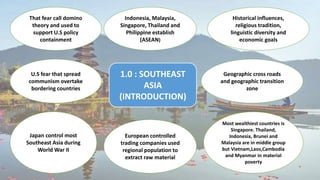
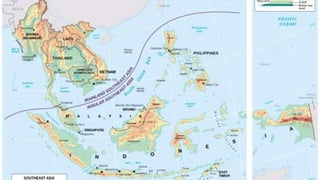
This document provides an overview of Southeast Asia, including its climate, environmental problems, cultural history, and colonial influences. Some key points:
- Southeast Asia has both equatorial and monsoon tropical climates, with high rainfall and temperatures year-round in equatorial regions and distinct wet/dry seasons in monsoon regions.
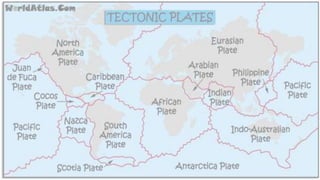
- Major environmental problems include natural hazards like volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis as well as pollution, deforestation, and mining impacts.
- Culturally, the region was influenced by Khmer, Burmese, Thai, and Vietnamese empires as well as Indian and Chinese traders. Major religions like Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam spread throughout Southeast Asia