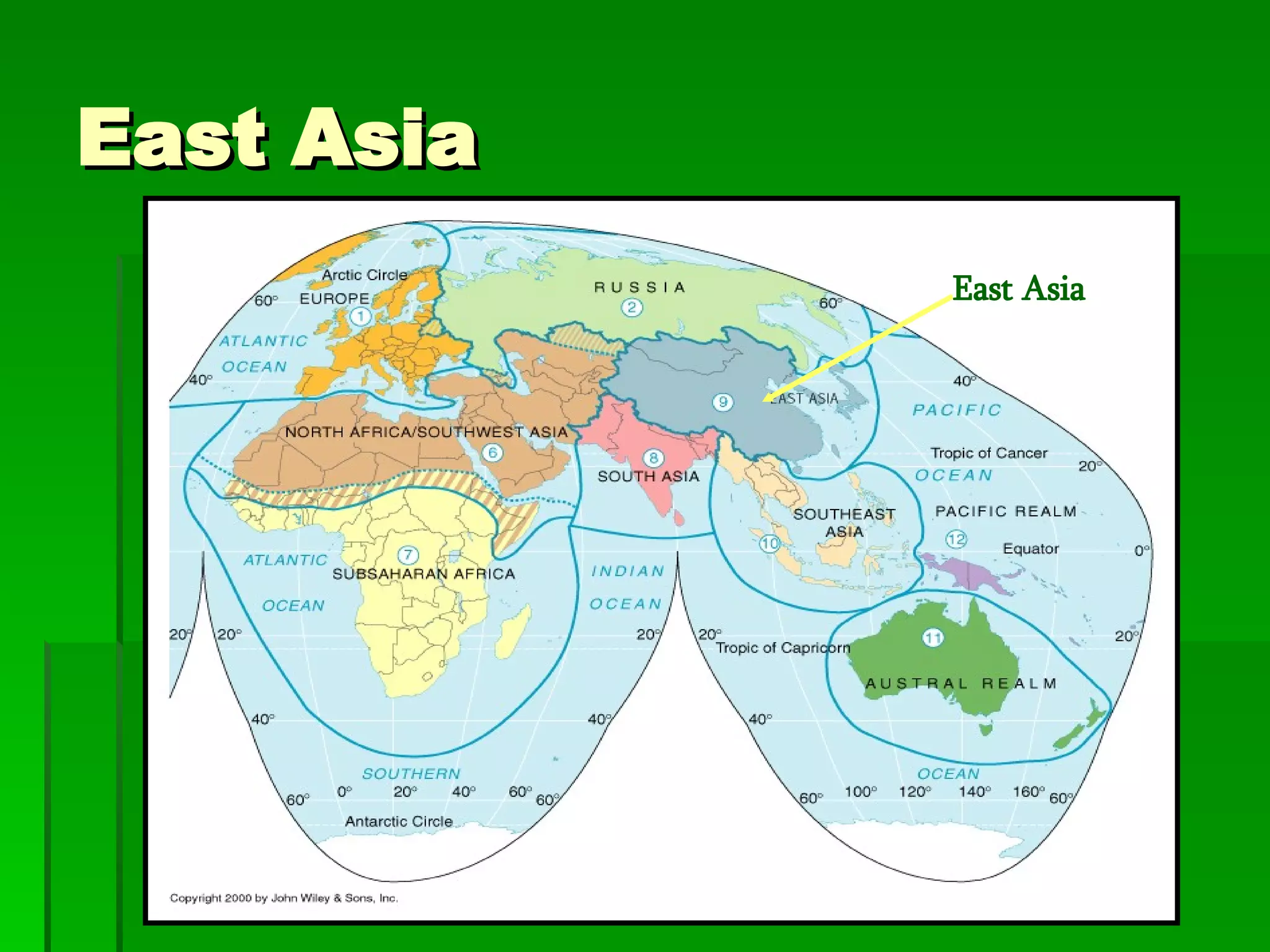
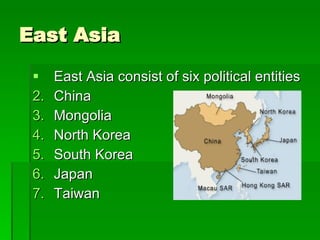
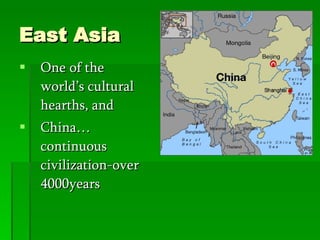
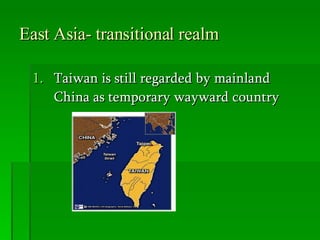
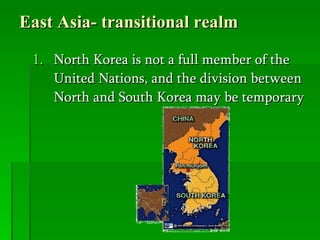
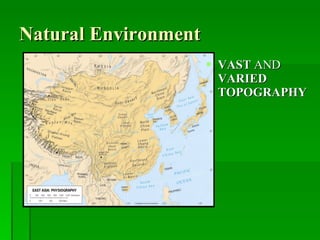
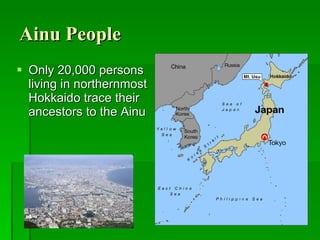
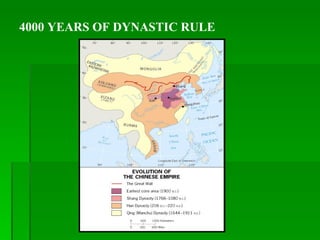
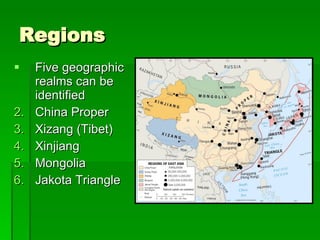
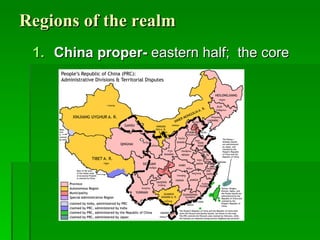
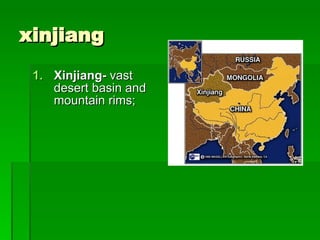
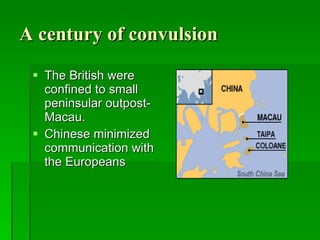
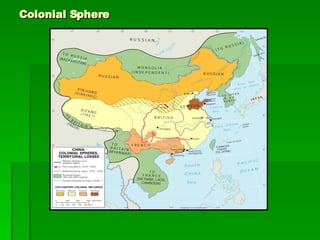
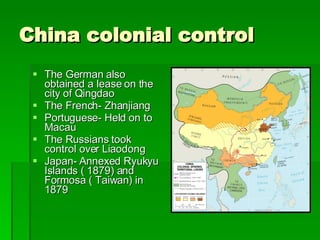
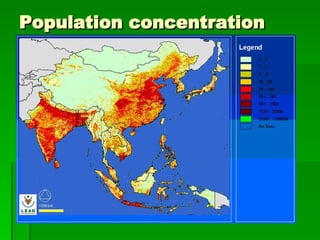
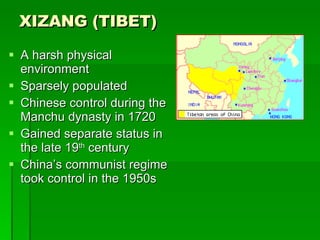
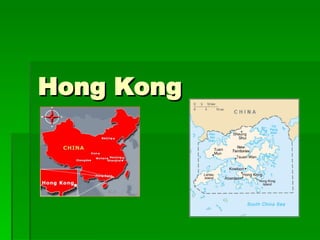
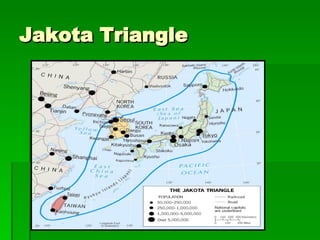
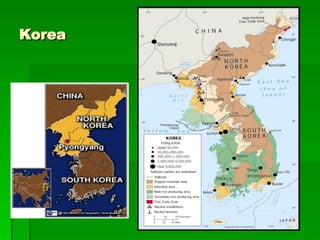
The document provides an overview of East Asia, focusing on China, Japan, the Korean peninsula, and surrounding regions. It discusses the transitional political situation in the region and the varied topography, including mountains, deserts, and earthquake-prone areas. It also summarizes the early cultural history and dynasties of China, as well as the colonial influence of European powers in the 19th century and the rise of nationalism and communism in China in the 20th century.