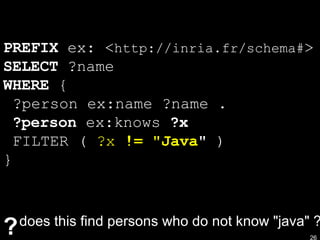
SPARQL is a query language, result format, and access protocol for querying and accessing RDF data. SPARQL queries use a SELECT-FROM-WHERE structure to match triple patterns against RDF graphs. The WHERE clause contains a conjunction of triple patterns that can be extended with filters, optional patterns, and unions of patterns. SPARQL results are returned in an XML format and the protocol defines HTTP and SOAP bindings for sending queries and receiving results over the web.