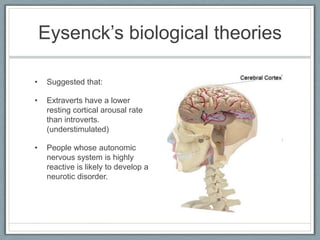
Here are some potential strengths and weaknesses of the trait approach that could be discussed:
Strengths:
- Allows comparison across individuals
- Attempts to describe average behaviors
- Focuses on relatively stable characteristics
- Has led to identification of core personality dimensions
Weaknesses:
- May oversimplify human personality
- Does not fully capture within-person variability
- Prone to cultural bias in trait definitions
- Offers limited explanation of behavior
- Assumes traits are stable across situations