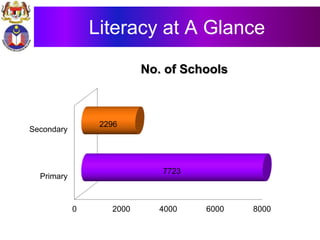
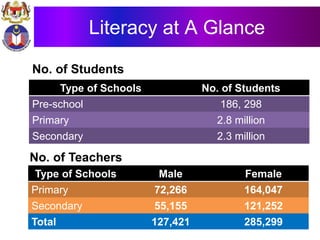
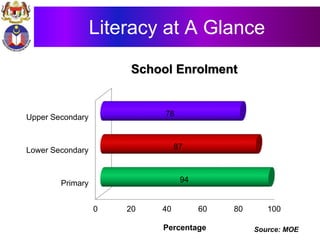
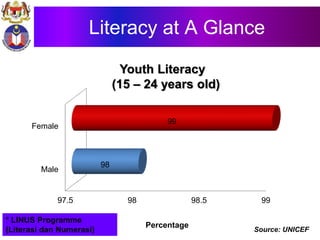
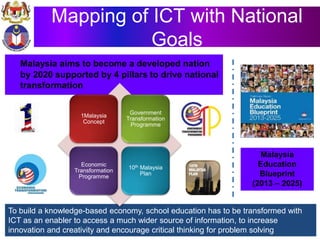
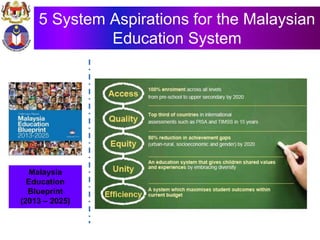
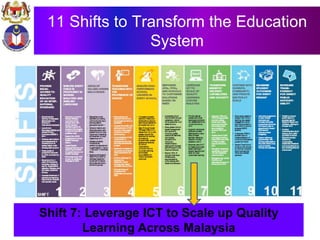
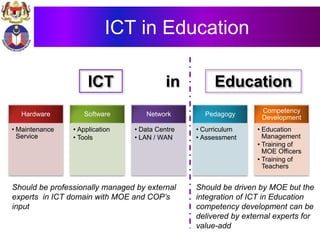
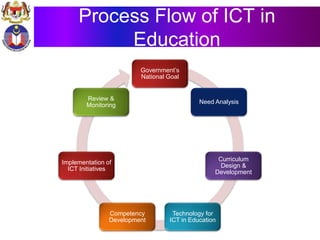
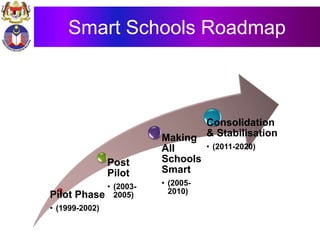
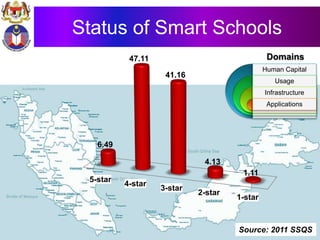
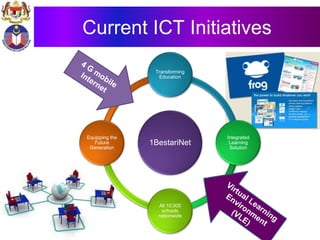
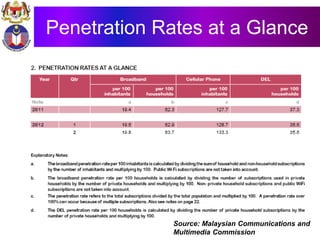
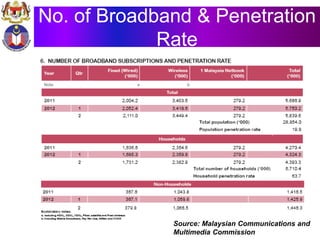
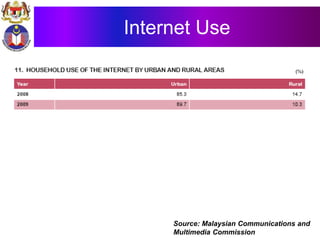
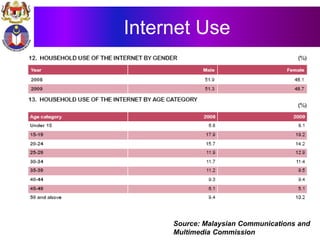
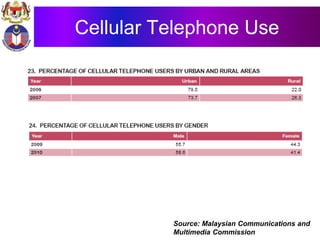
The document discusses the development of literacy in Malaysia through mobile technology, emphasizing the integration of ICT in education to transform learning. It outlines the current state of education, including enrollment statistics and the objectives of the Malaysian Education Blueprint (2013-2025). Challenges and initiatives regarding mobile phone usage in schools and broader ICT integration are also highlighted.