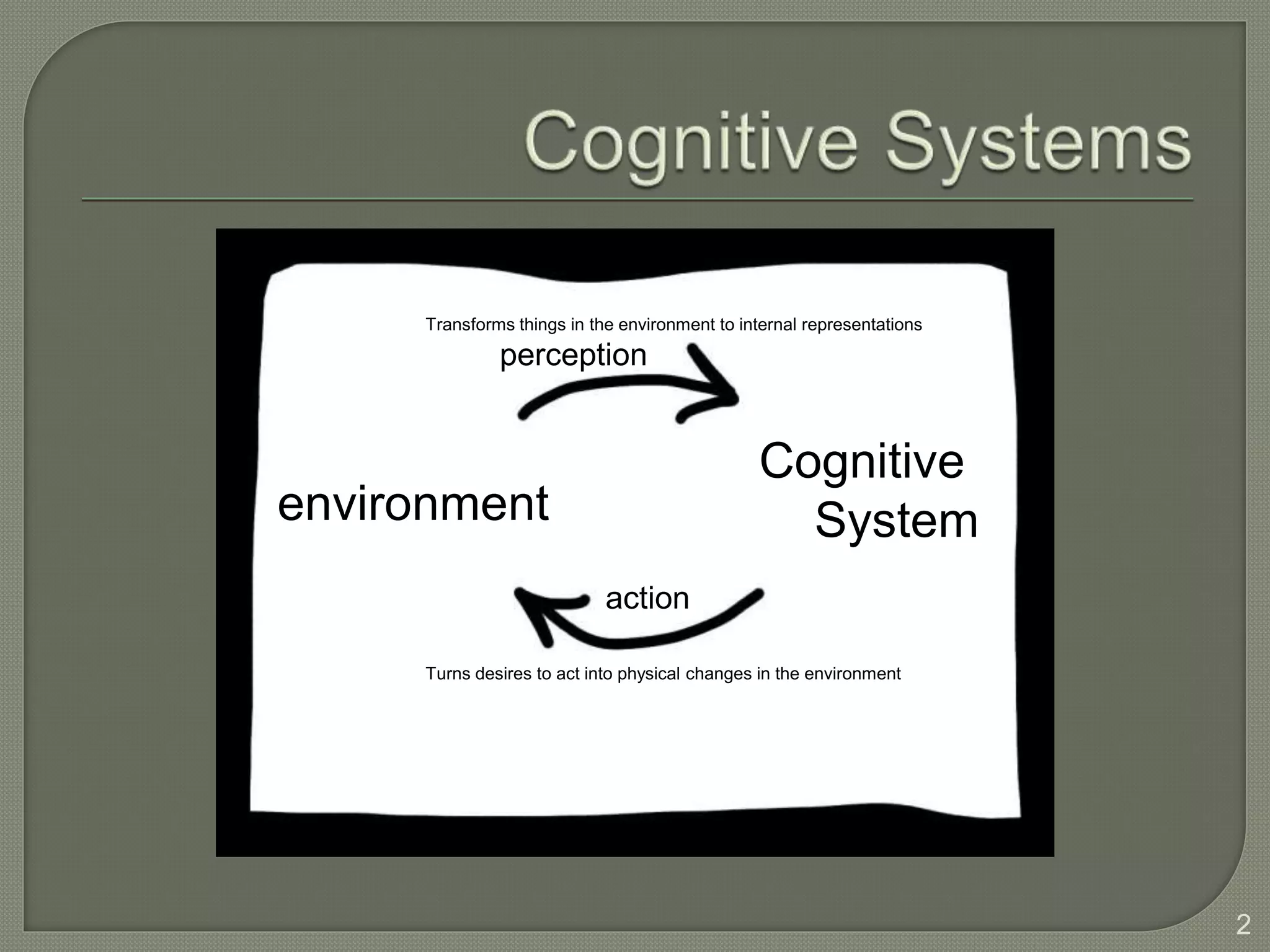
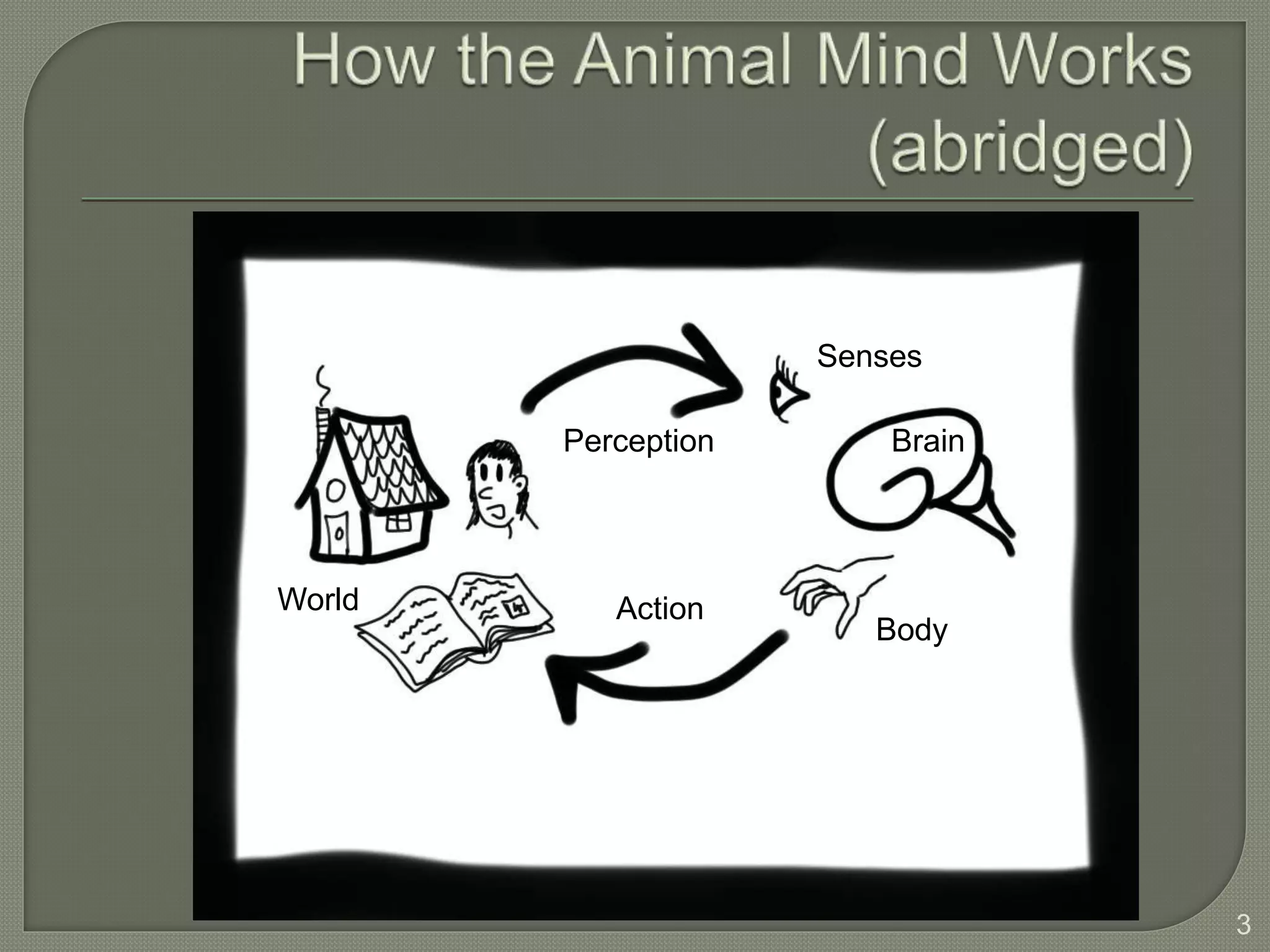
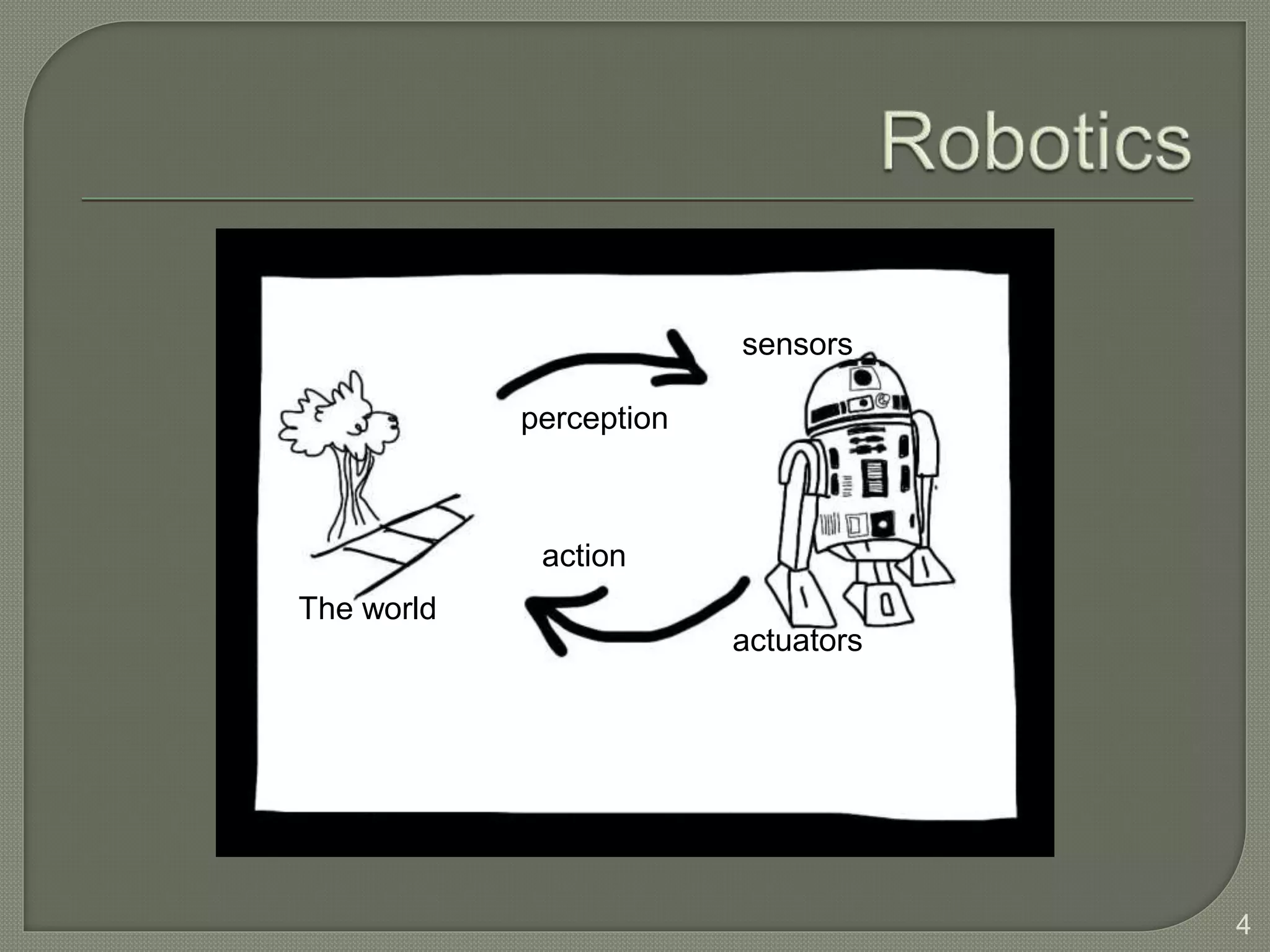
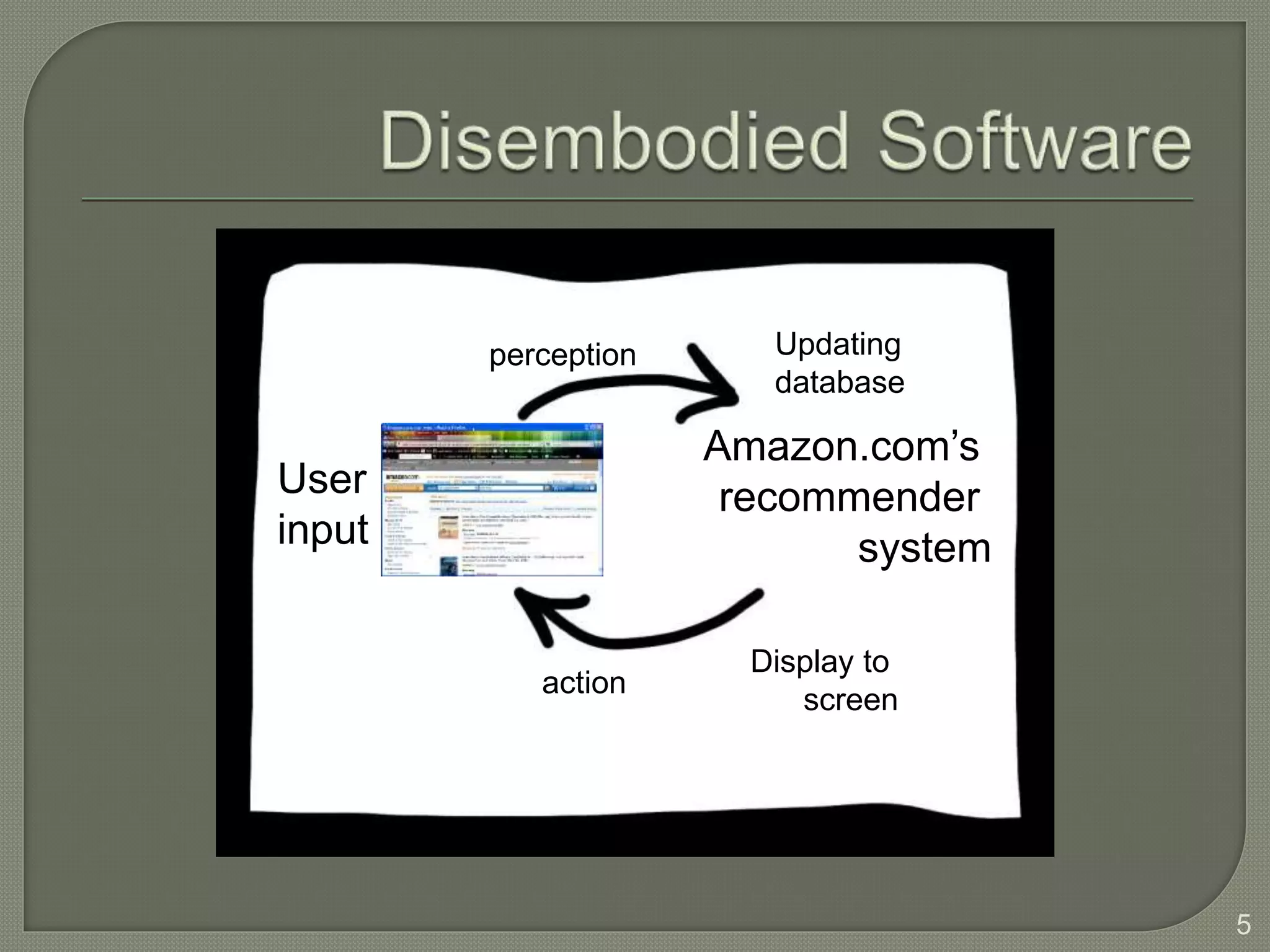
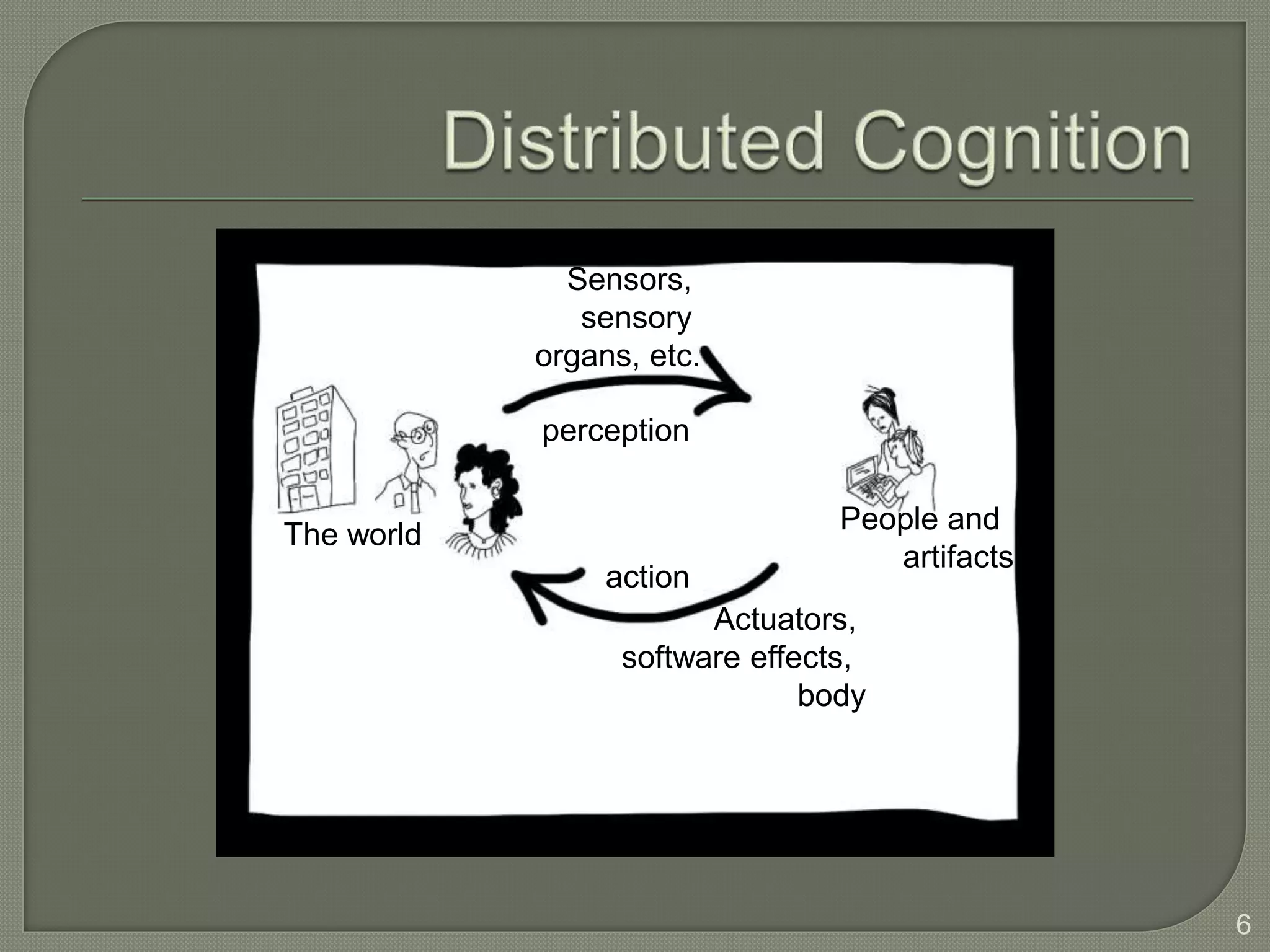
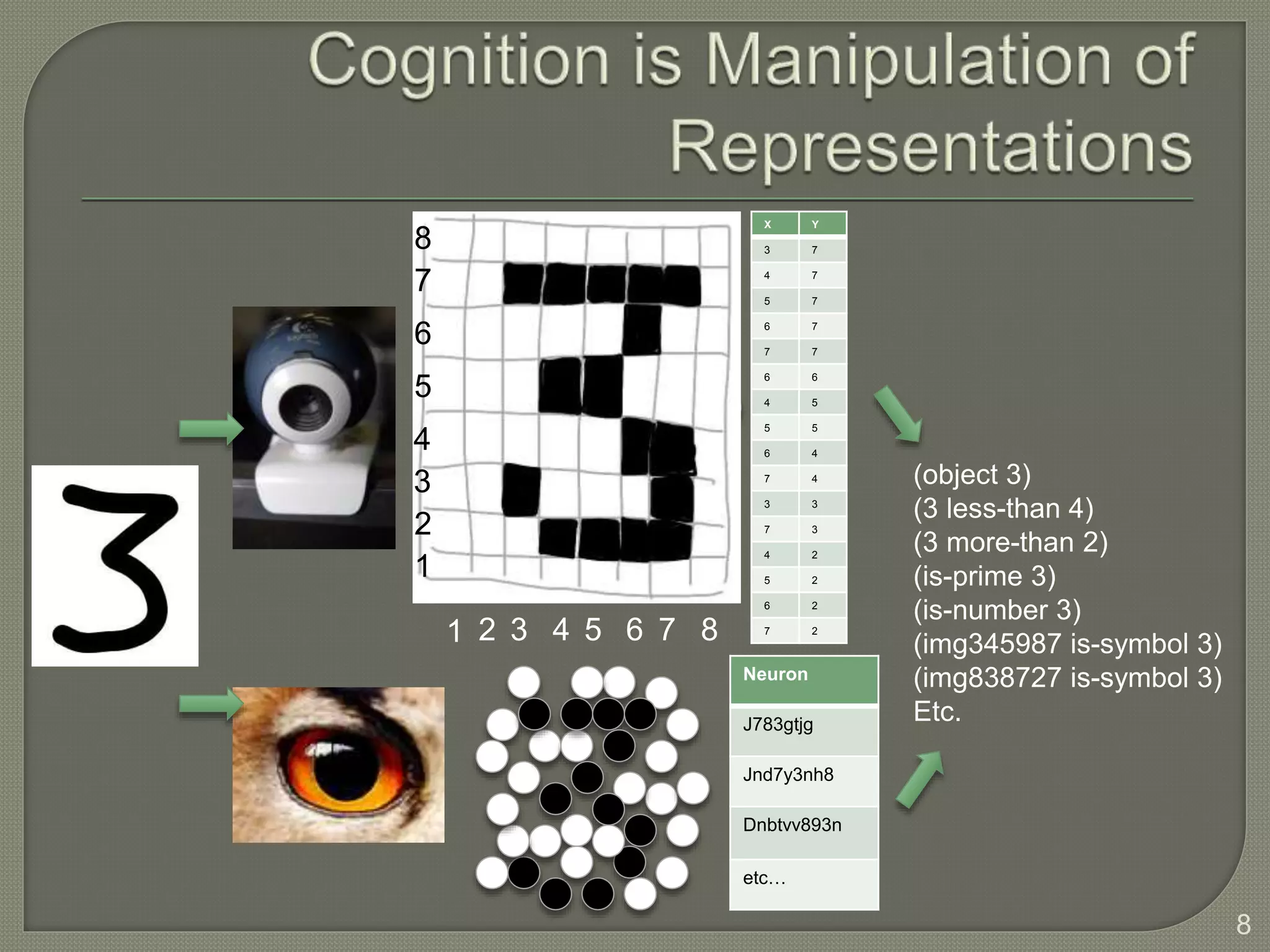
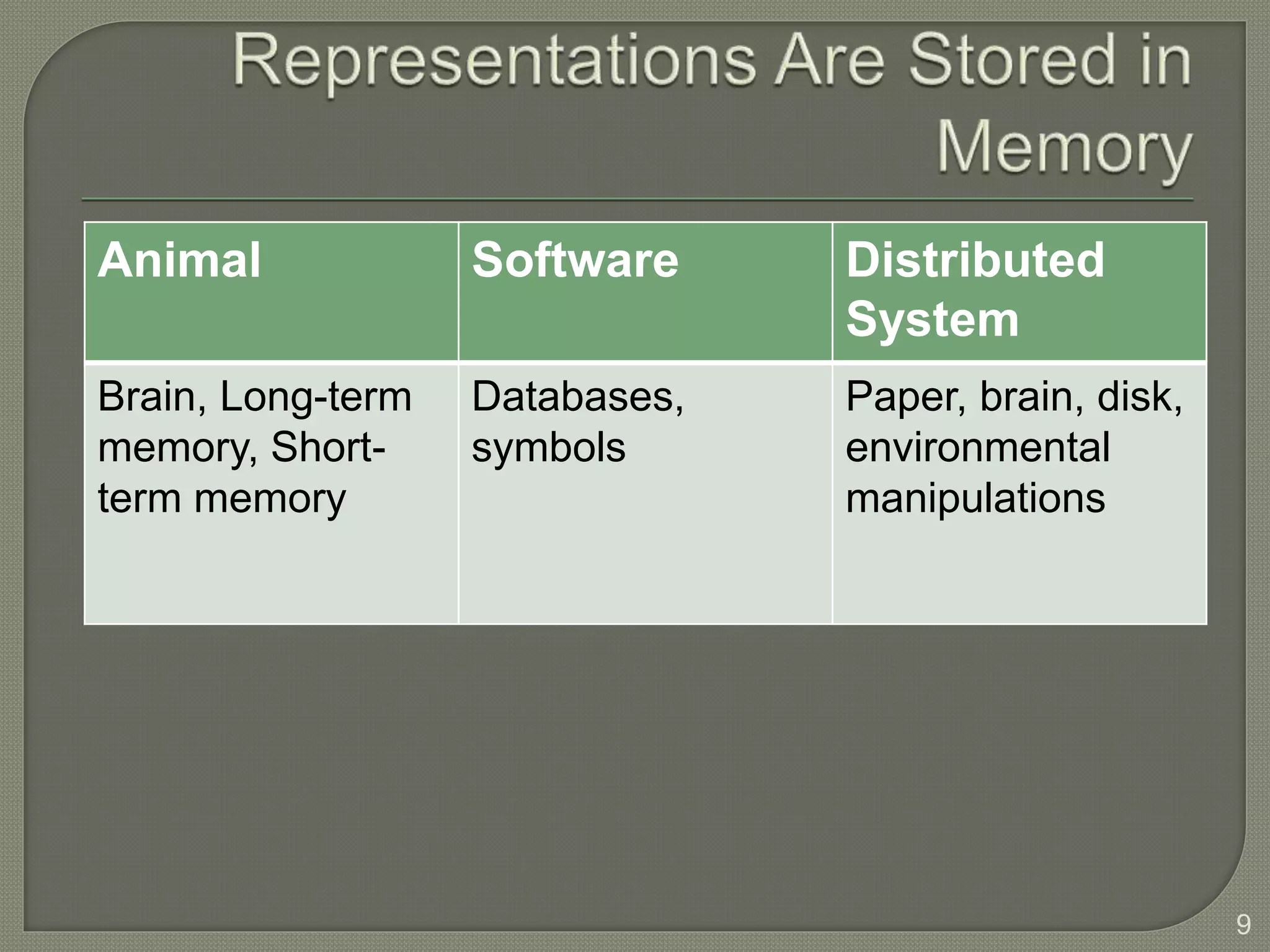
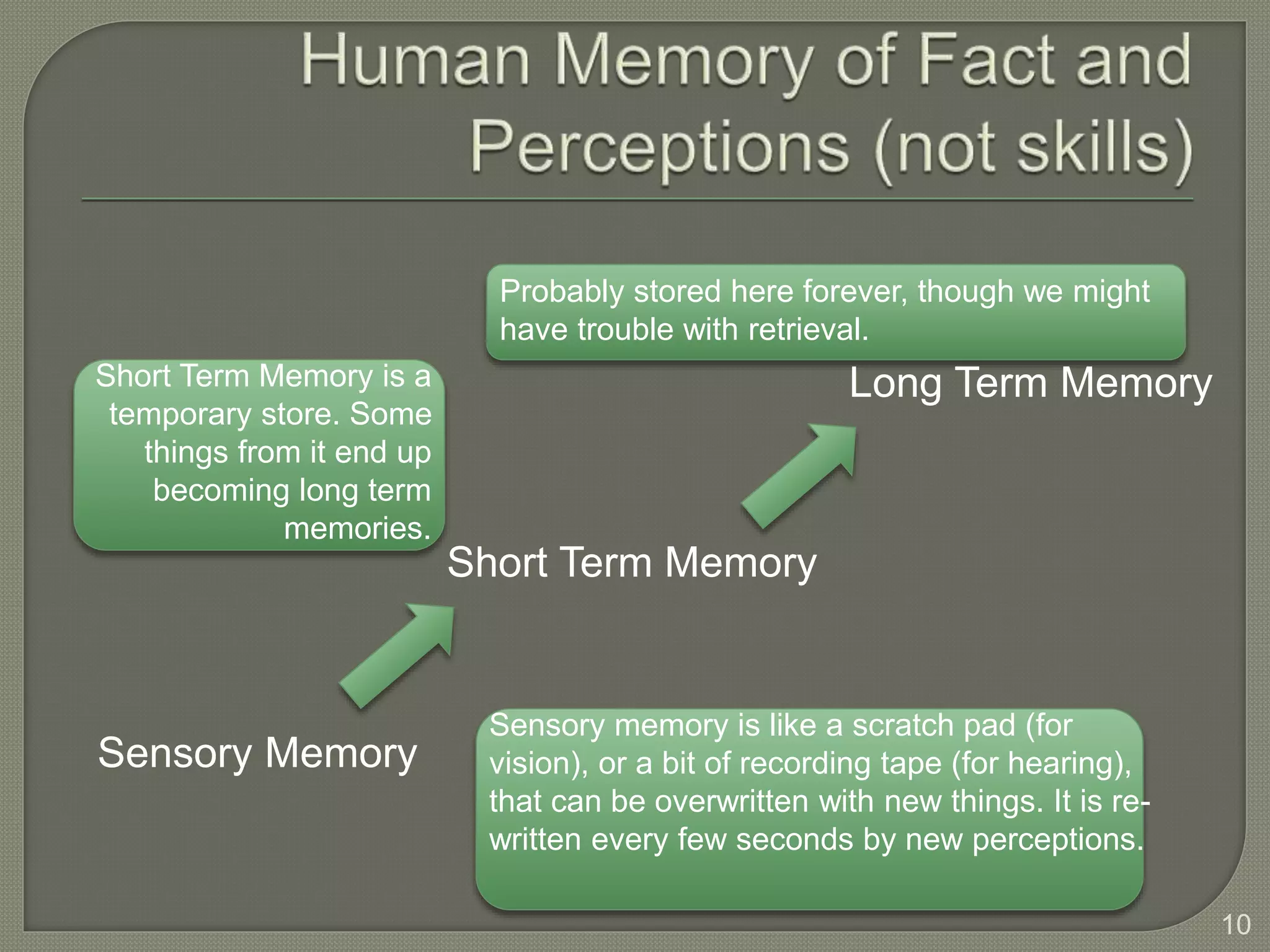
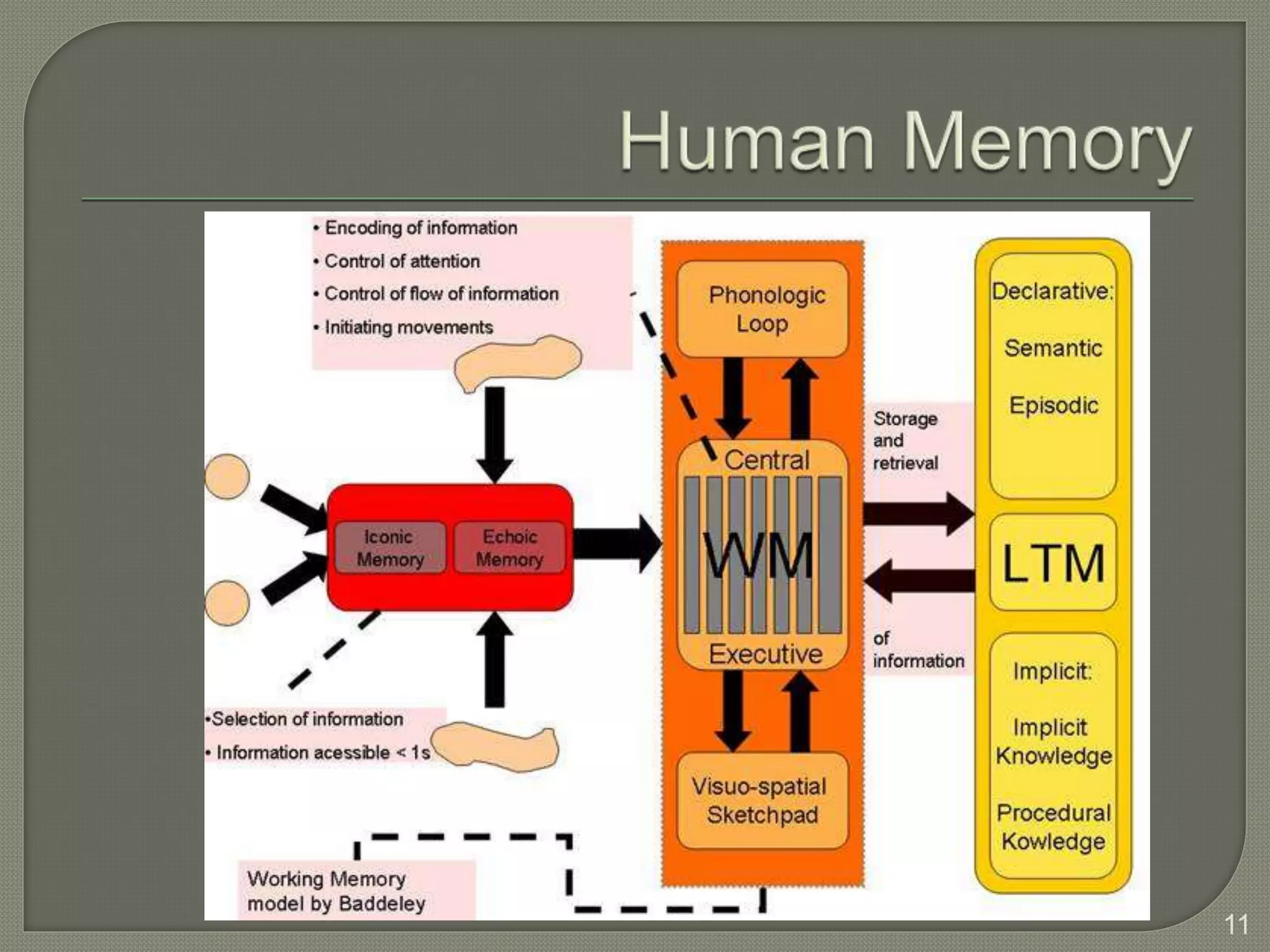
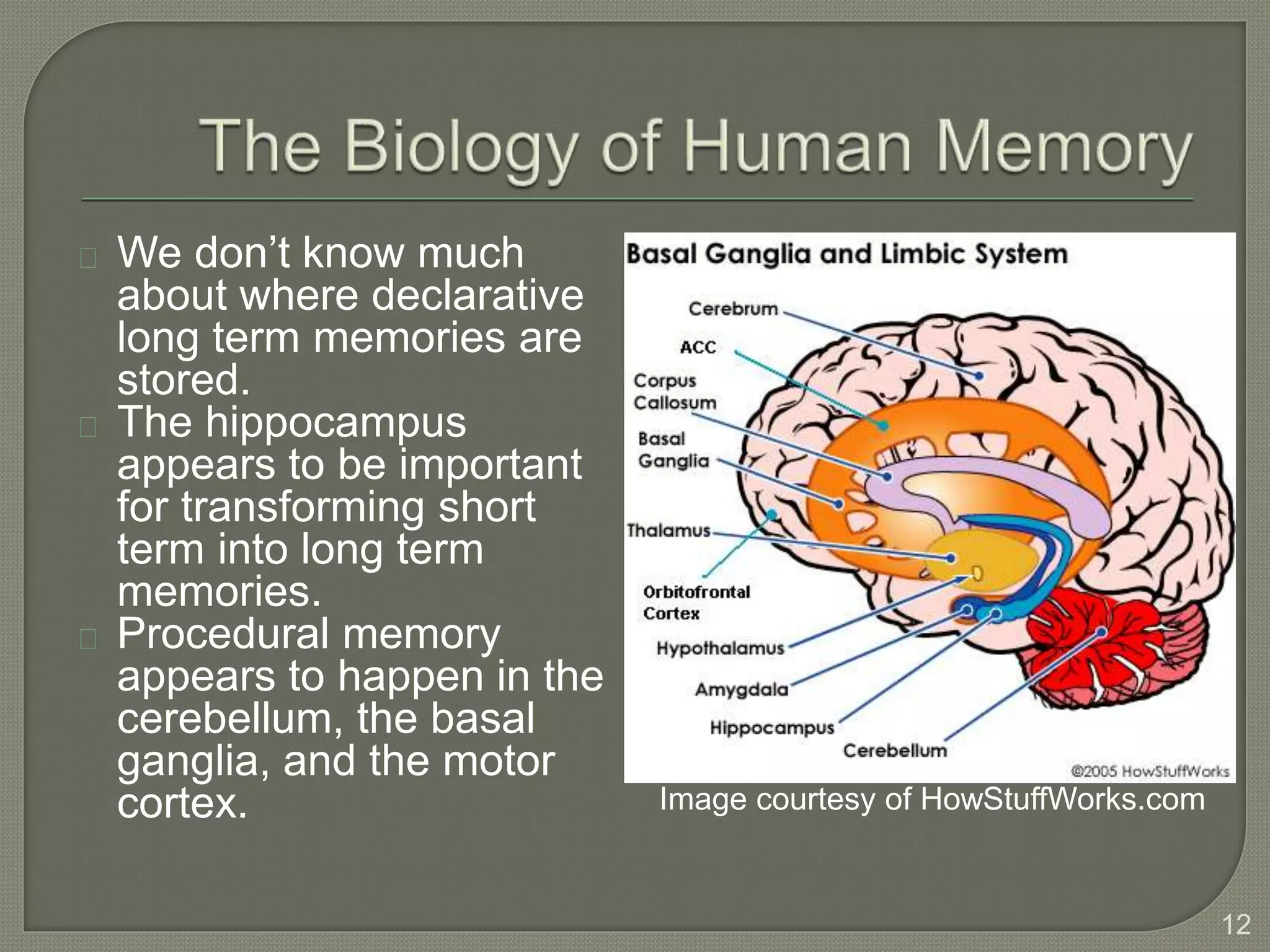
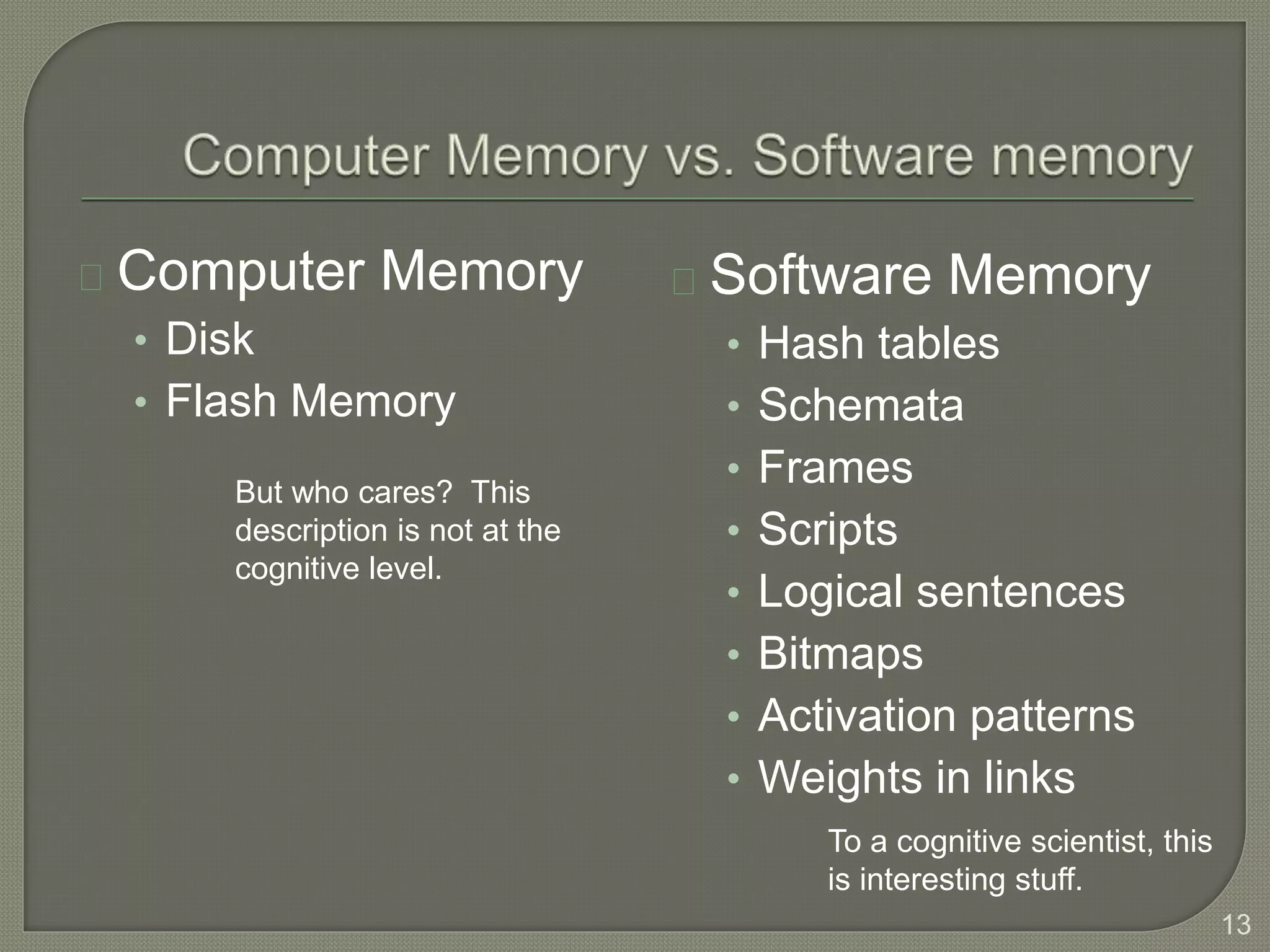
This document discusses cognitive systems and distributed cognition. It provides examples of cognitive systems including the human brain, computer systems, software programs, and social groups. It also discusses how cognition is distributed across internal mental representations, external environmental representations, and social interactions between people and technologies.