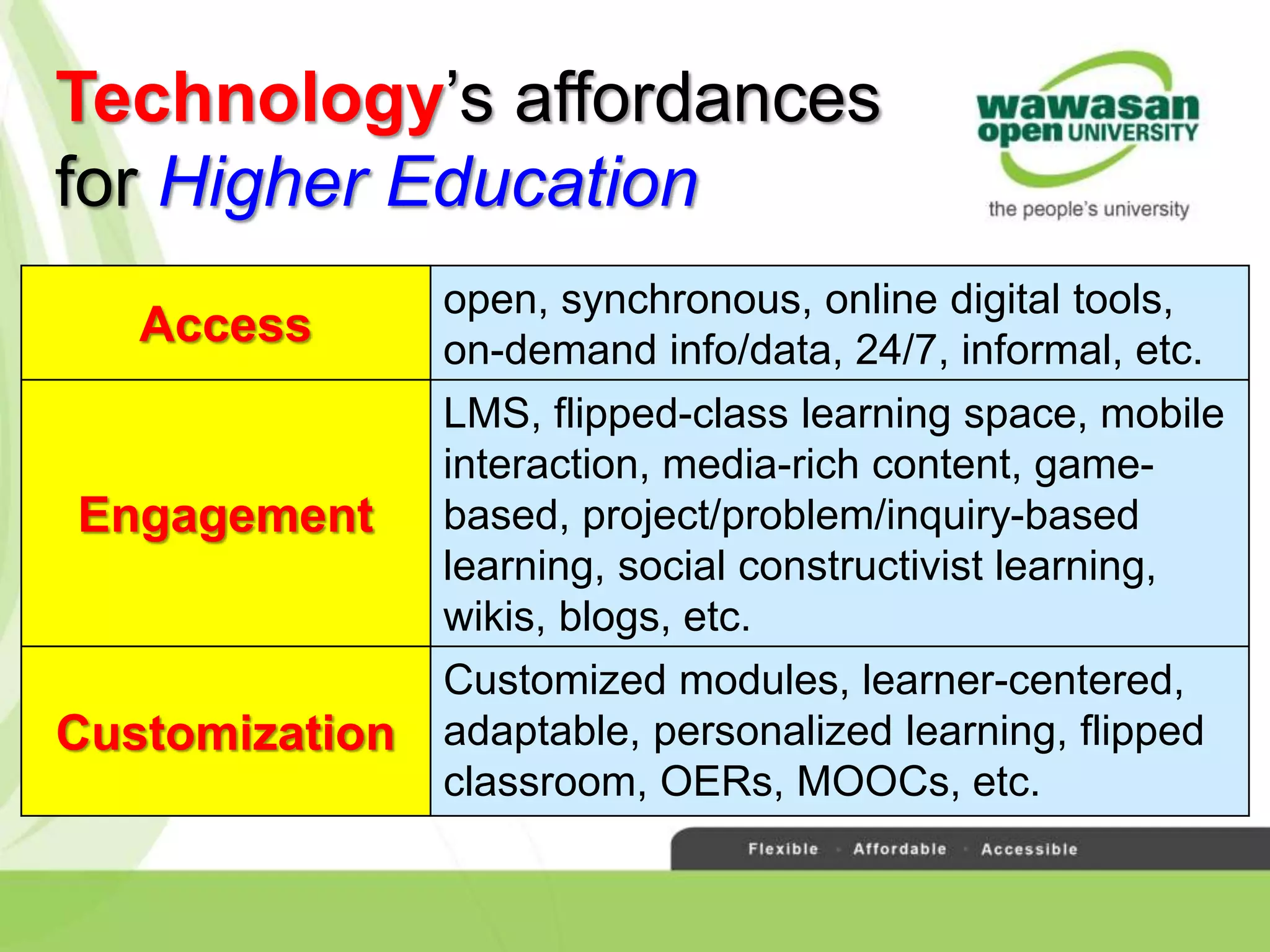
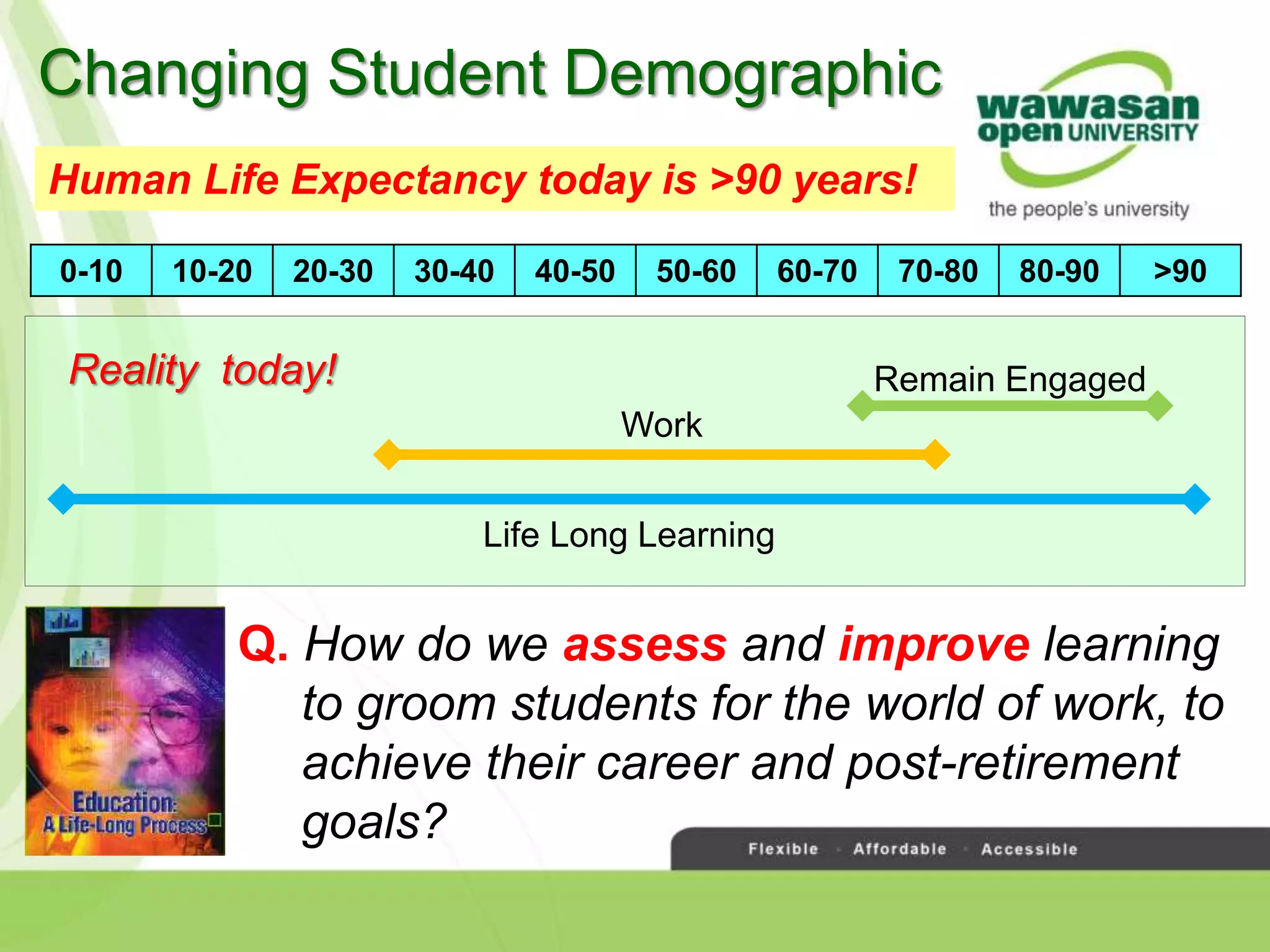
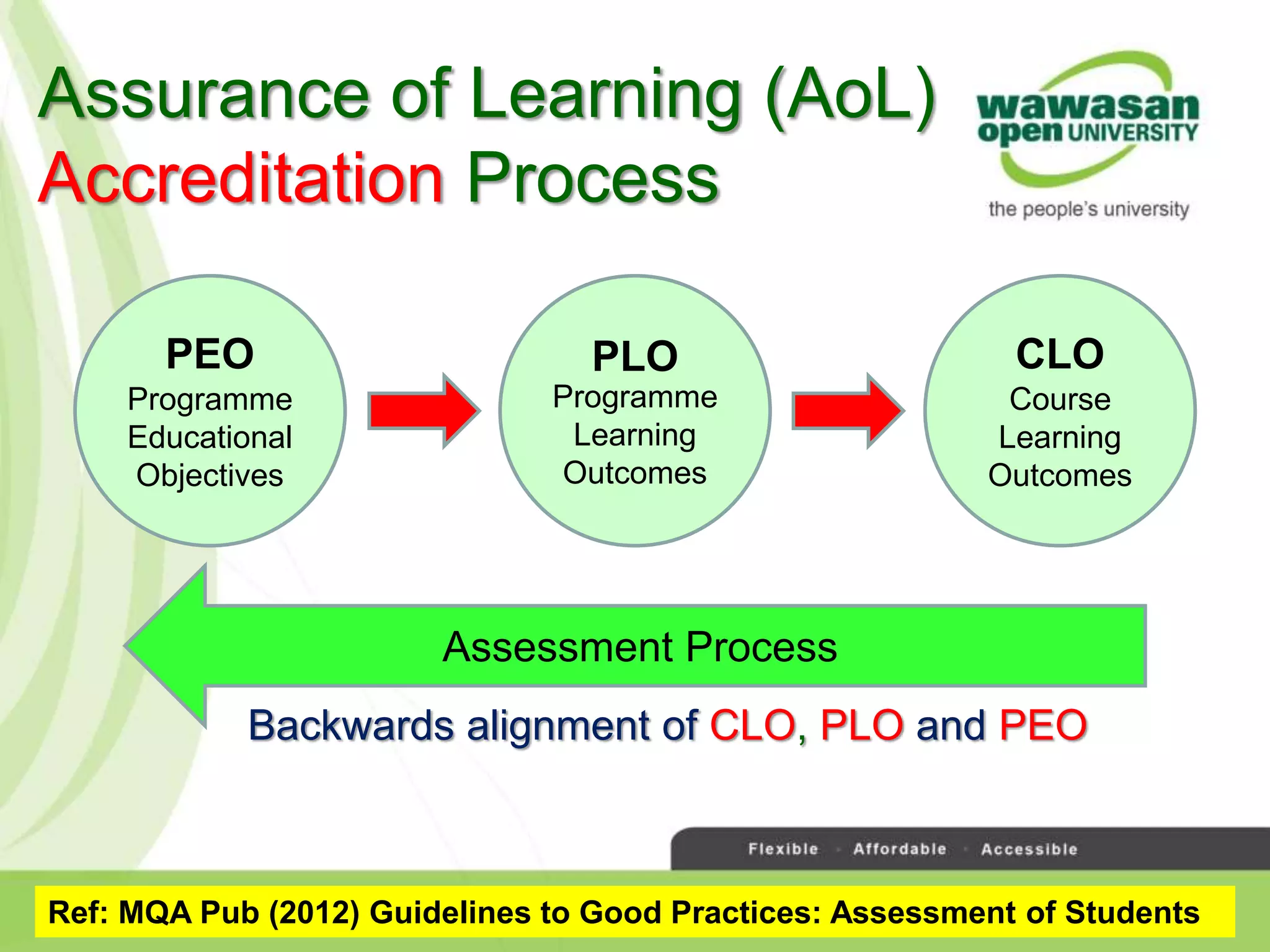
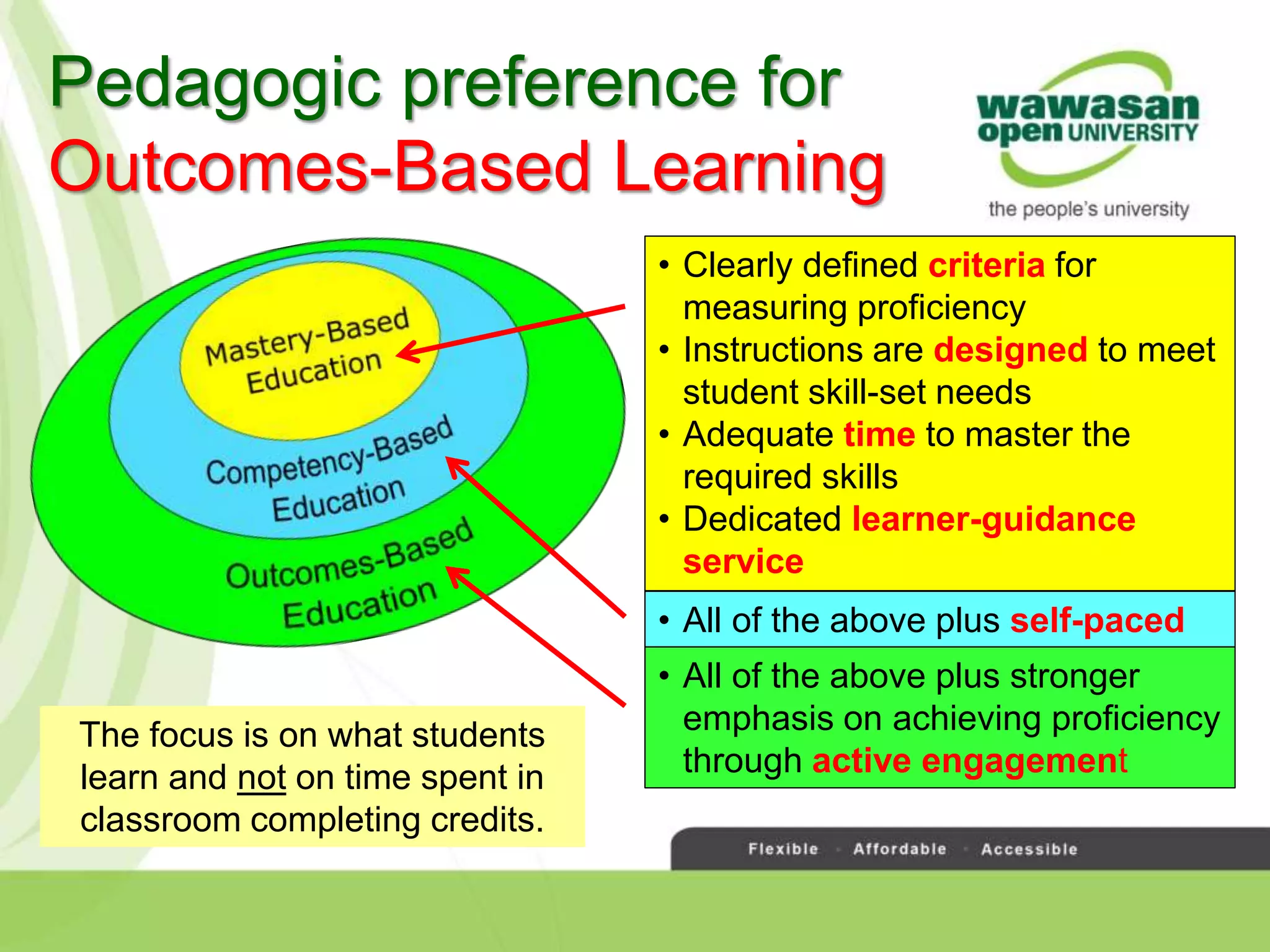
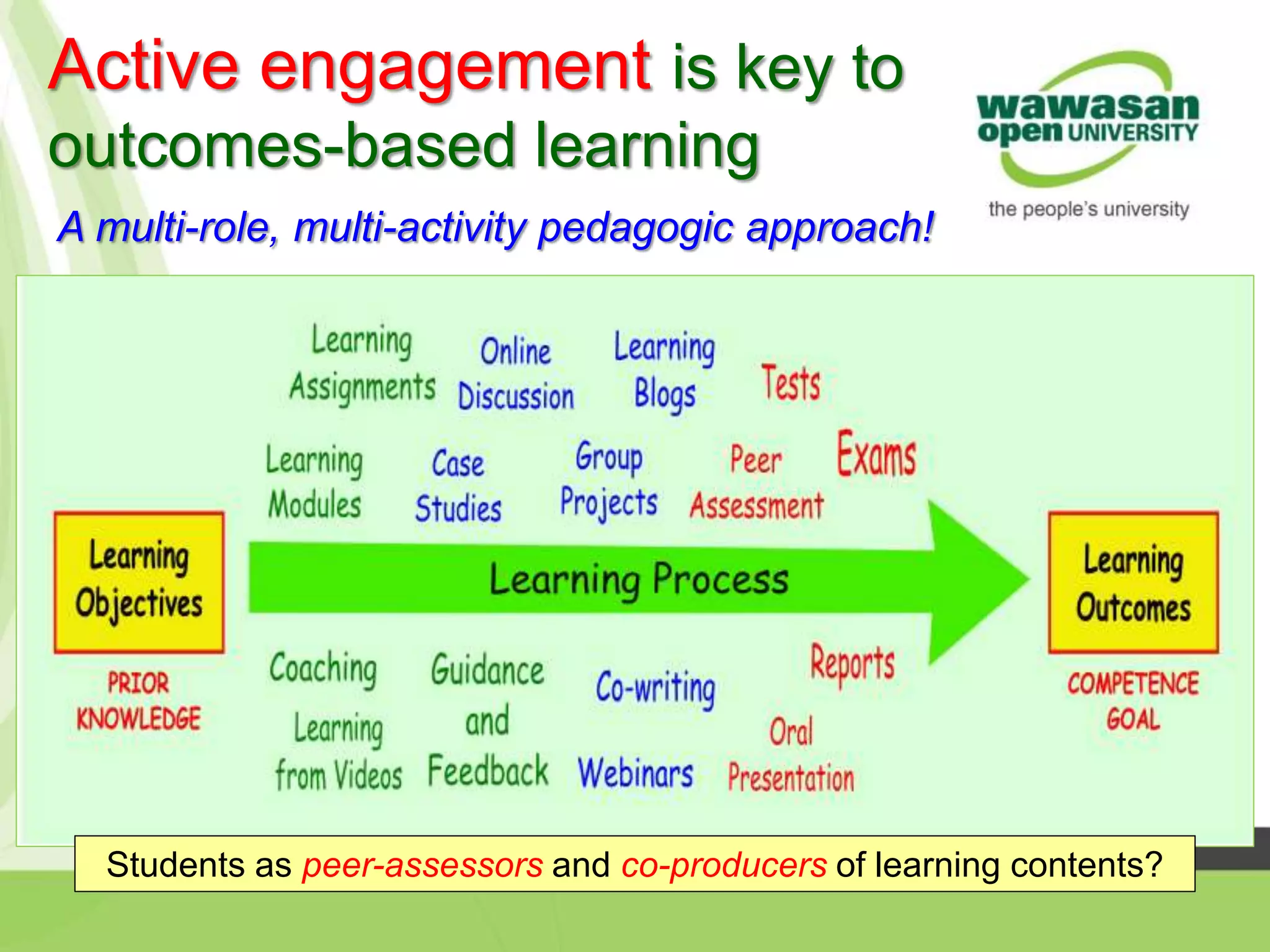
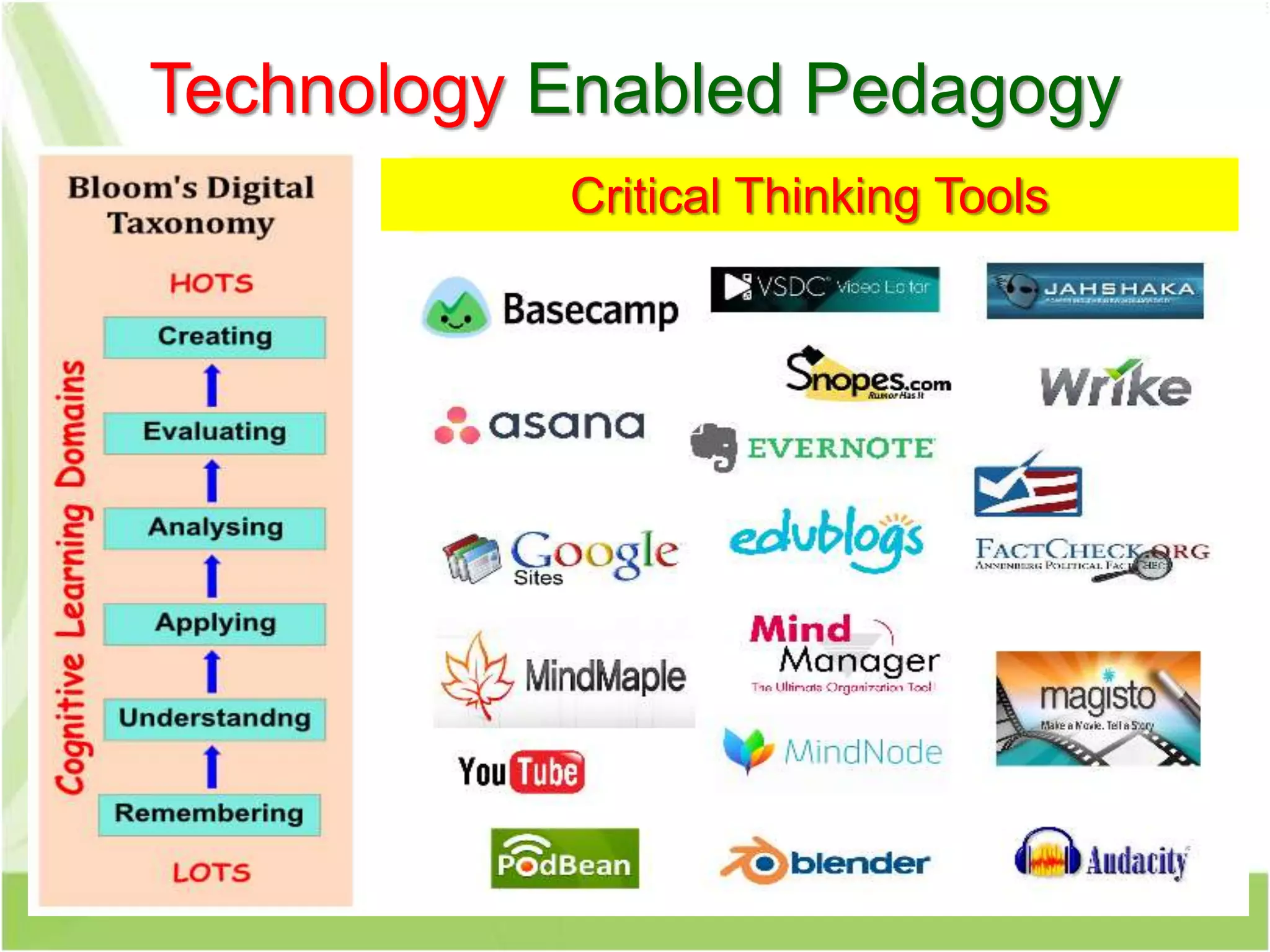
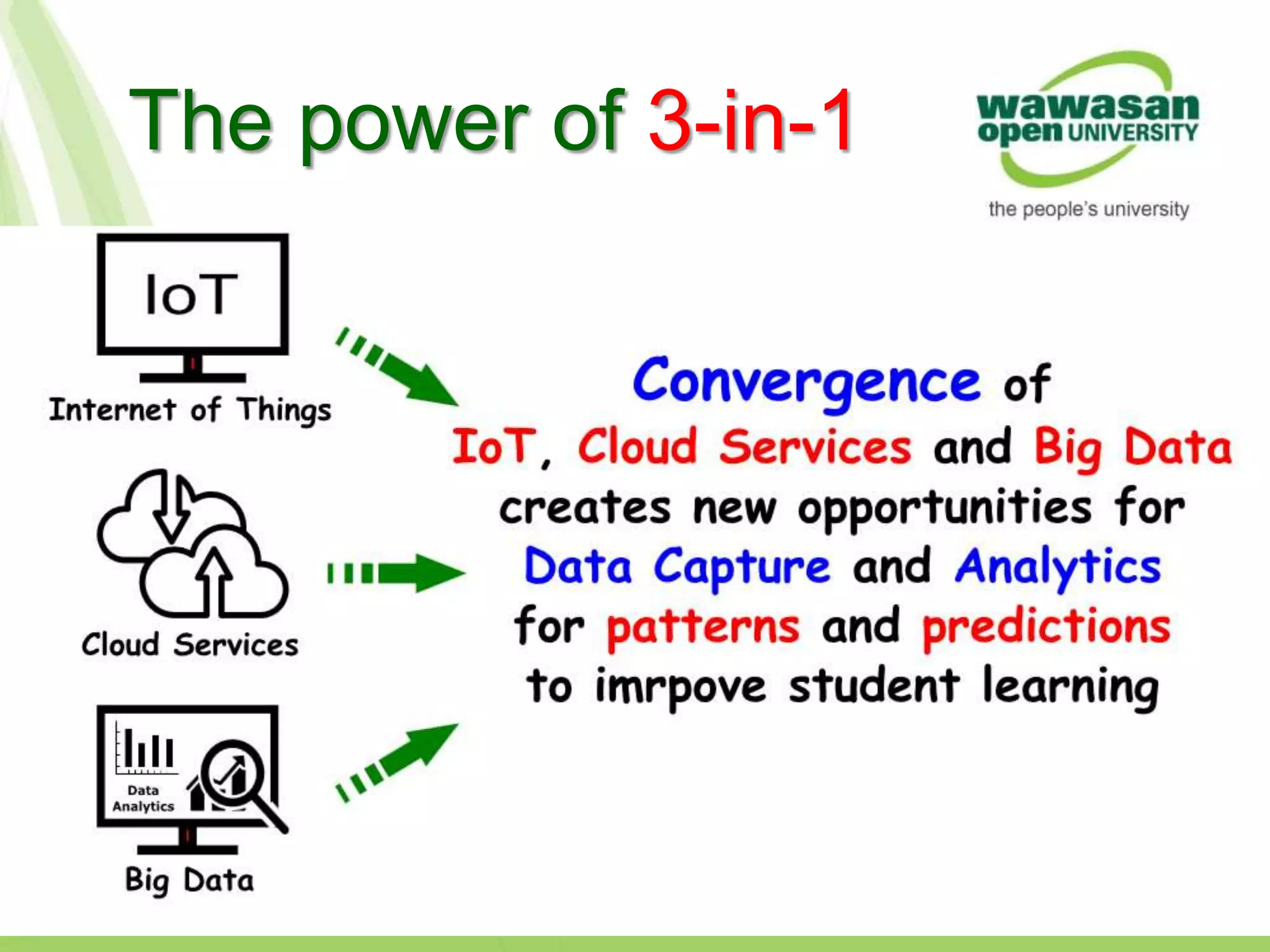
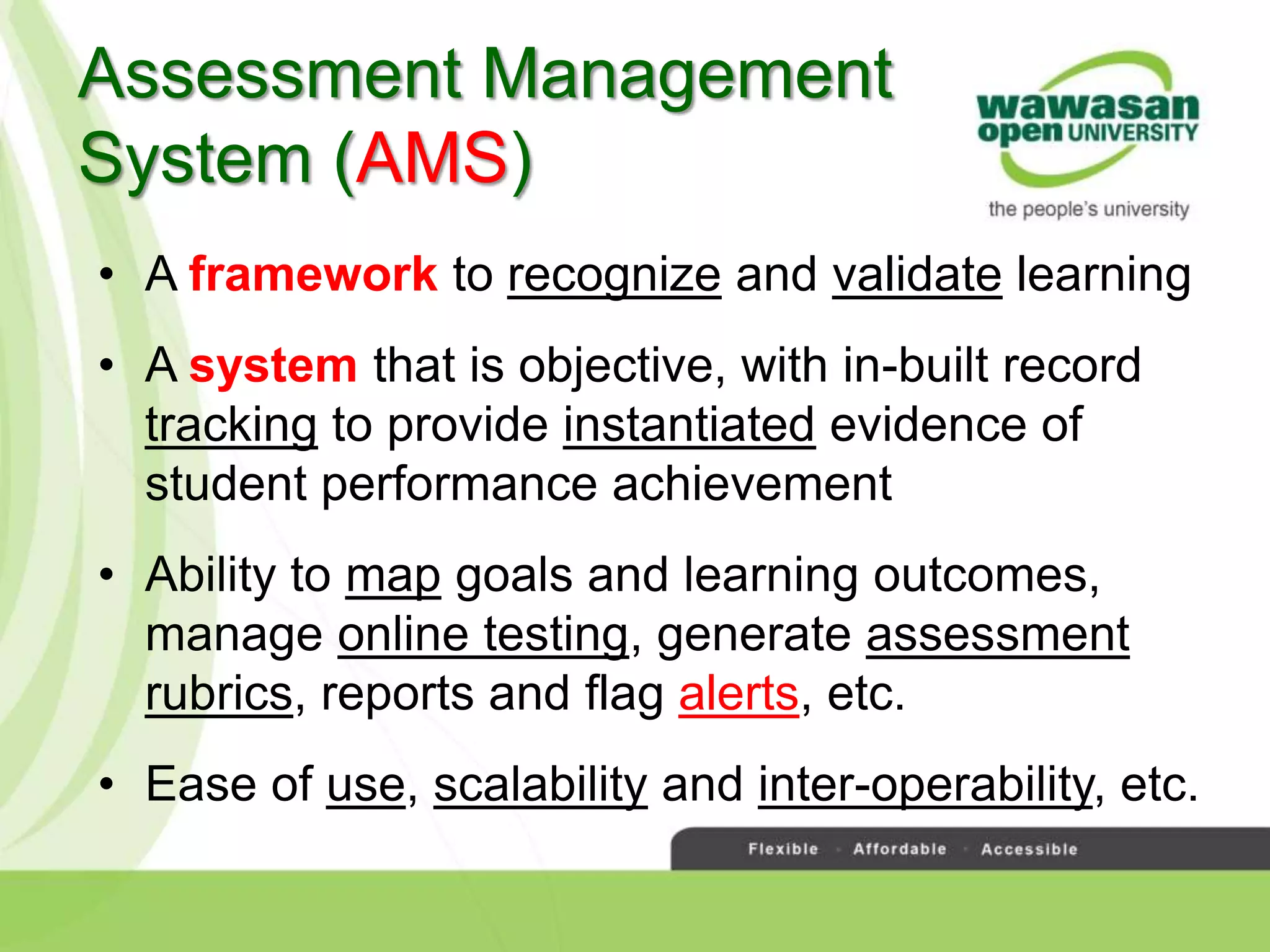
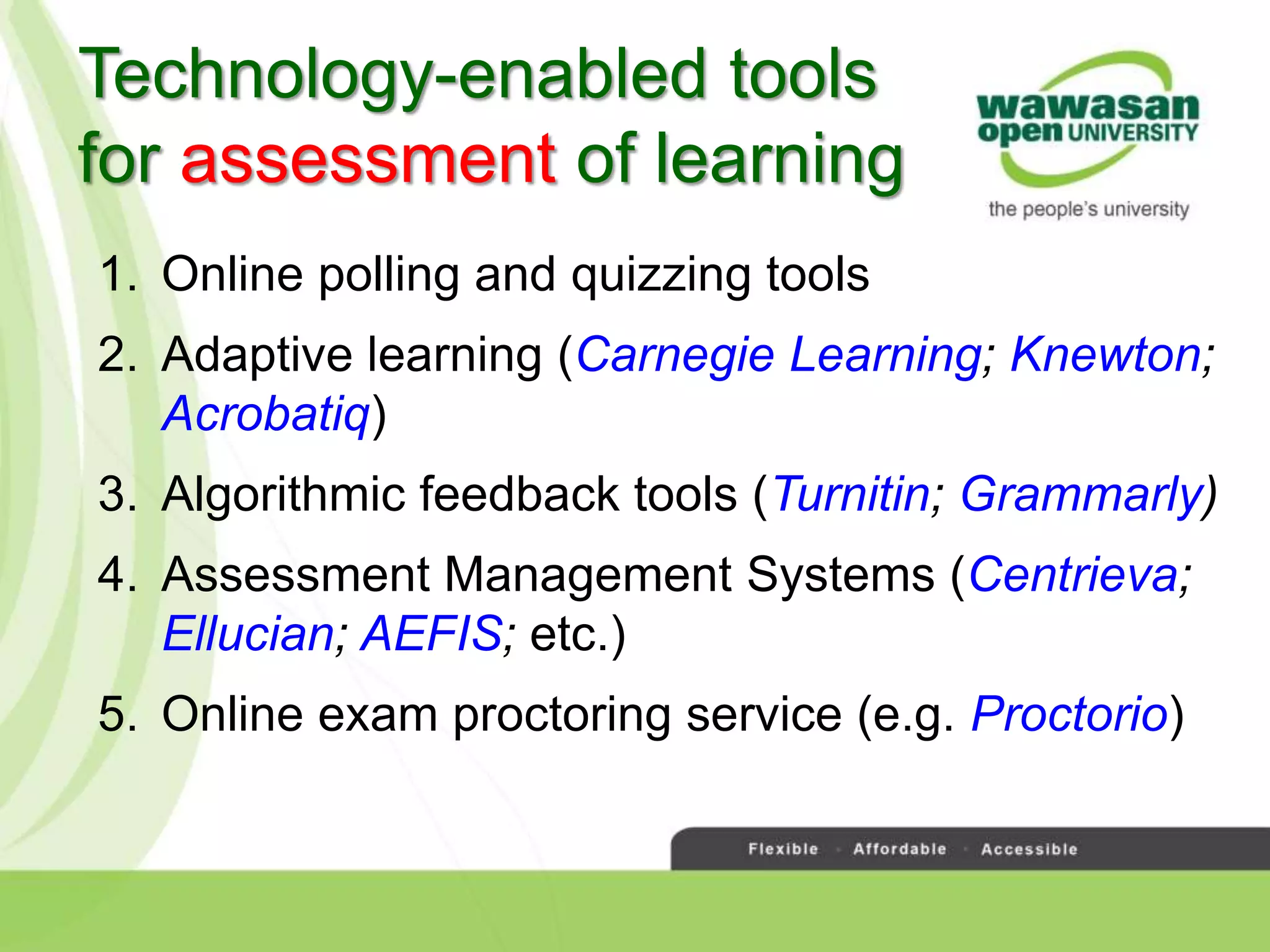
The document discusses the transformative role of technology in higher education assessment, focusing on personalized and competency-based learning to adapt to changing student demographics and industry demands. It emphasizes the need for reliable assessment tools and validation processes to ensure quality learning outcomes, with a shift towards outcomes-based education and active student engagement. Additionally, it outlines the importance of stakeholder roles in achieving effective assessment and accreditation in educational programs.