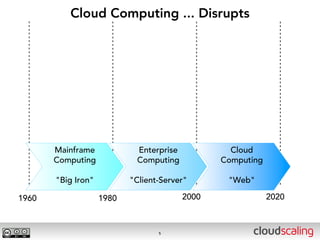
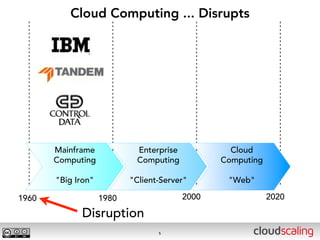
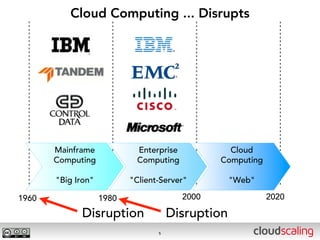
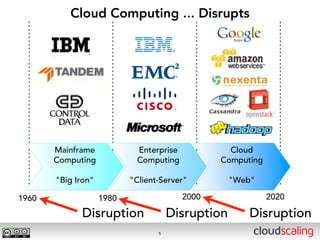
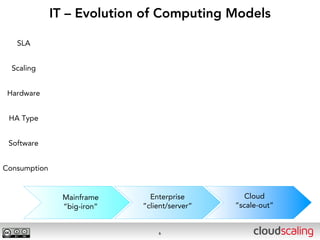
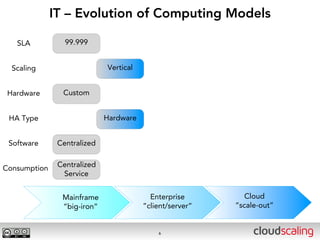
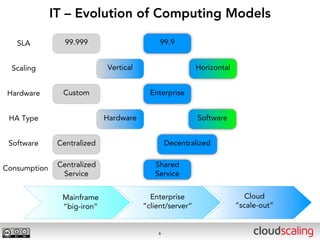
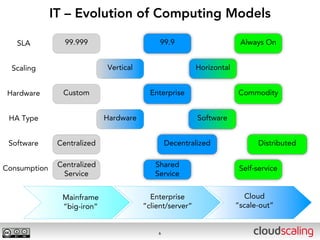
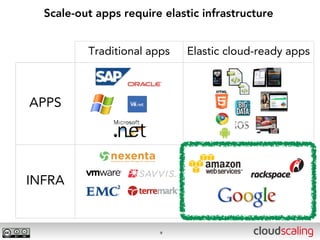
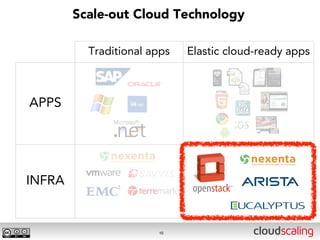
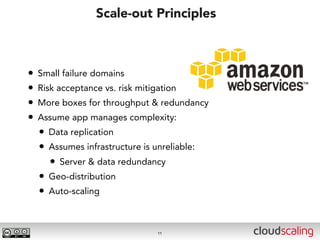
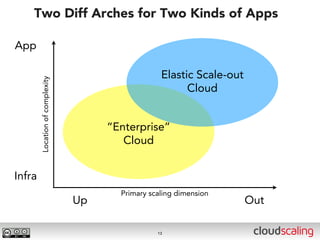
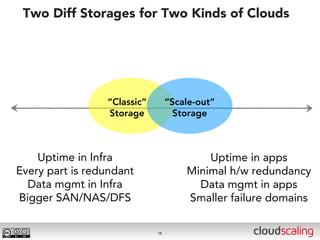
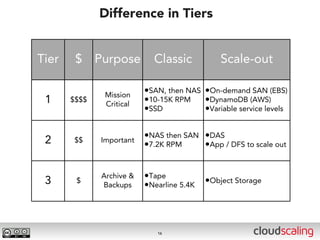
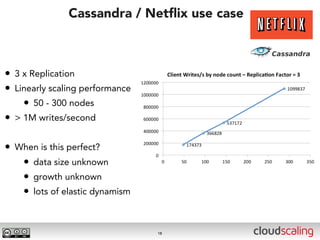
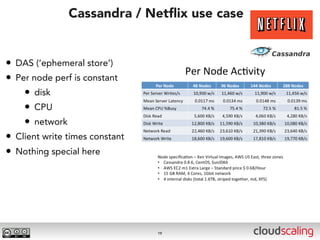
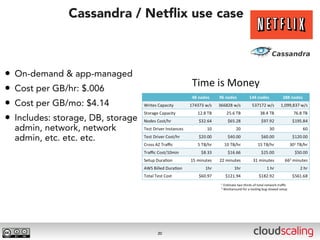
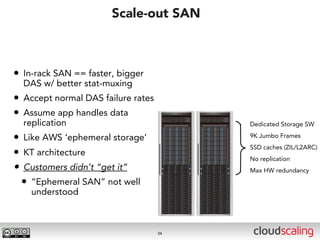
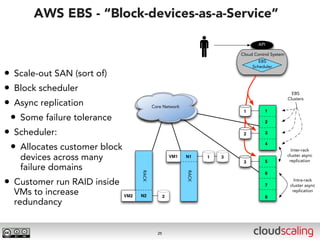
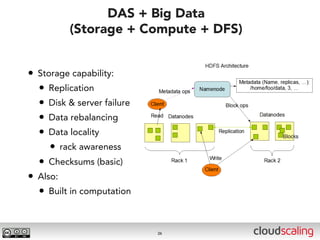
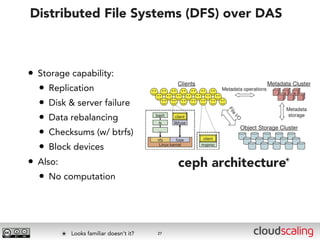
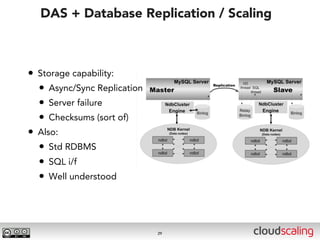
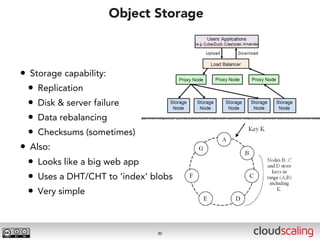
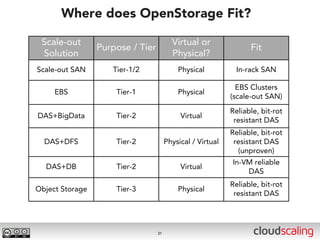
The document discusses the evolution of cloud storage architectures, contrasting traditional 'big-iron' enterprise models with modern elastic scale-out systems that cater to different application needs. It emphasizes the shift in data management from infrastructure to applications and outlines the principles and technologies behind scale-out storage, including the use cases for systems like Cassandra. The conclusion highlights the importance of designing the appropriate storage solutions to effectively support diverse cloud environments.