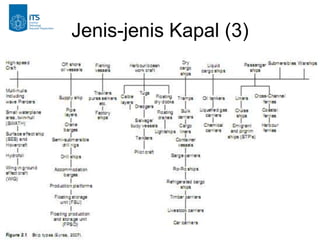
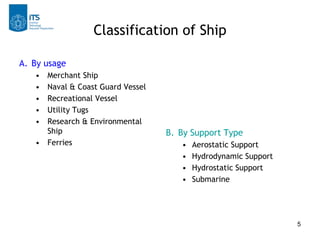
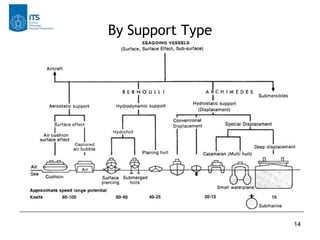
This document discusses ship classification and types. It classifies ships by usage into merchant ships, naval and coast guard vessels, recreational vessels, utility tugs, research and environmental ships, and ferries. It further breaks down merchant ships into general cargo vessels, tanker vessels, bulk carriers, and container ships. The document also classifies ships by their support type, such as aerostatic, hydrodynamic, hydrostatic, and submarines.