1) Barbara Fredrickson proposes the broaden-and-build theory, which argues that positive emotions broaden people's thought-action repertoires and build their personal resources.
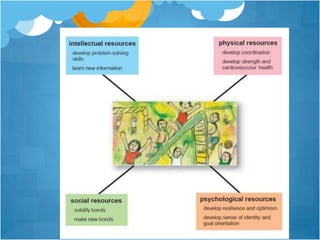
2) Positive emotions broaden people's scopes of attention, cognition, and potential actions. This expanded state is proposed to improve coping and survival odds by building physical, intellectual, and social resources over time.
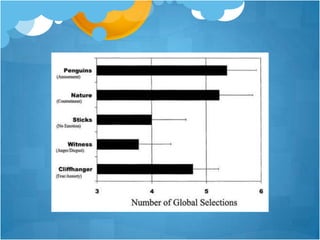
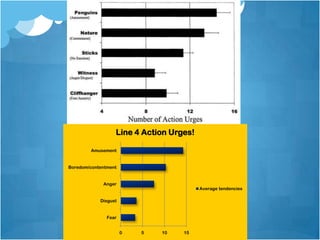
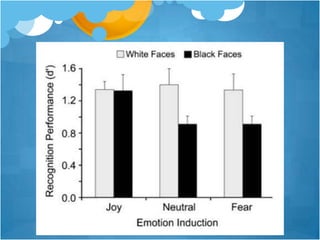
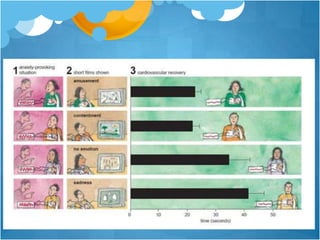
3) Fredrickson has conducted experiments providing evidence that positive emotions undo the effects of cardiovascular reactivity caused by negative emotions, and that increasing positive emotions leads to benefits in health and well-being over time by building various resources.