This document discusses and compares graph data structures represented as linked data/RDF and property graphs. It provides examples of linked data/RDF graphs using Turtle syntax and JSON-LD, and how they can be queried with SPARQL. It also demonstrates how to represent the same graph data as a property graph using TinkerPop and Gremlin, and how the graph can be queried using Gremlin and Cypher languages. Key graph concepts like nodes, edges, and properties are also introduced.





![JSON-LD
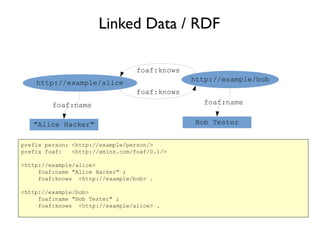
● Links and semantics for the JSON ecosystem
{
"@context" : "http://example/person.jsonld",
"@graph" : [ {
"@id" : "http://example/alice",
"knows" : "http://example/bob",
"name" : "Alice Hacker"
}, {
"@id" : "http://example/bob",
"knows" : "http://example/alice",
"name" : "Bob Tester"
} ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-03graphdata-pg-rdf-140507021312-phpapp01/85/Graph-Data-RDF-and-Property-Graphs-11-320.jpg)
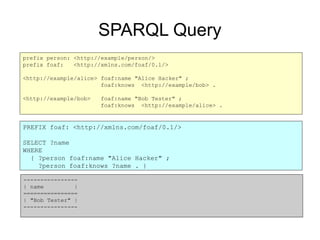

![GSON
{
"edges" : [
{
"_id" : "k1" ,
"_inV" : "bob" ,
"_label" : "knows" ,
"_outV" : "alice" ,
"_type" : "edge"
} ,
{
"_id" : "k2" ,
"_inV" : "alice" ,
"_label" : "knows" ,
"_outV" : "bob" ,
"_type" : "edge"
}
] ,
"mode" : "NORMAL" ,
"vertices" : [
{
"_id" : "bob" ,
"_type" : "vertex" ,
"name" : "Bob Coder"
} ,
{
"_id" : "alice" ,
"_type" : "vertex" ,
"name" : "Alice Hacker"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-03graphdata-pg-rdf-140507021312-phpapp01/85/Graph-Data-RDF-and-Property-Graphs-15-320.jpg)

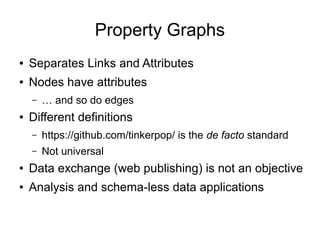
![Cypher Query
● Neo4J specific
● Property Graph + “labels” (= types) – node names
CREATE (alice { name: 'Alice Hacker'} ) ,
(bob { name: 'Bob Tester'} ) ,
(alice) -[:knows]-> (bob) ,
(bob) -[:knows]-> (alice)
MATCH (a)-[:knows]->x
WHERE a.name = 'Alice Hacker'
RETURN x.name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-03graphdata-pg-rdf-140507021312-phpapp01/85/Graph-Data-RDF-and-Property-Graphs-17-320.jpg)