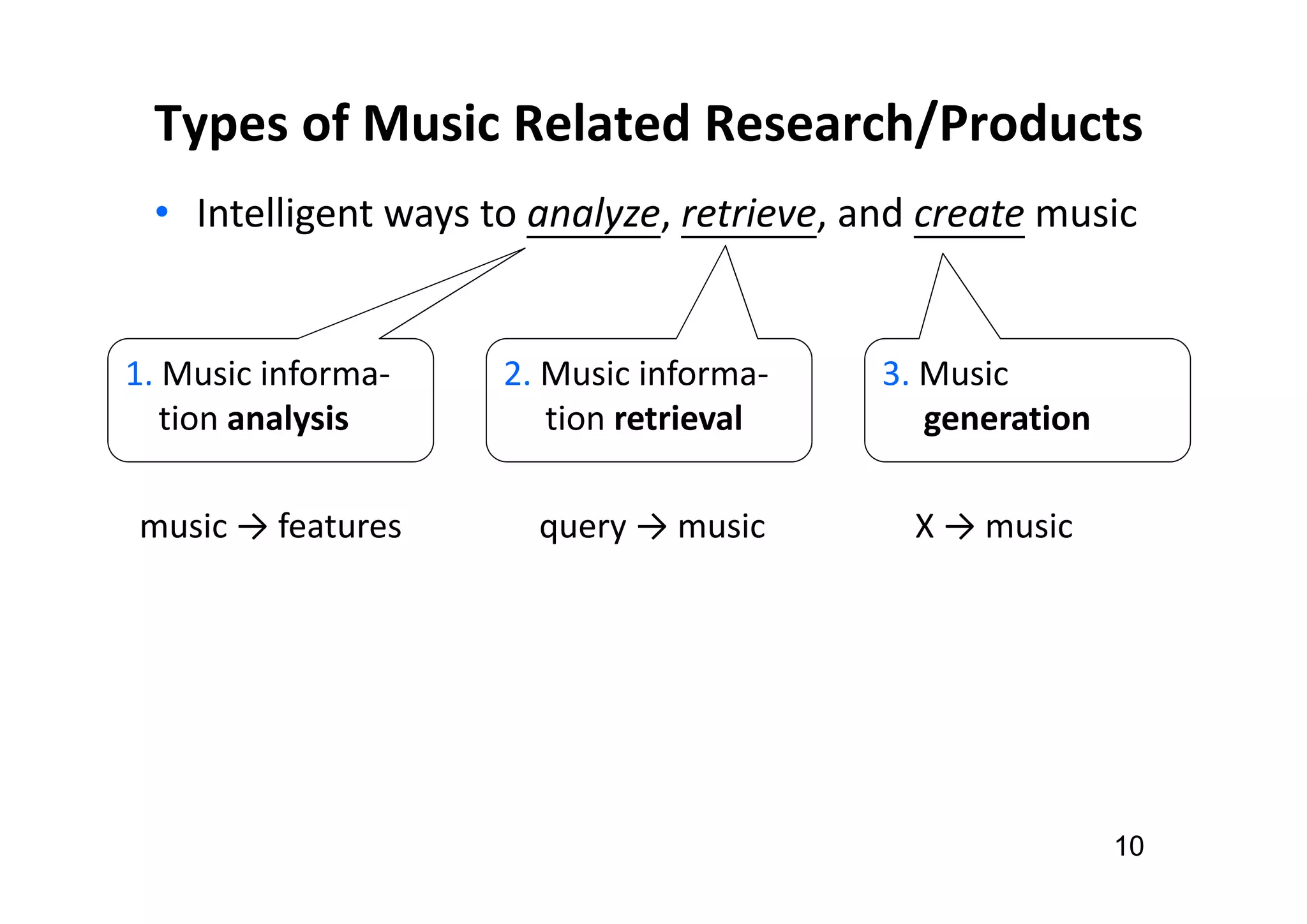
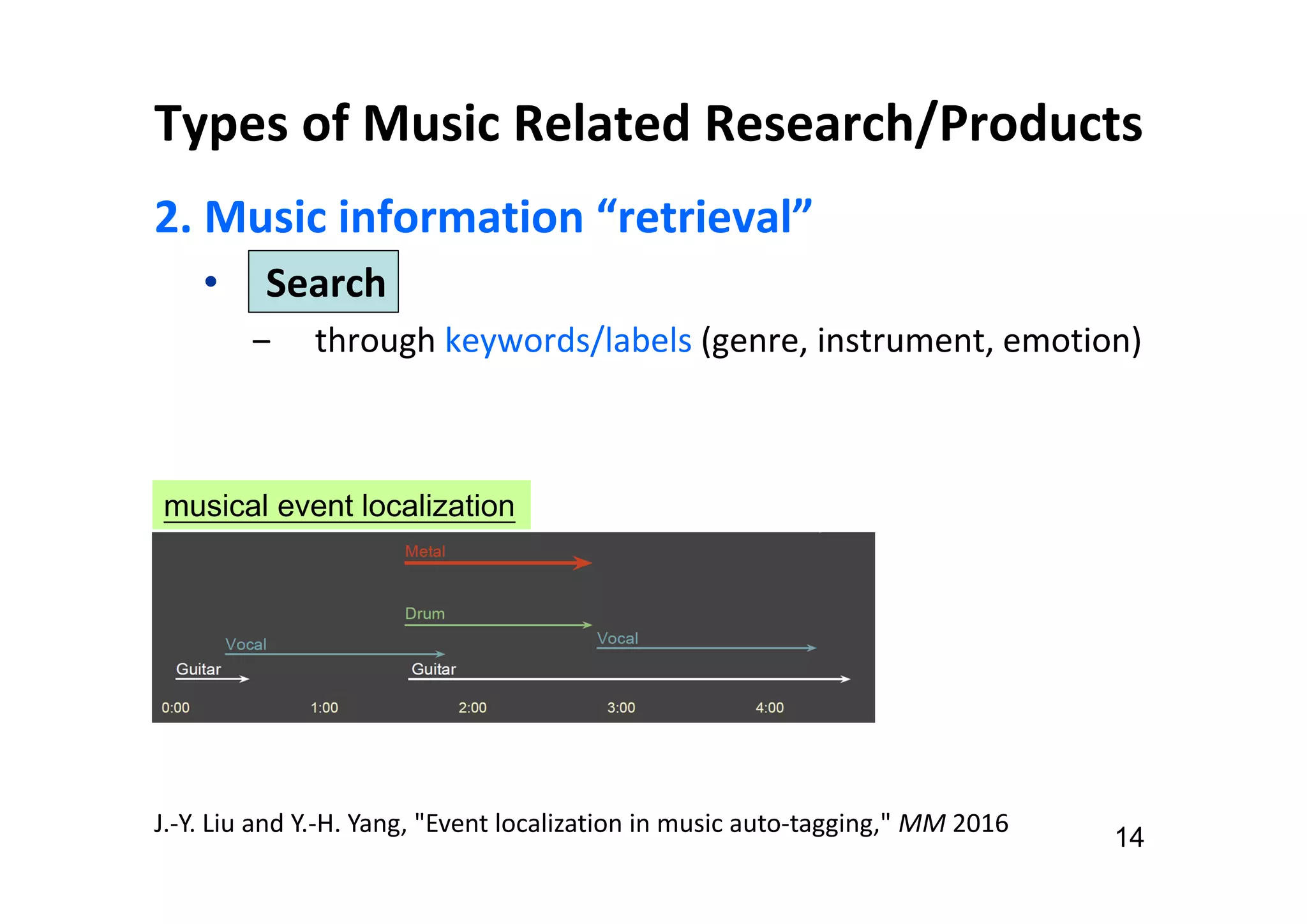
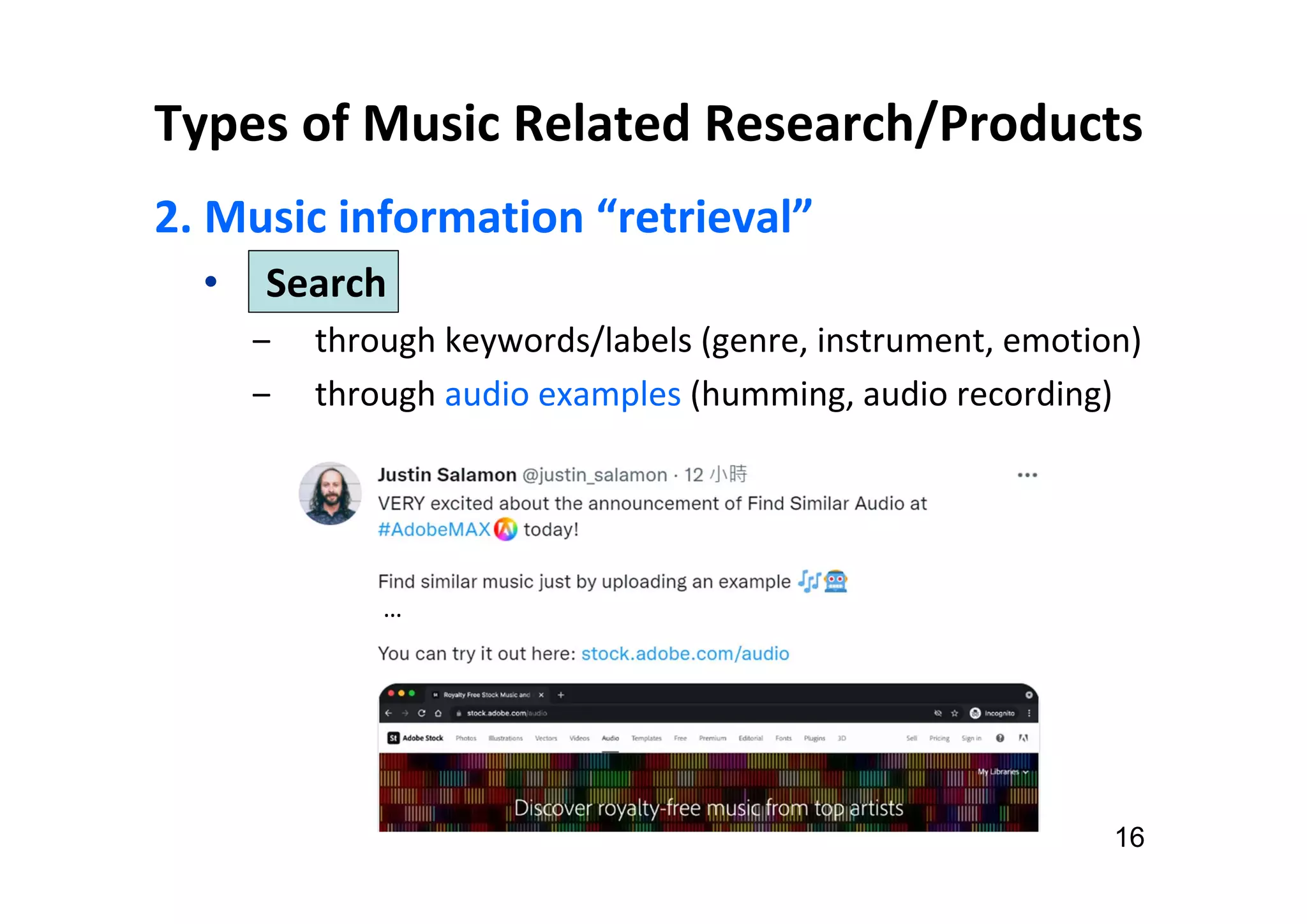
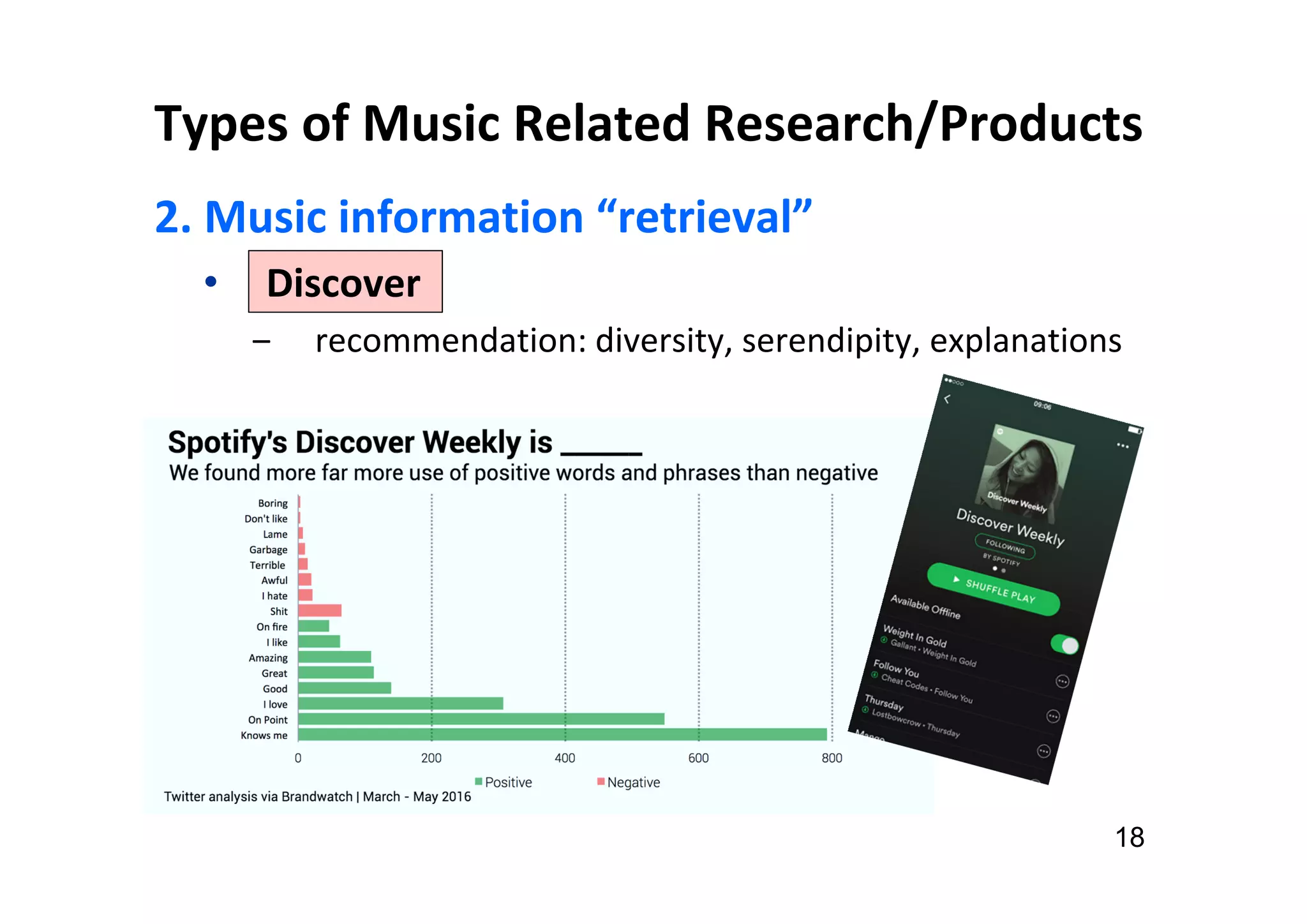
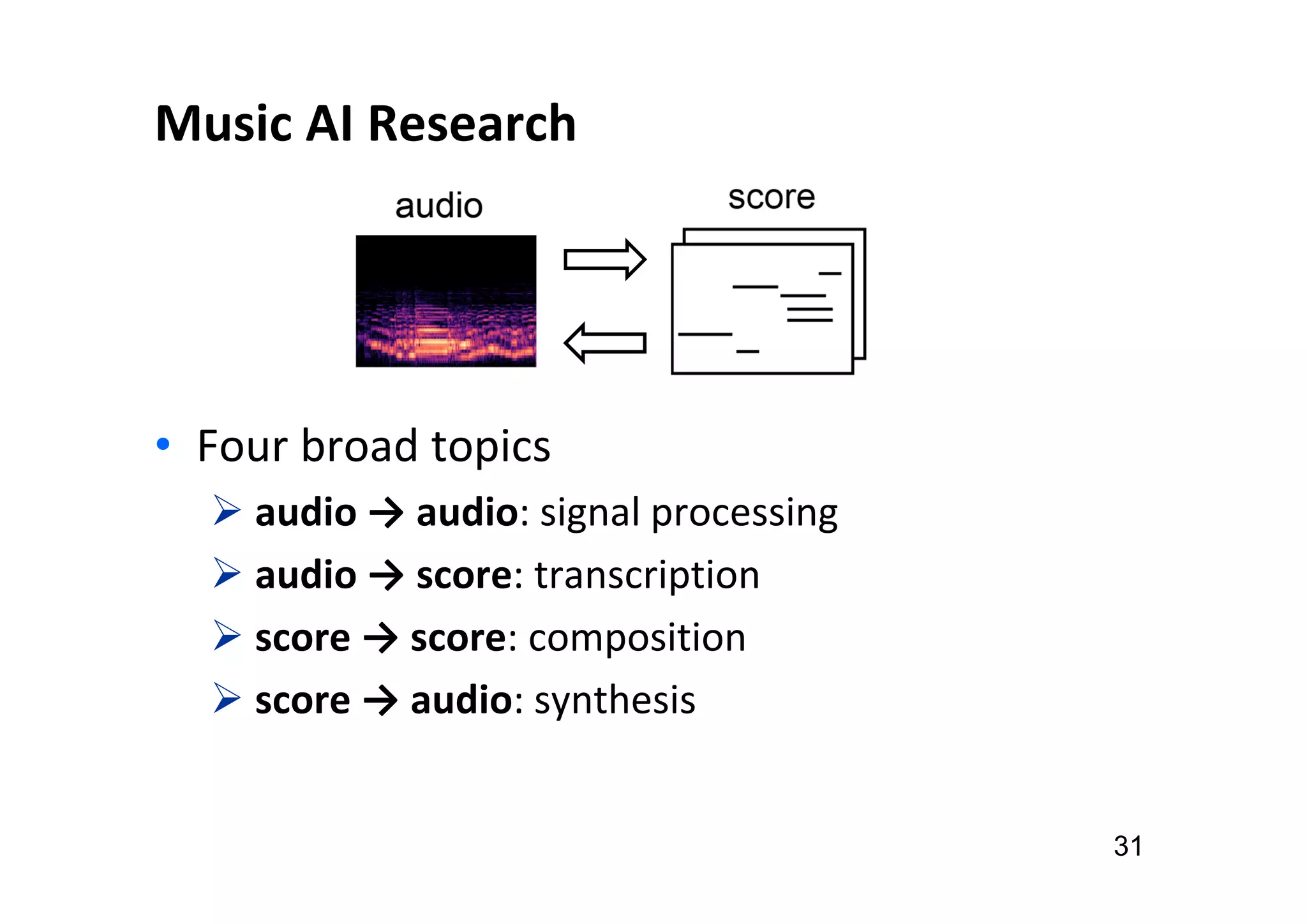
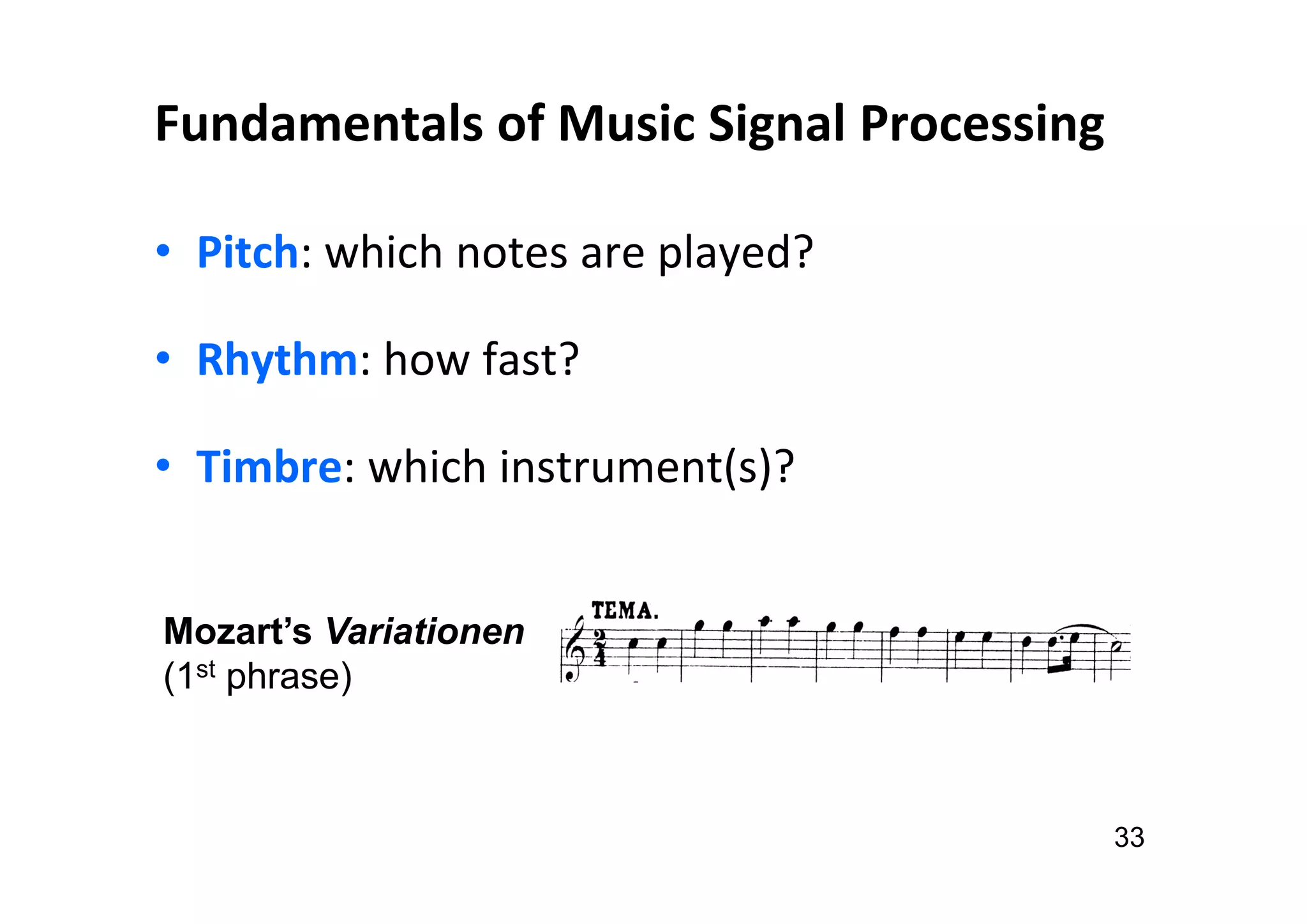
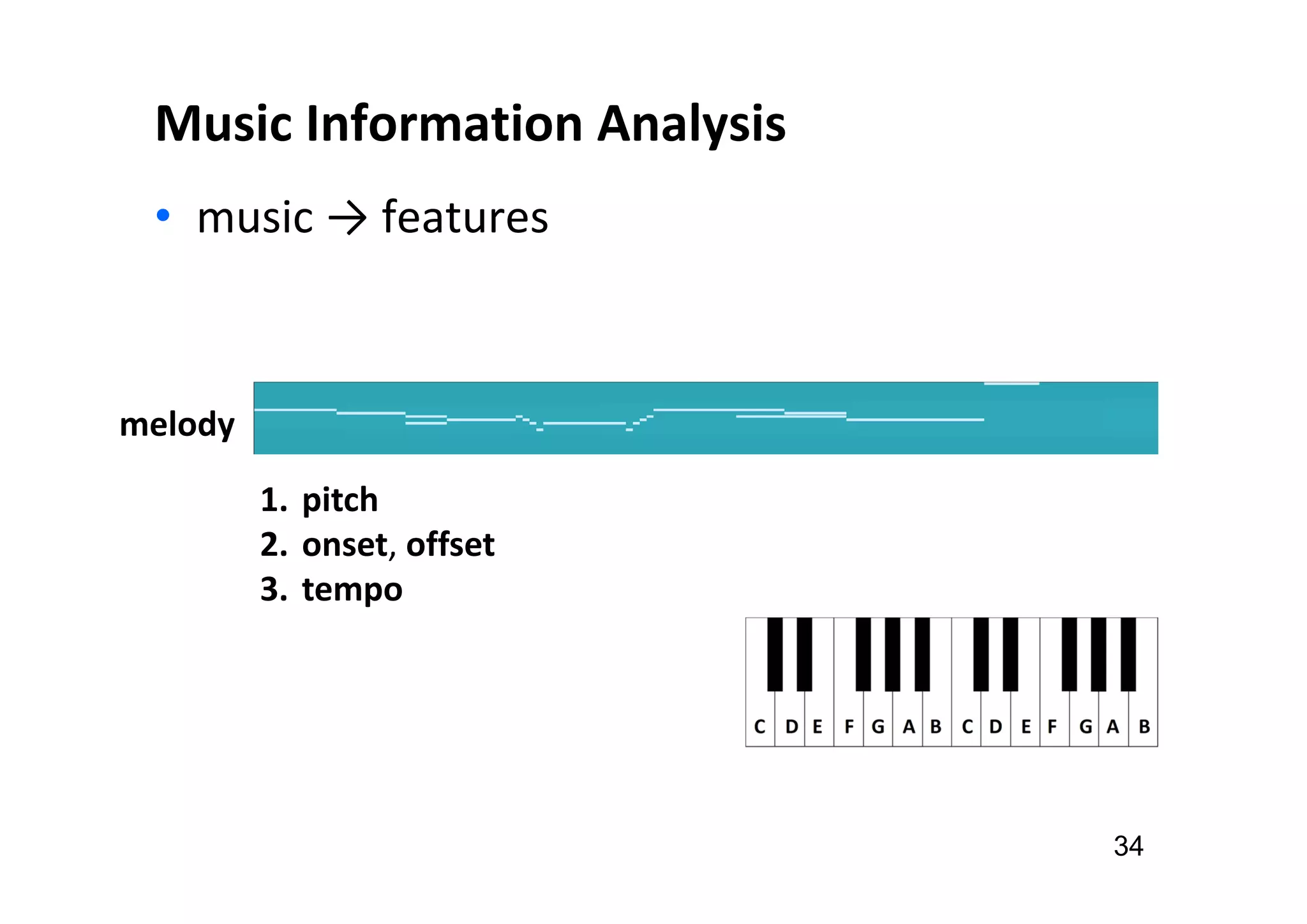
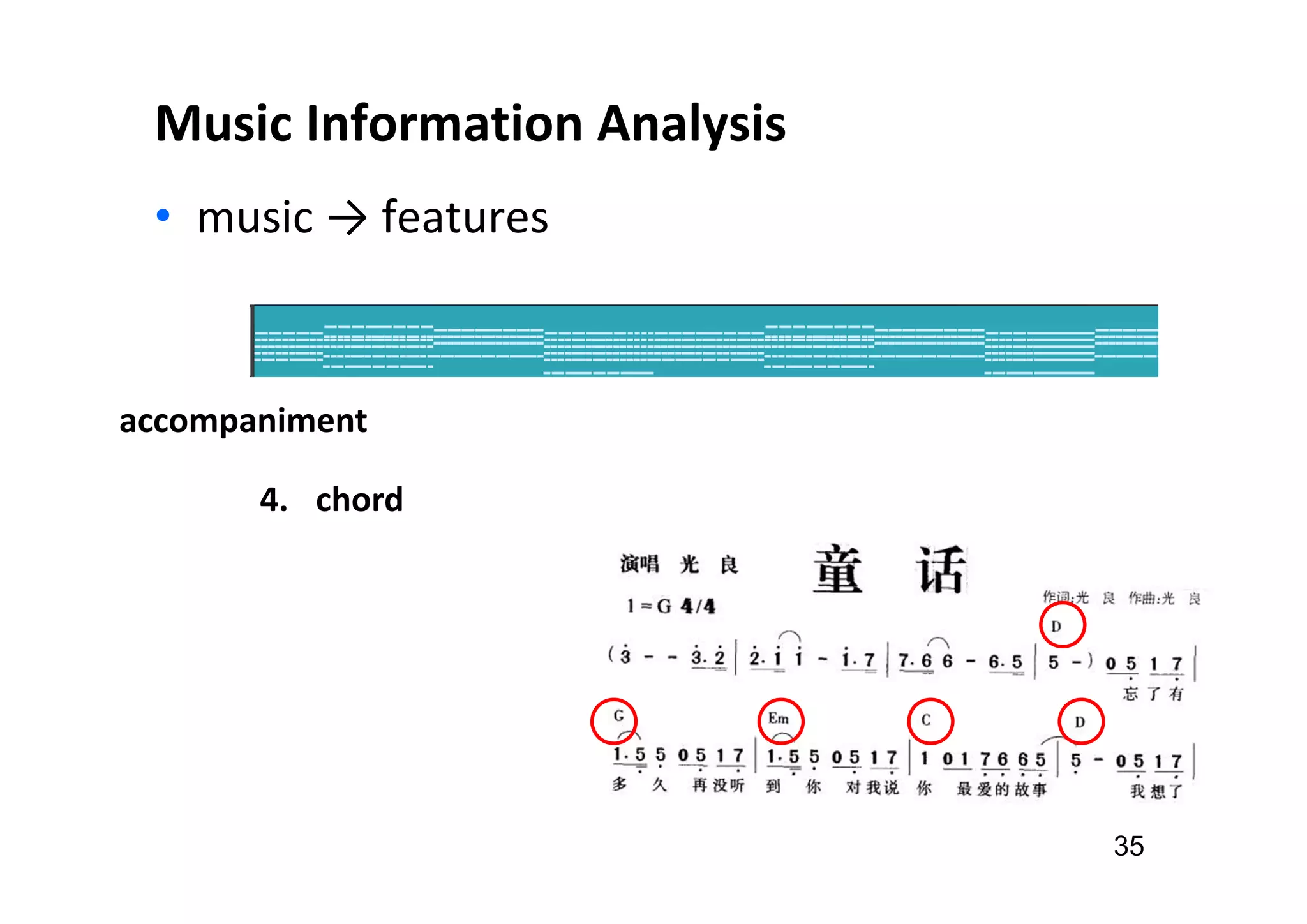
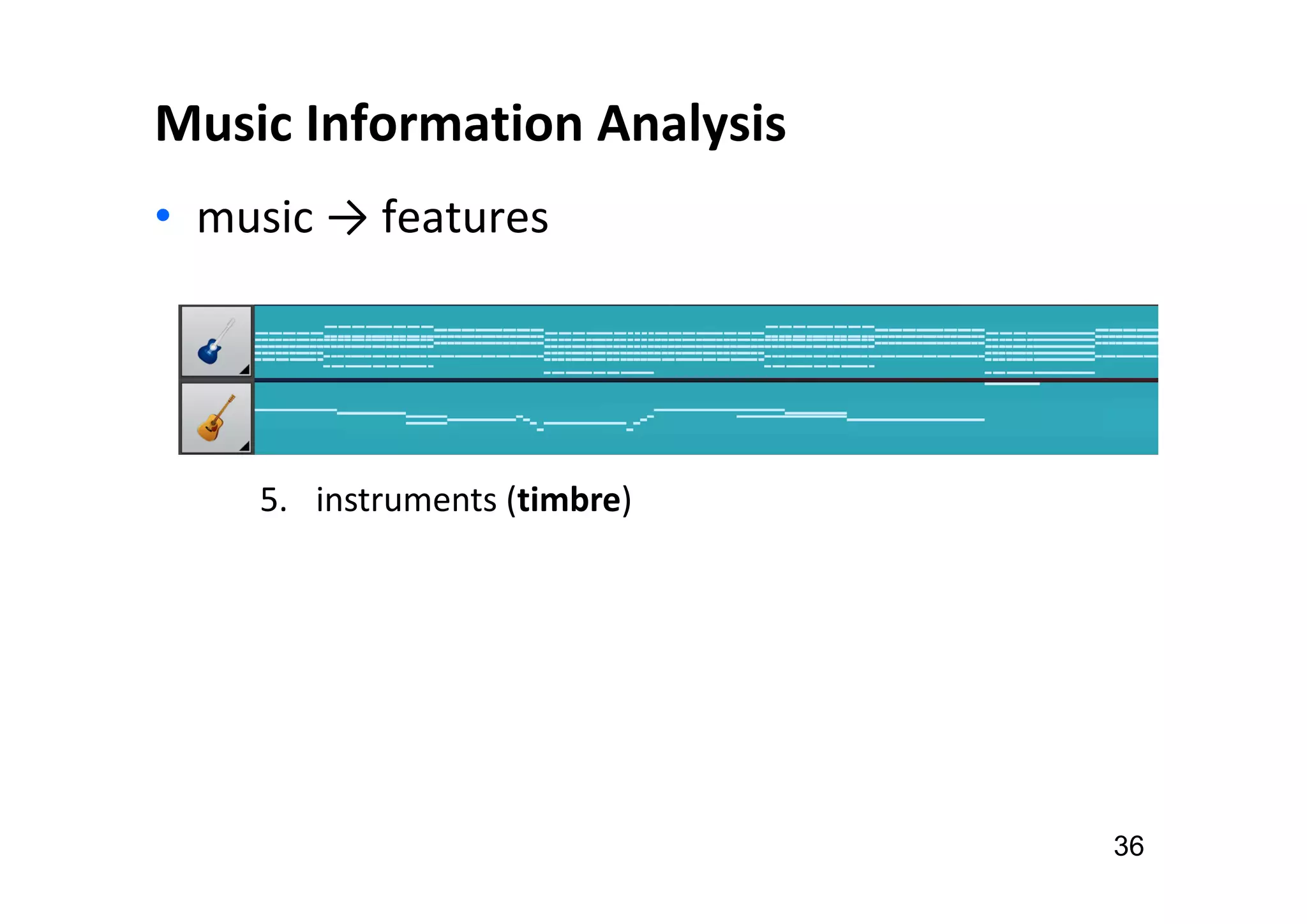
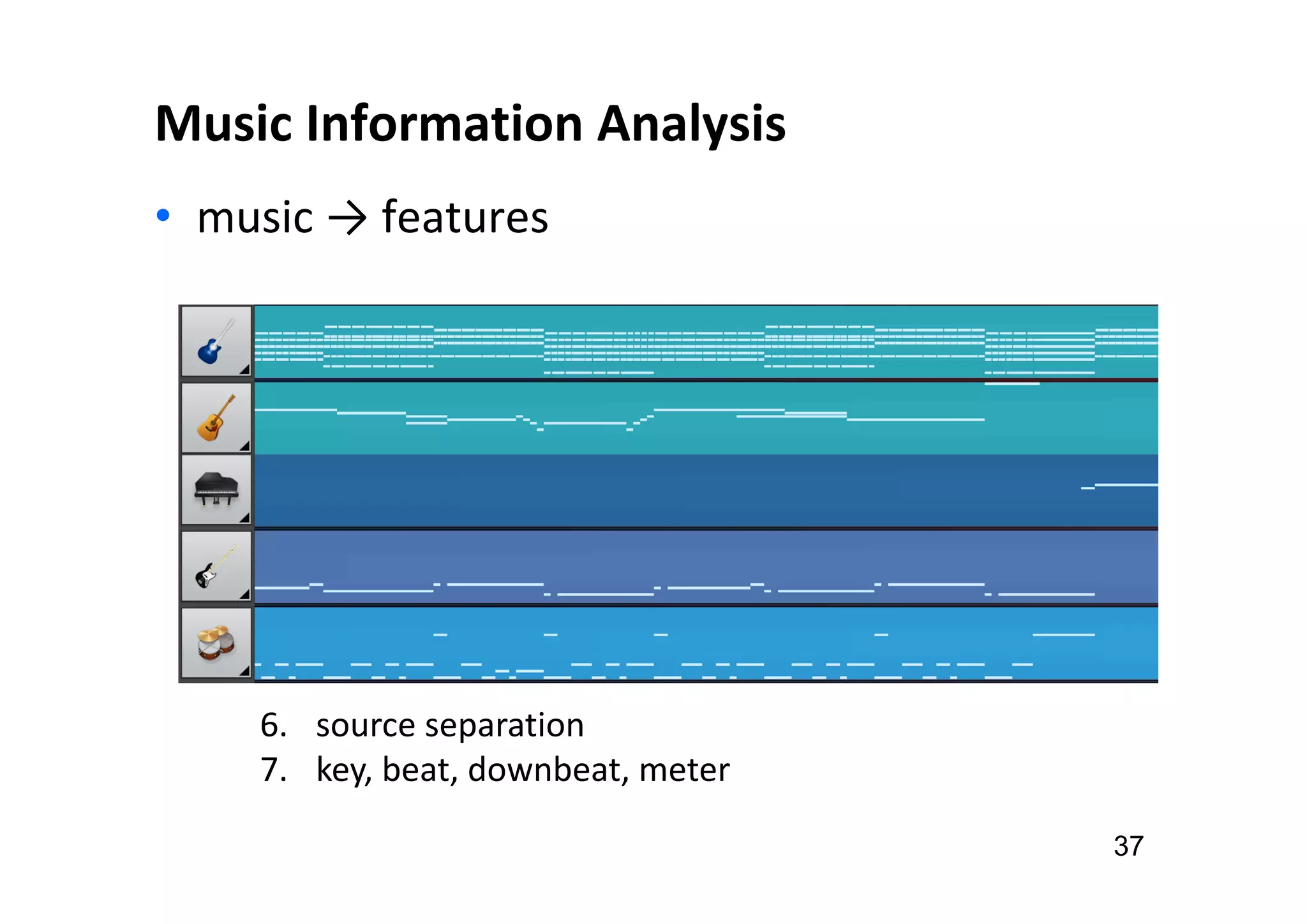
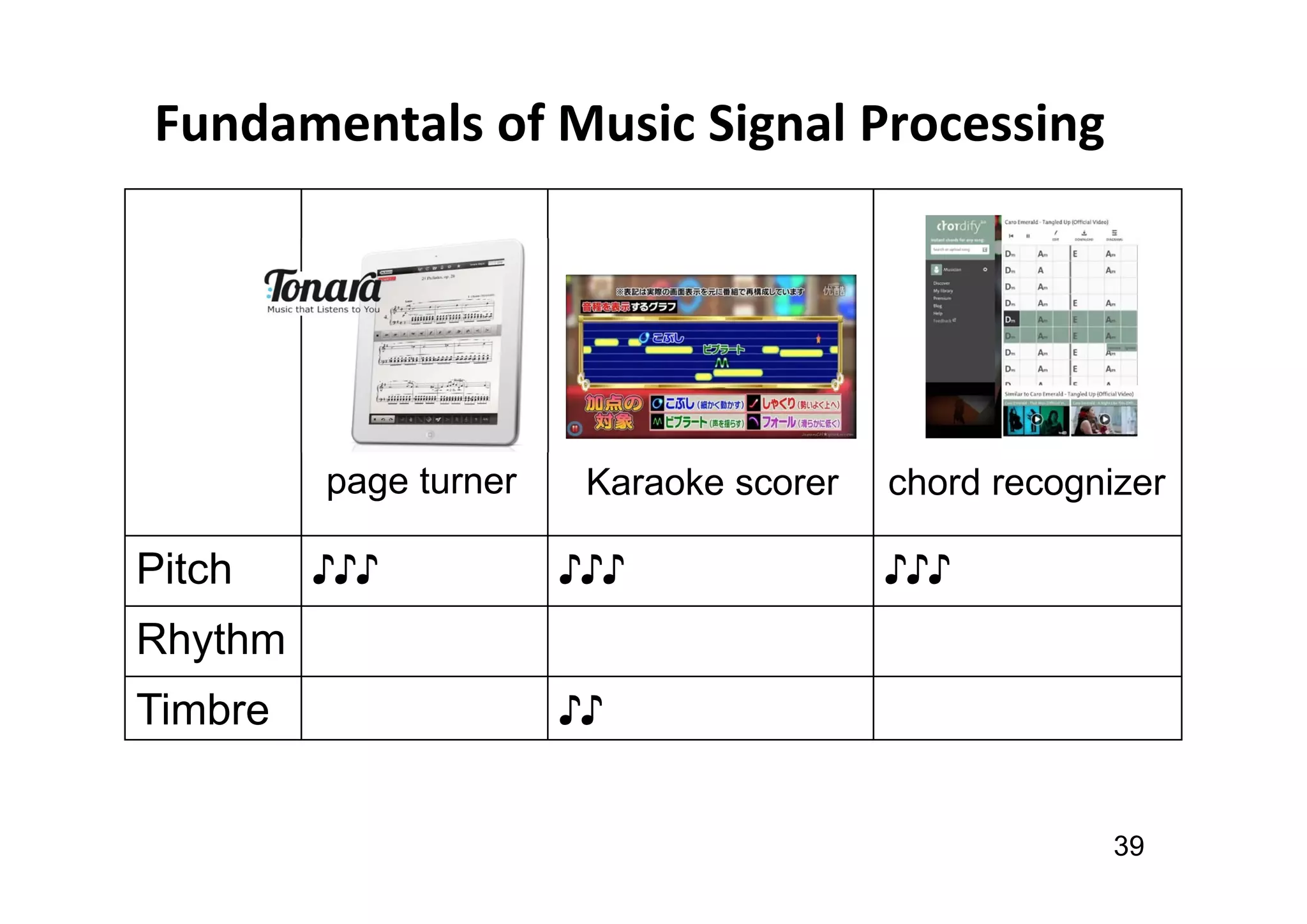
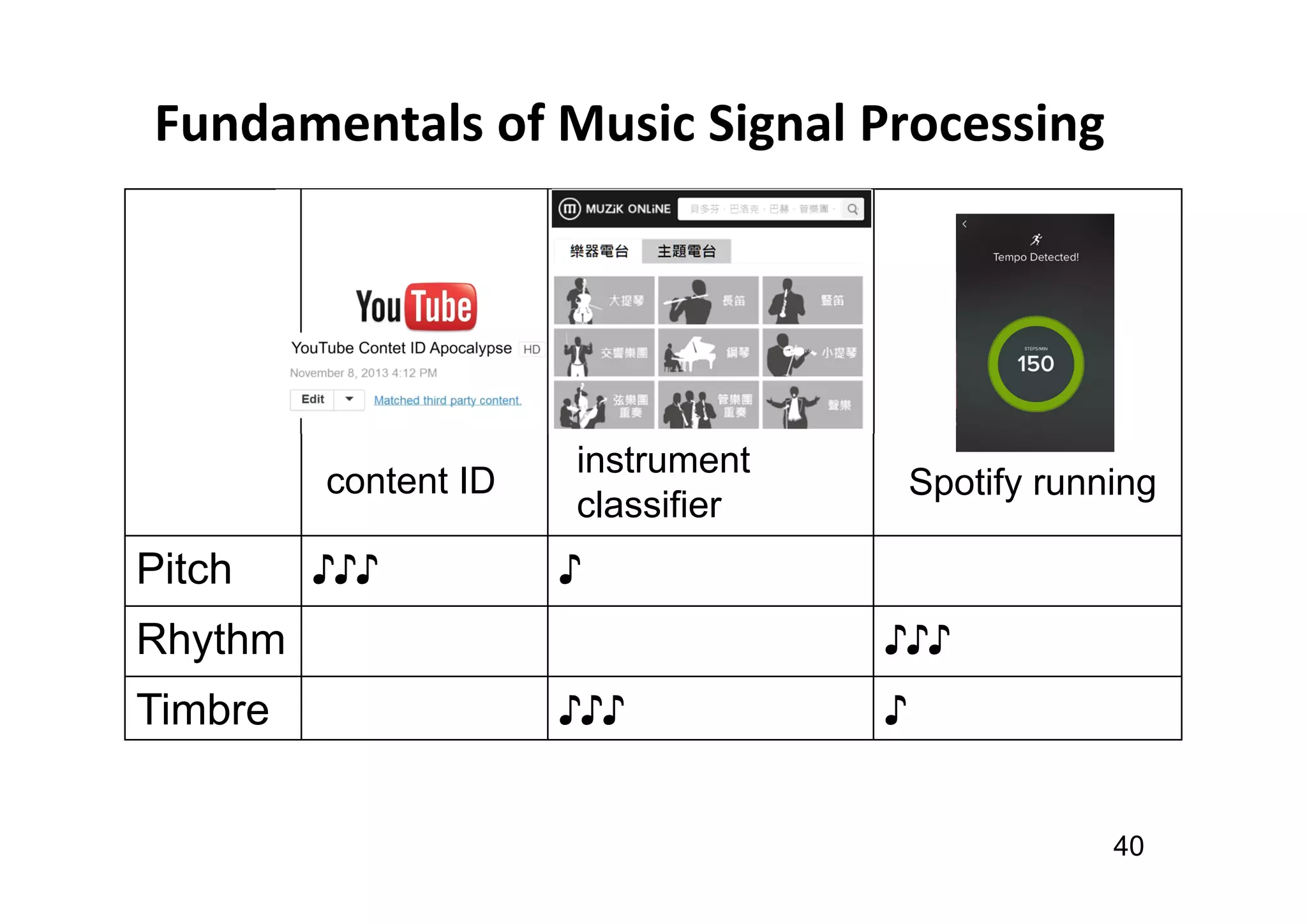
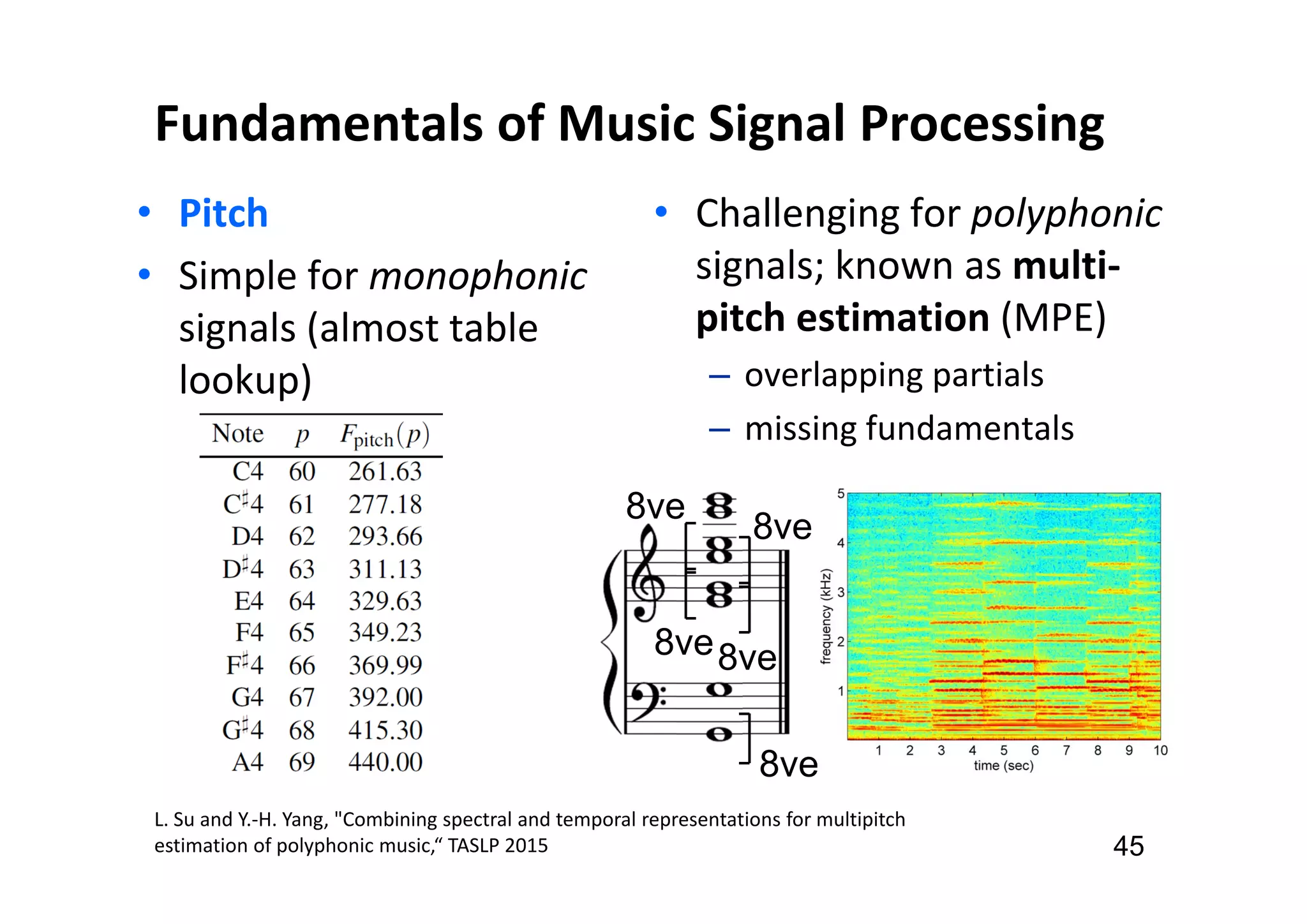
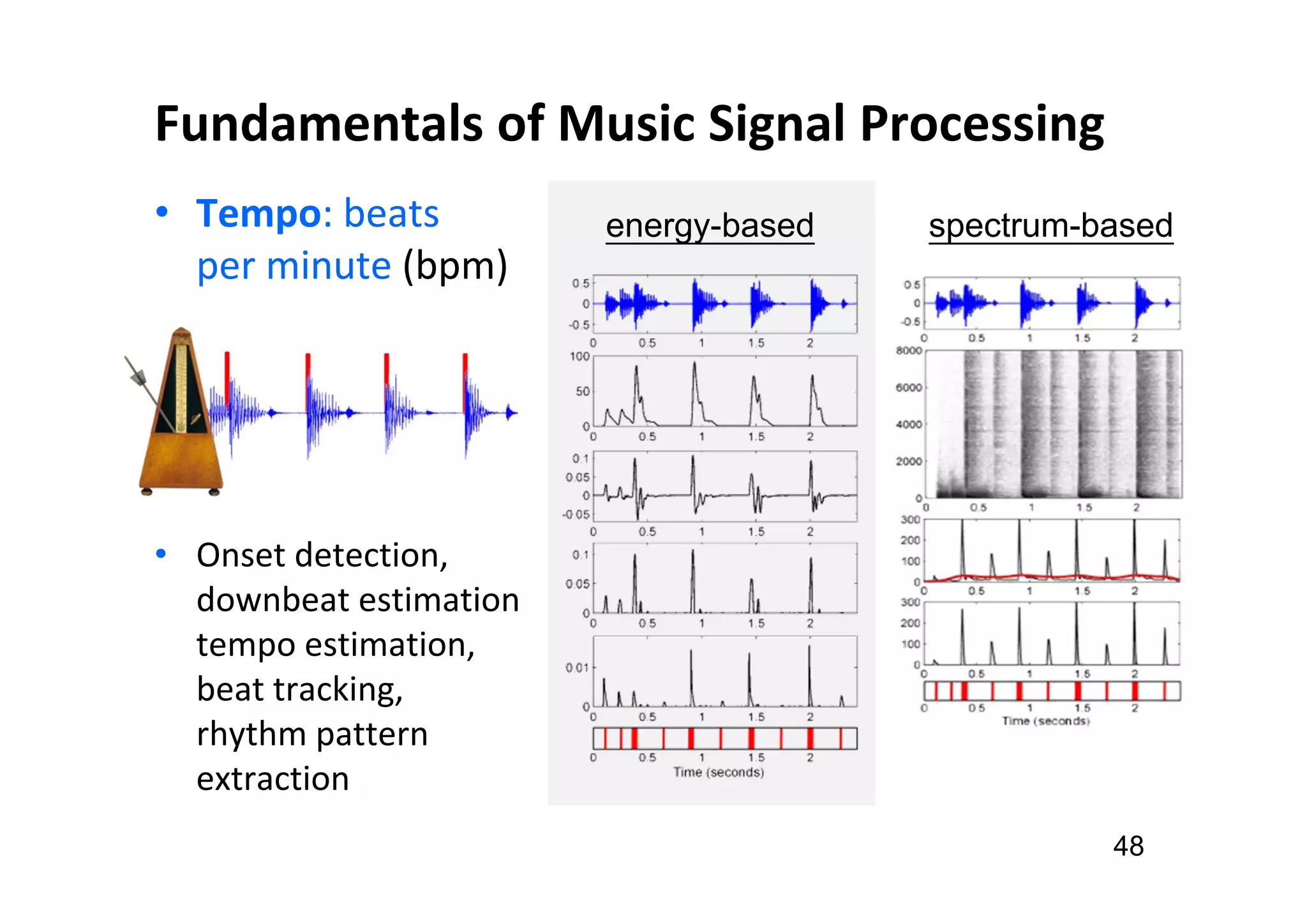
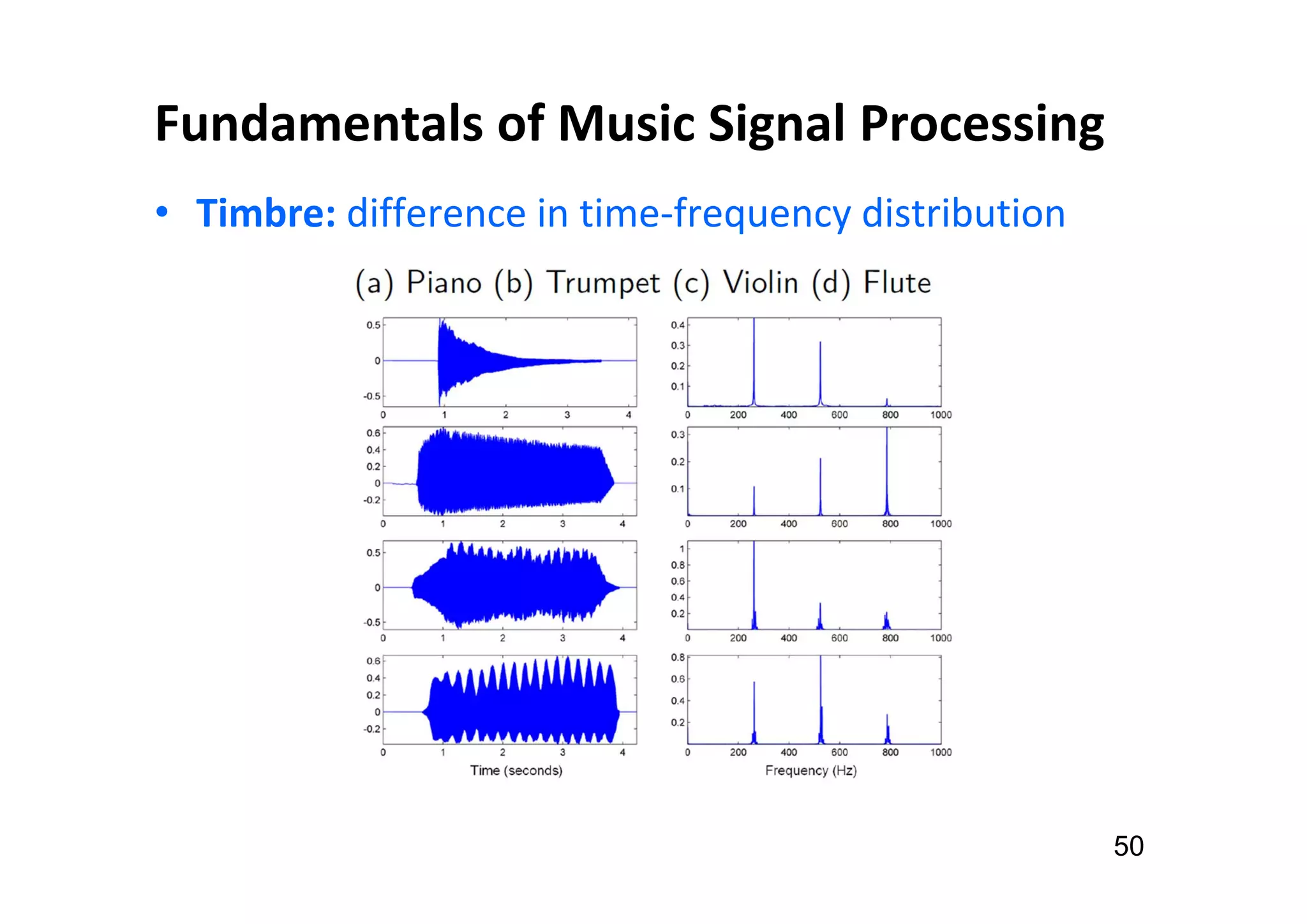
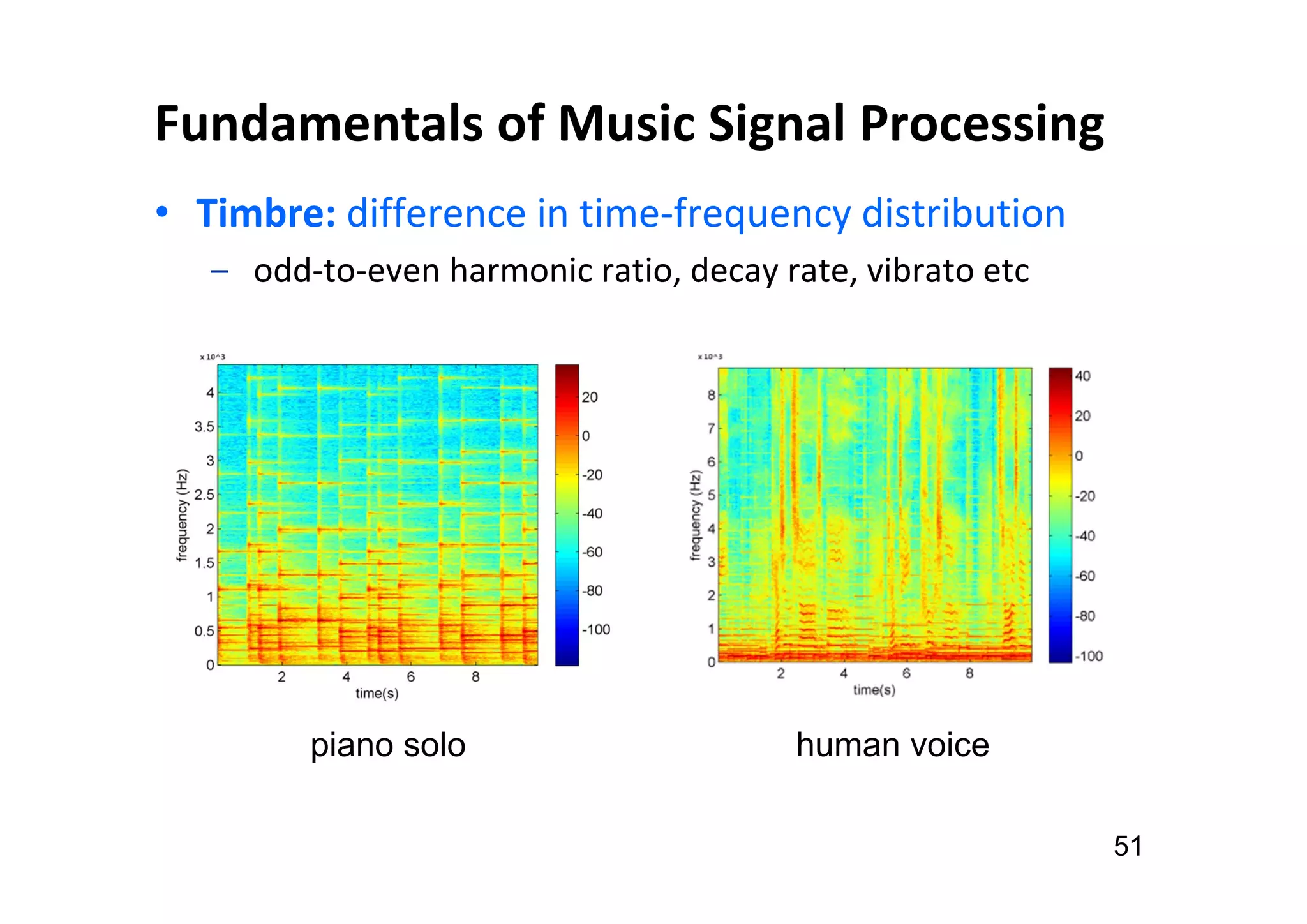
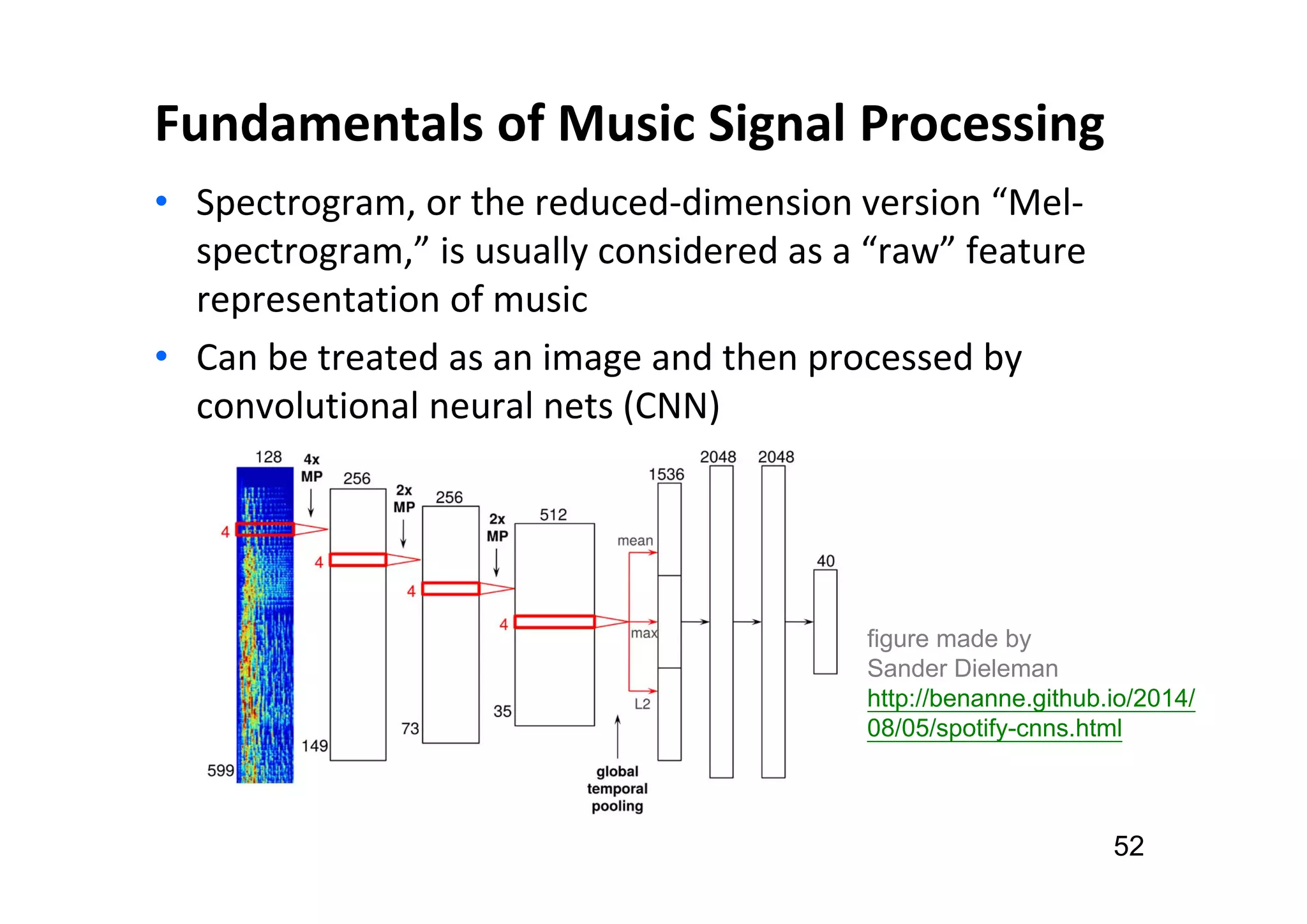
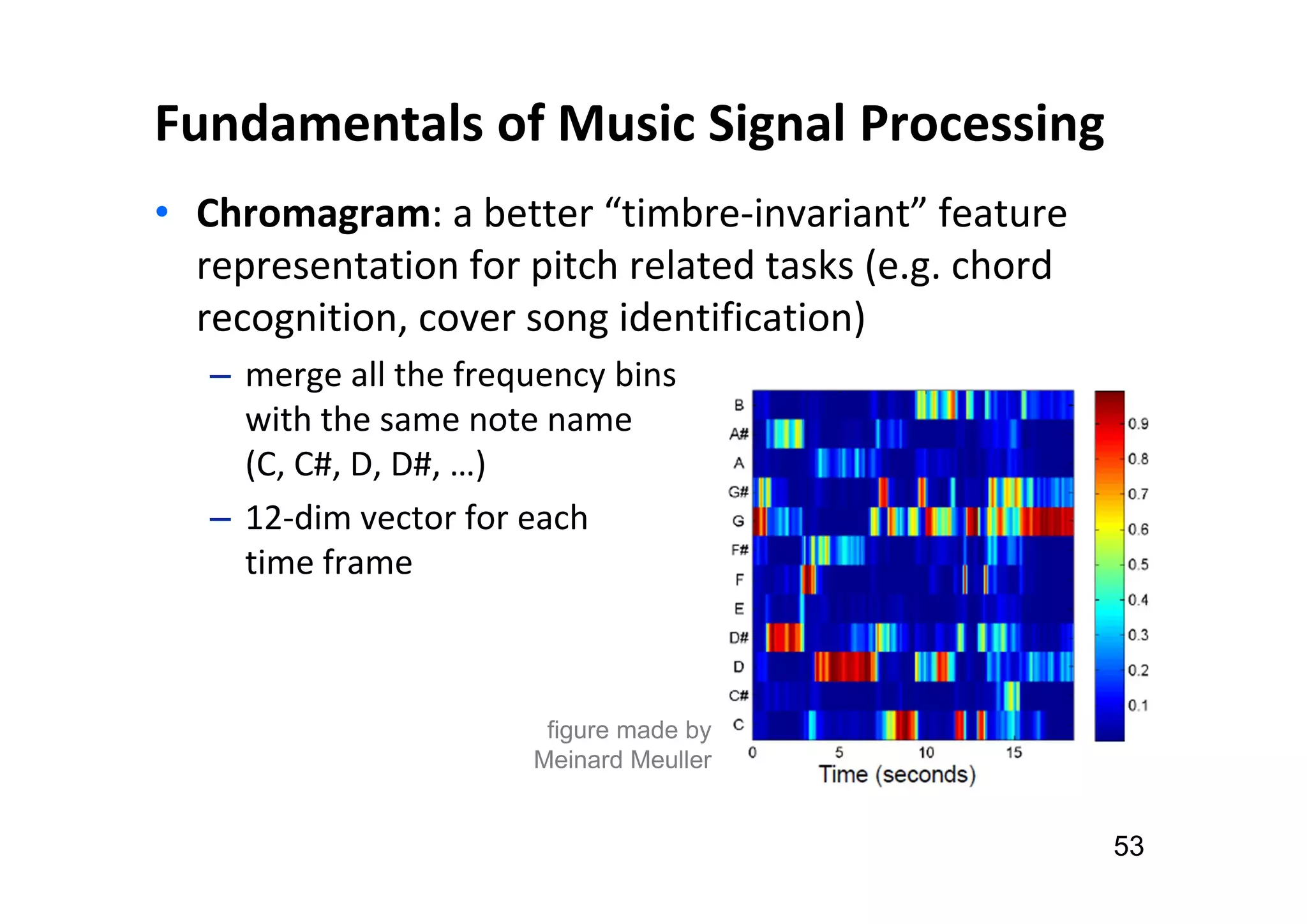
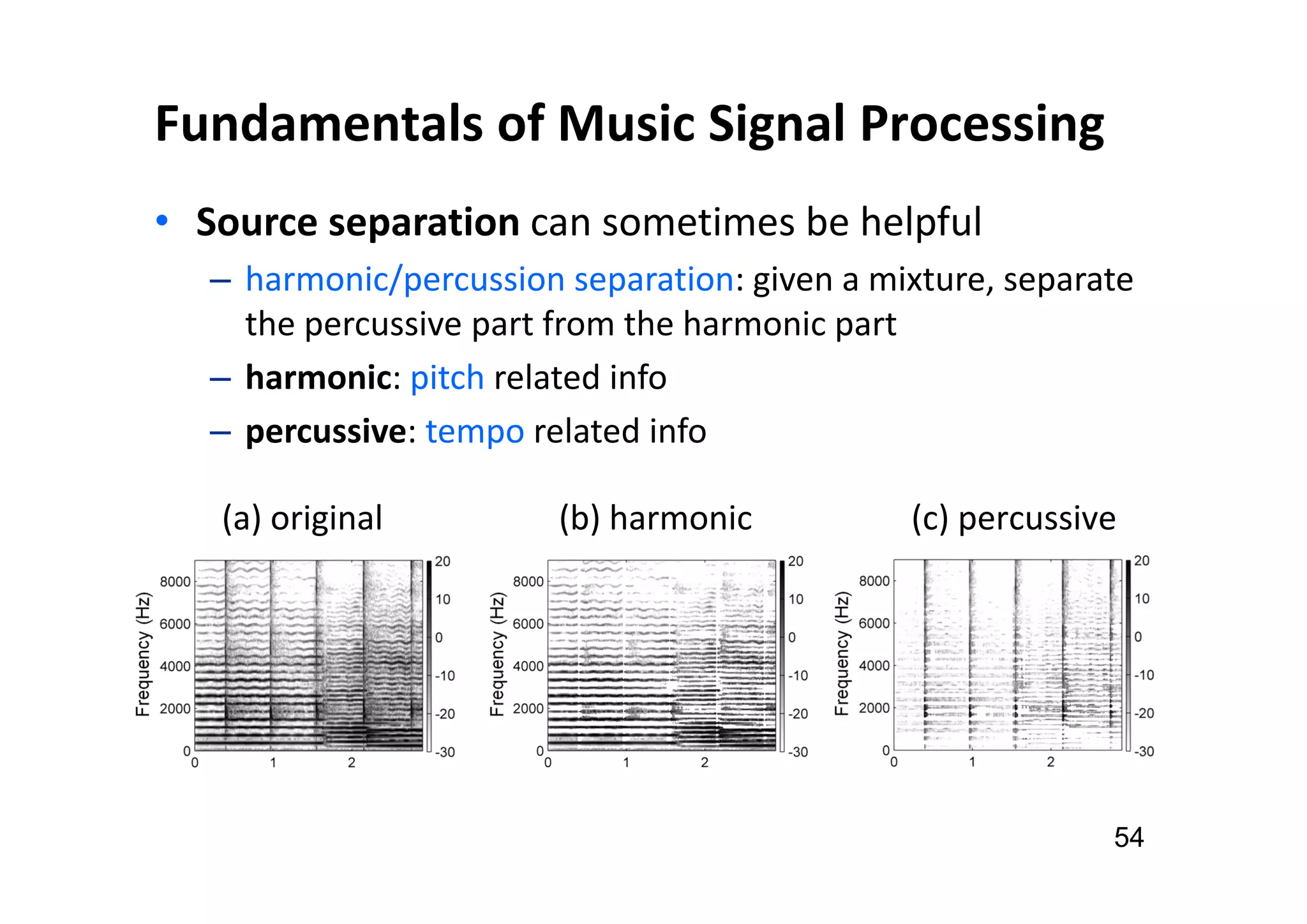
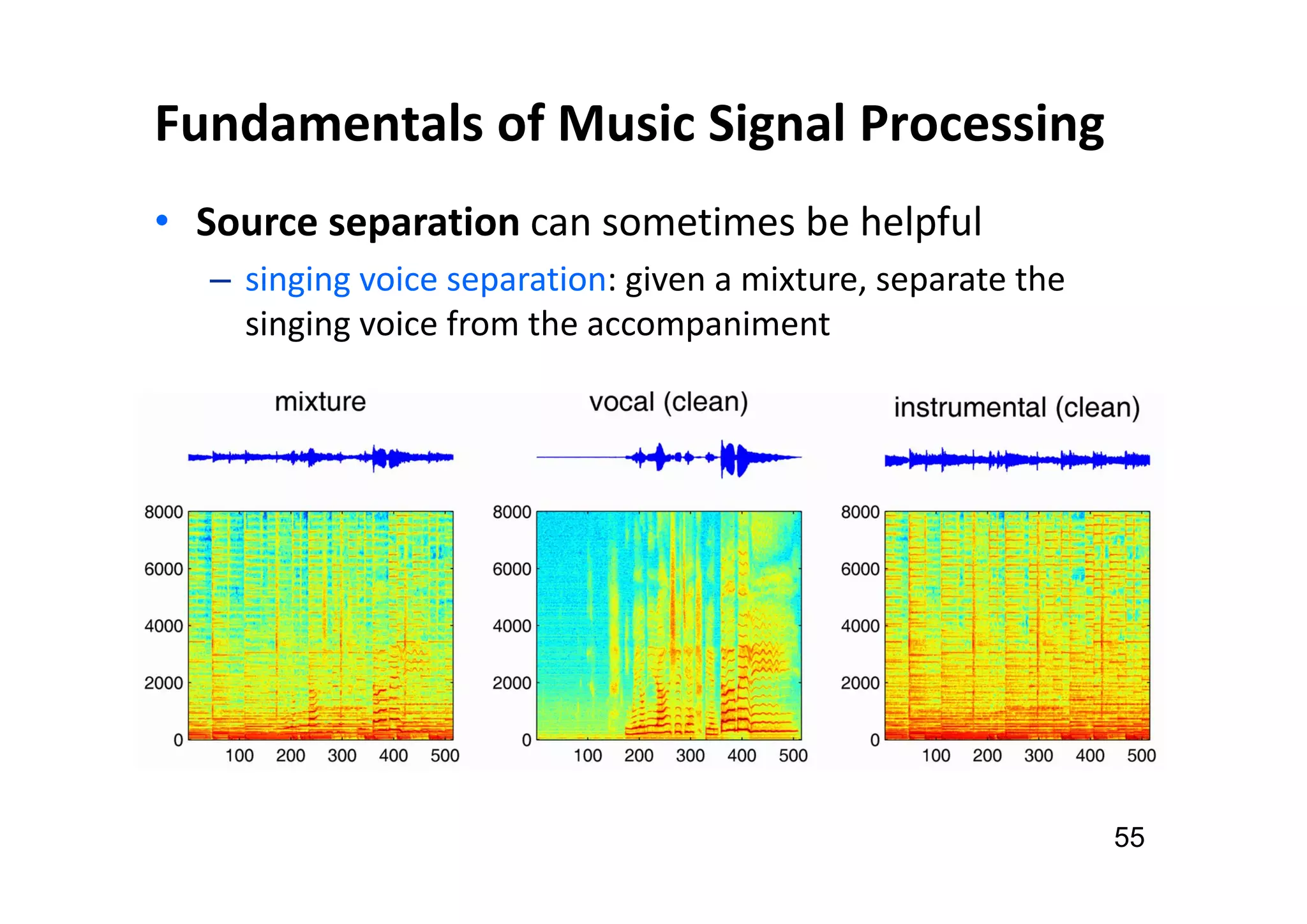
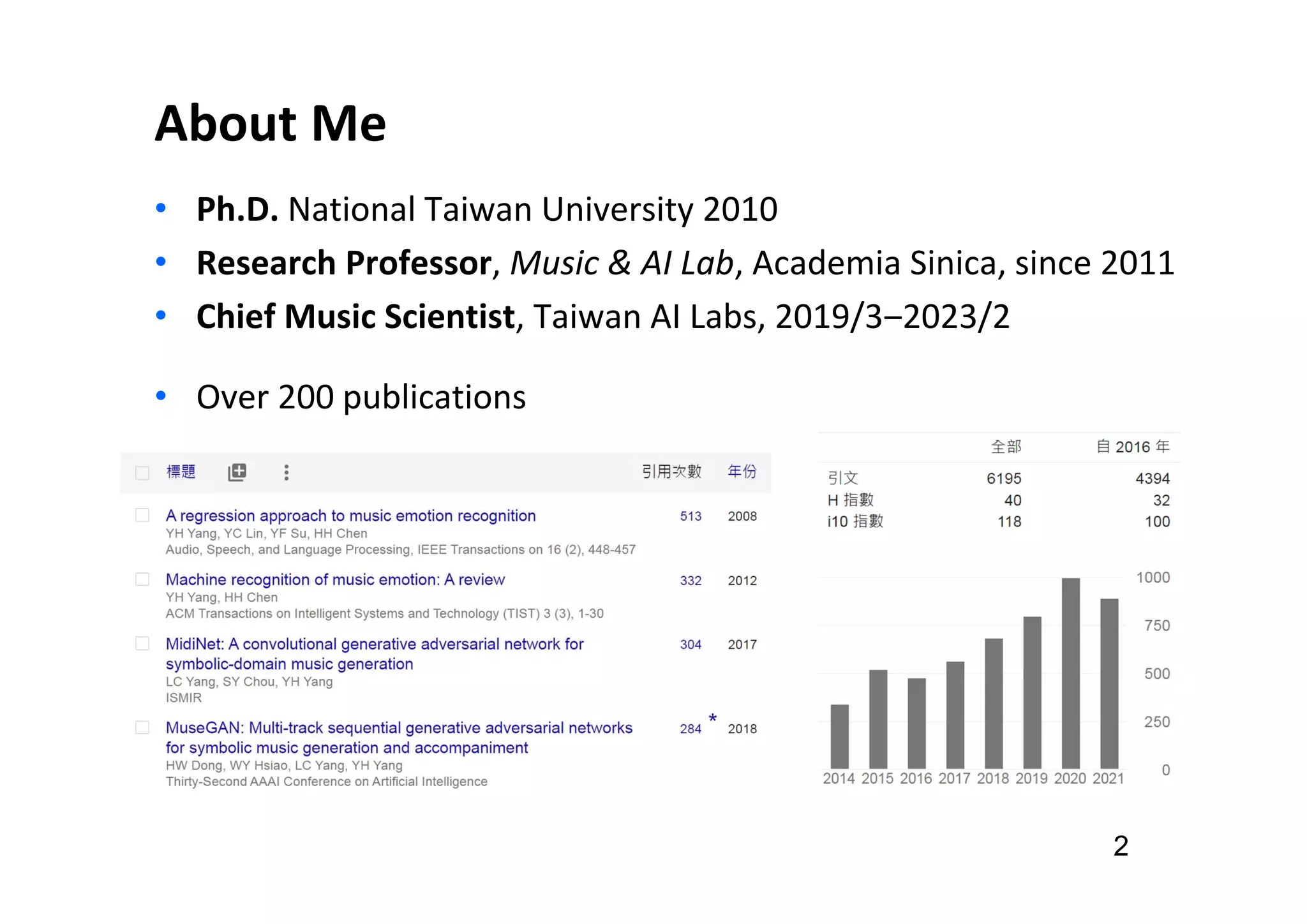
The document presents the profile of Yi-Hsuan Yang, a research professor at Academia Sinica and chief music scientist at Taiwan AI Labs, highlighting his extensive work in music information analysis, retrieval, and generation. It outlines various research products and methodologies used in the Music AI Lab, including intelligent music analysis tools and context-aware music retrieval systems, along with foundational concepts in music signal processing. Additionally, it discusses the types of data utilized in music research, emphasizing the integration of signal processing, machine learning, and musicology.

![About the Music and AI Lab @ Sinica
About Academia Sinica
National academy of Taiwan, founded in 1928
About 1,000 Full/Associate/Assistant Researchers
About Music and AI Lab (musicai)
Since Sep 2011
Members
PI [me]
research assistants
PhD/master students
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20211026taicca-1introtomir-211027091454/75/20211026-taicca-1-intro-to-mir-3-2048.jpg)
![About the Music AI Team @
About Taiwan AI Labs
Privately-funded research organization,
founded by Ethan Tu (PTT) in 2017
Three main research area: 1) HCI, 2) medicine, 3) smart city
About the Music AI team
Members
scientist [me; since March 2019]
ML engineers (for models)
musicians
program manager
software engineers (for frontend/backend)
4
(an image of our musicians)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20211026taicca-1introtomir-211027091454/75/20211026-taicca-1-intro-to-mir-4-2048.jpg)