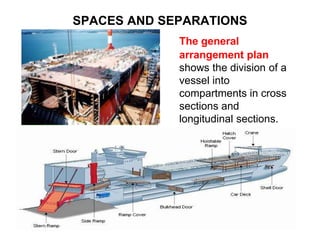
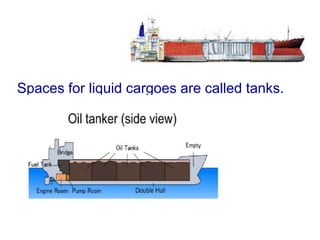
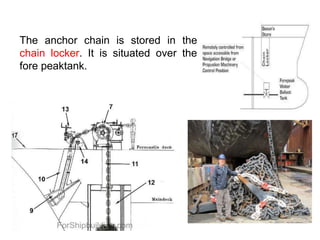
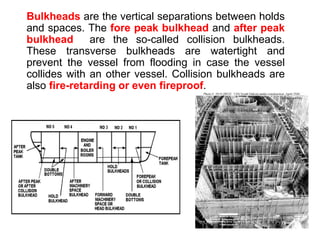
The general arrangement plan shows the divisions of a vessel into compartments using vertical bulkheads and horizontal decks. Compartments are used to store cargo, equipment, liquids and serve as crew and passenger accommodation. The upper deck, also called the weather deck, provides shelter. Fore and aft ends are the stem and stern. The forecastle deck houses anchor winches. Cargo is stored in holds divided by the tweendeck and tanktop. Liquid cargo spaces are called tanks. Peak tanks at each end absorb collision impacts. The anchor chain is in the chain locker above the fore peak tank. Collision bulkheads are watertight and fireproof. The engine room and steering gear room are also watertight. The