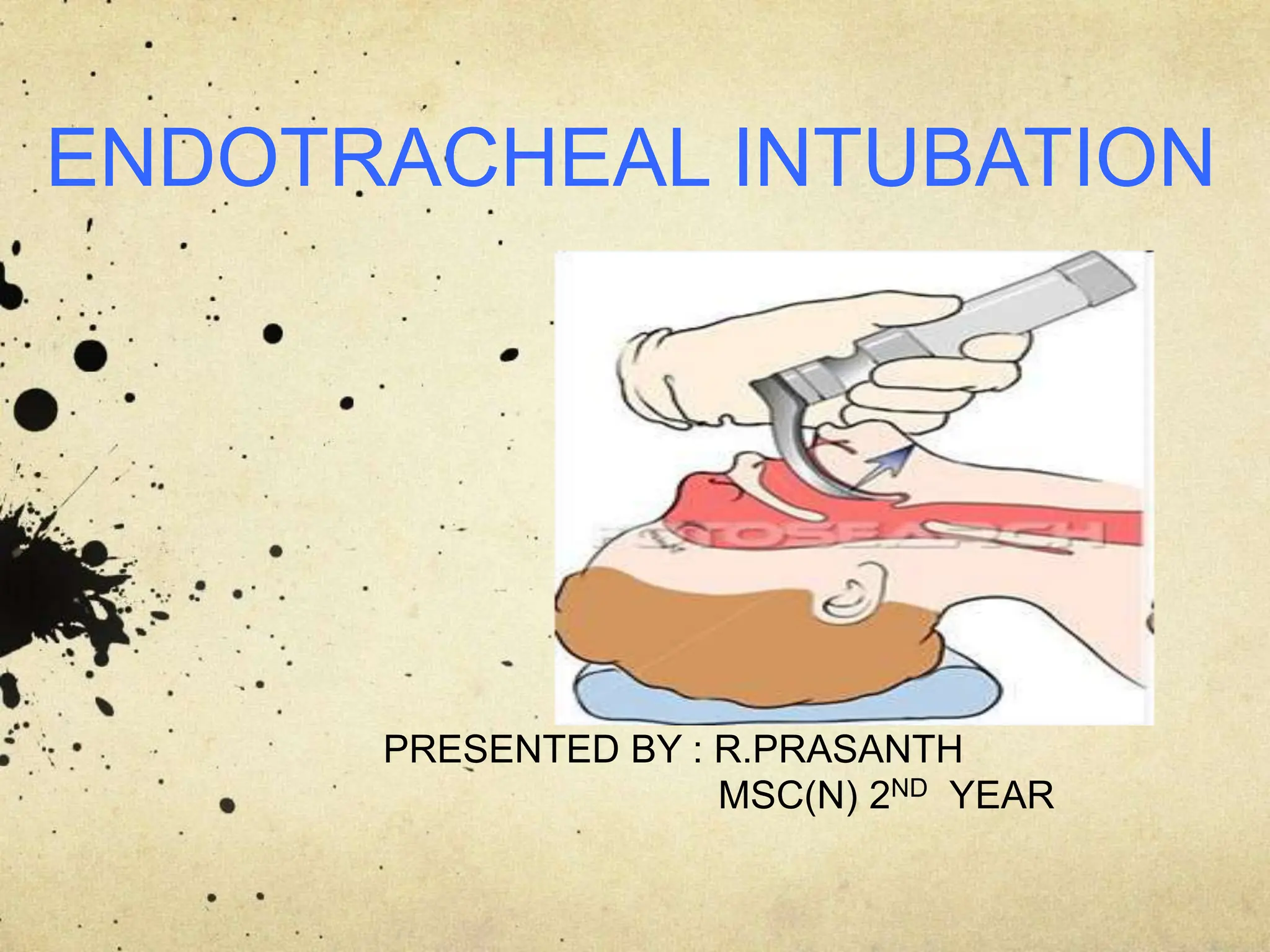
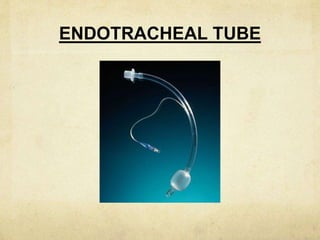
This document provides information about endotracheal intubation including definition, purpose, equipment used, procedure steps, and confirmation of proper placement. Endotracheal intubation involves passing an endotracheal tube into the trachea through the mouth or nose to secure the airway and facilitate ventilation. Key equipment includes a laryngoscope, endotracheal tubes of varying sizes, and devices to confirm proper placement like end-tidal CO2 detectors. The procedure involves positioning, visualization of the vocal cords, and passing the tube between the cords into the trachea. Placement is then confirmed using physical exam, auscultation, and secondary confirmation with devices.