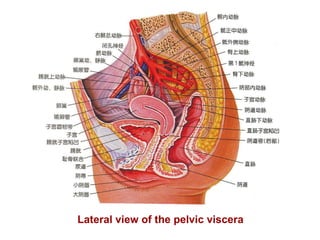
This document provides an overview of the female reproductive system in three chapters. Chapter 1 covers anatomy, including the bony pelvis, external and internal genital organs. Chapter 2 discusses female reproductive physiology, including puberty, the menstrual cycle, and menopause. It explains the hormonal regulation of the ovarian and uterine cycles. Chapter 3 will discuss clinical skills for examining the female reproductive system. The goal is for students to understand the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive and endocrine systems.