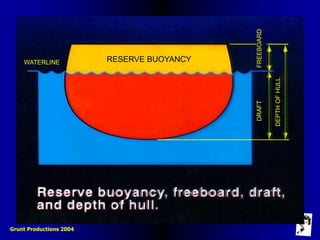
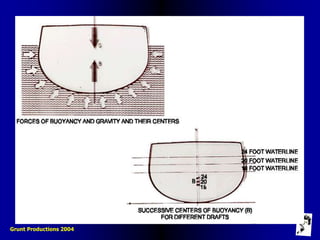
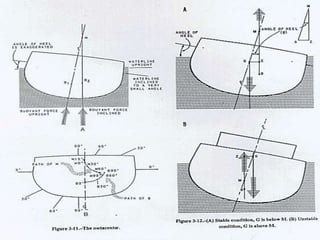
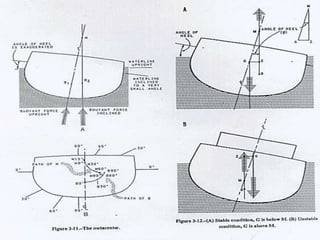
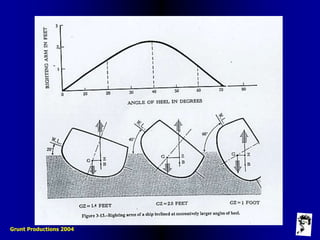
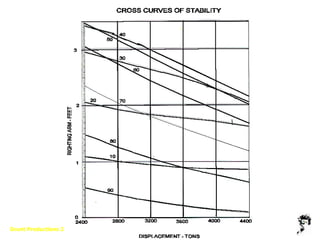
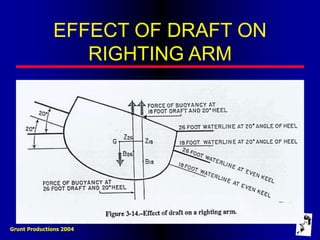
This document defines key terms and concepts related to ship stability, including Archimedes' principle, center of gravity, center of buoyancy, metacenter, righting arm, and free surface effect. It explains that a ship is stable when its center of buoyancy is below and to the side of the center of gravity, and that the metacenter indicates the ship's stability based on its position relative to the center of gravity. Additionally, it discusses how stability curves illustrate a ship's righting arm at different angles of heel and how the free surface effect can negatively impact stability when compartments are only partially filled with water.