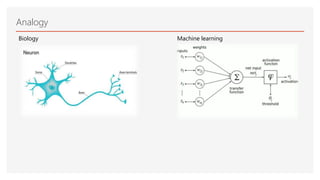
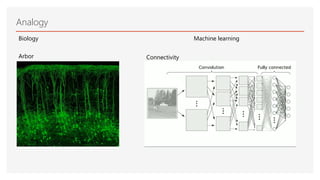
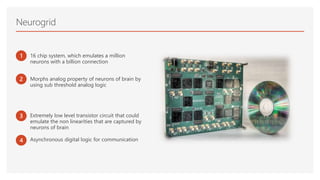
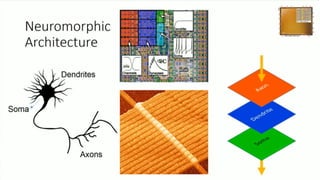
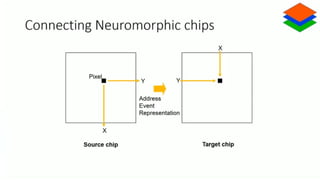
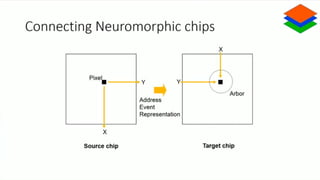
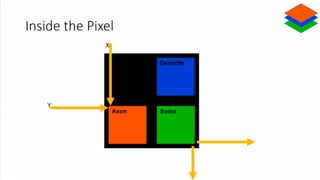
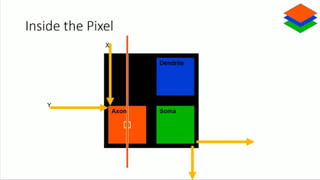
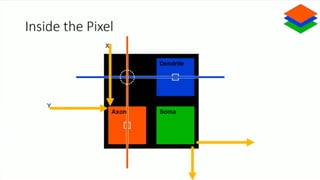
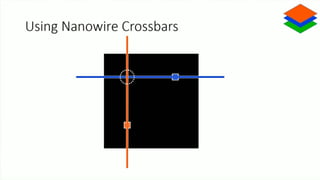
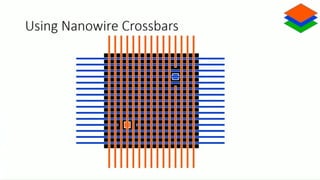
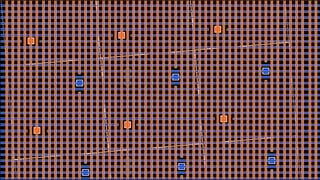
Neuromorphic computing is an emerging interdisciplinary field that takes inspiration from biology to design hardware models of neural systems. Specifically, it uses very-large-scale integrated circuits containing analog electronic circuits to mimic the neurobiological architectures in the nervous system, as conceived by Carver Mead in the late 1980s. Two examples are Neurogrid, a mixed-analog-digital multichip system emulating a million neurons and billion connections using subthreshold analog logic, and IBM's TrueNorth, which contains 16 neuromorphic cores and is completely digital. Both aim to achieve the scale and low power operation of the biological brain through novel computing architectures.