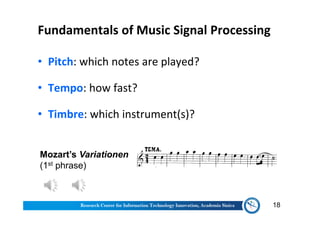
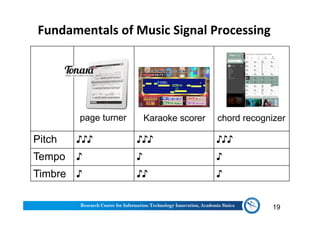
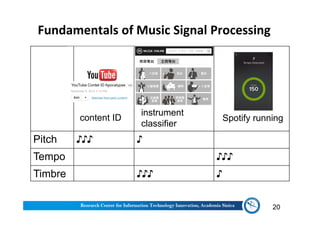
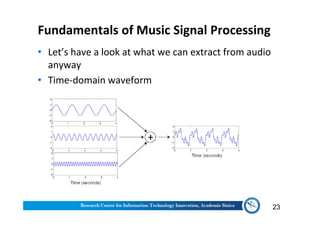
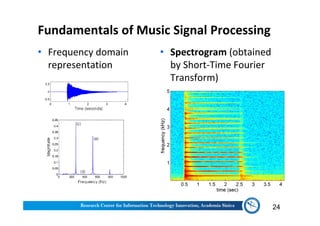
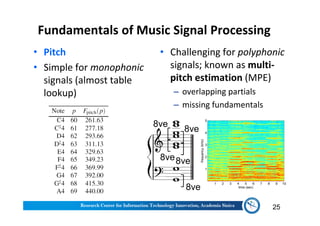
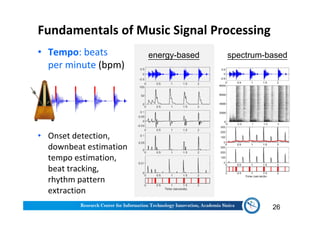
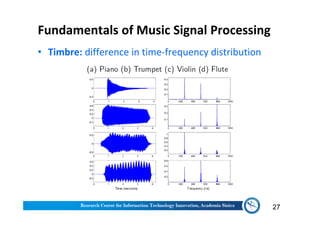
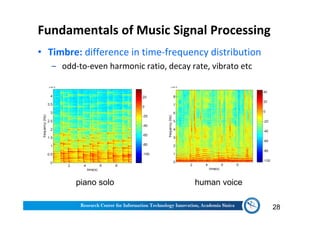
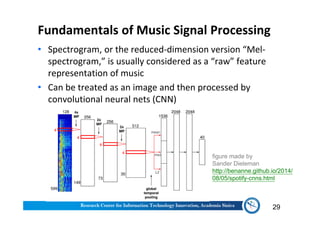
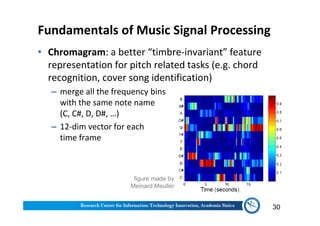
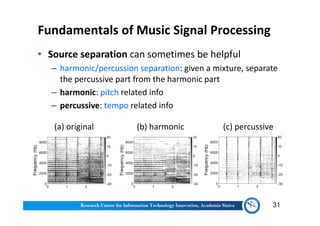
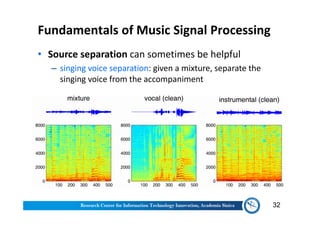
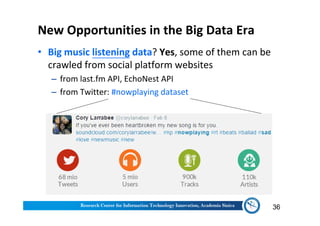
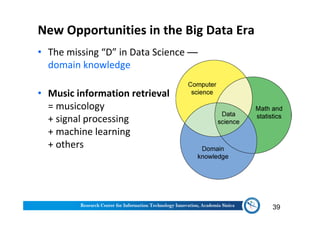
The document discusses various aspects of music information retrieval research conducted at the Music & Audio Computing Lab at Academia Sinica. It covers topics such as music creation, analysis, and retrieval techniques, along with the fundamentals of music signal processing across pitch, tempo, and timbre. It also highlights new opportunities in the big data era, including the potential use of large music datasets and non-audio data for enhancing music-related technologies.