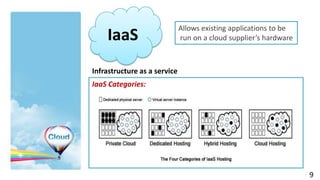
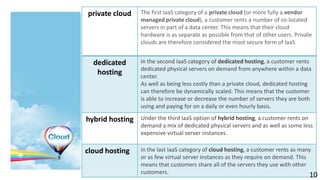
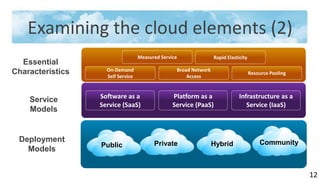
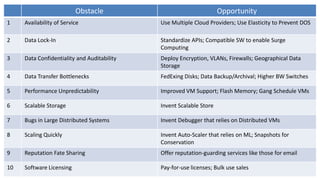
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, history, characteristics, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and green benefits. It examines cloud computing elements like on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity. The document also previews top obstacles for cloud computing growth, like availability of service, data lock-in, and data transfer bottlenecks, as well as opportunities to address them through approaches like using multiple cloud providers, standardizing cloud computing, and deploying encryption.