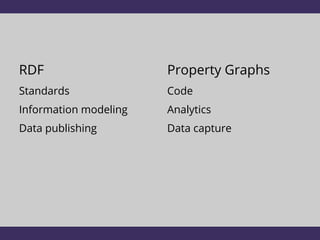
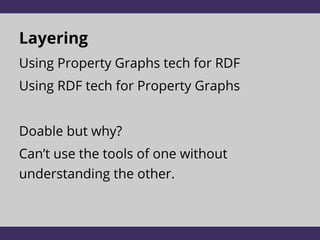
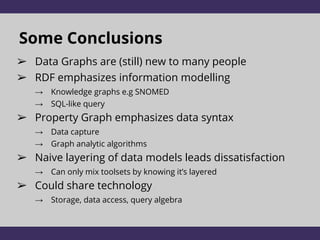
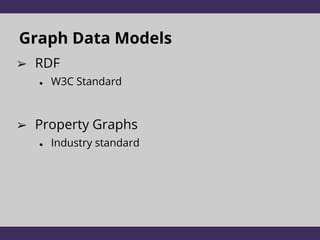
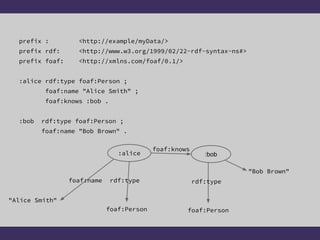
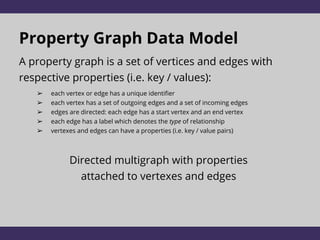
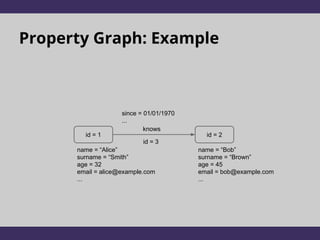
The document discusses two graph data models: RDF and Property Graphs. It provides an overview of each model, including examples and technologies used to access and query each type of graph. The key conclusions are that RDF emphasizes information modeling and knowledge graphs, while Property Graphs emphasize data syntax and graph algorithms. Simply layering the data models on top of each other leads to dissatisfaction, but the models could potentially share technologies while still keeping their separate focuses and tools.










![Property Graphs : Access
➢ Tinkerpop Gremlin
DSL for various languages
g.V().as('person').out('knows').as('friend')
.select().by{it.value('name').length()}
➢ Cypher
MATCH (you:Person {name:"You"})
FOREACH (name in ["Johan","Rajesh","Anna","Julia","Andrew"] |
CREATE (you)-[:FRIEND]->(:Person {name:name}))
➢ Connect : API](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-02voxx-pgrdf-180120170045/85/2016-02-Graphs-PG-RDF-19-320.jpg)