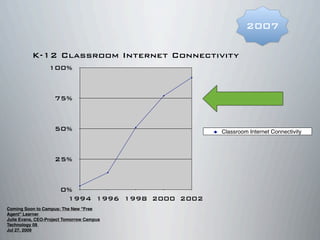
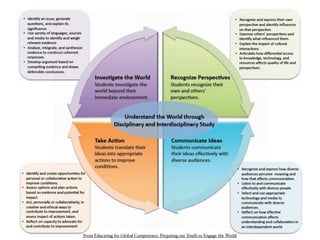
This document provides a summary of Lucy Gray's keynote presentation on modernizing education at the Interlochen Arts Academy on April 2, 2012. The presentation discusses the state of teaching and learning in the 21st century, highlighting trends like increased use of social media, the importance of developing 21st century skills in students, and the need for personalized and globally connected learning. Recommendations are made around leveraging mobile technologies, incorporating web tools into instruction, and expanding digital resources to make learning more experiential. Examples of innovative schools adopting these approaches are also provided.