Embed presentation
Downloaded 51 times







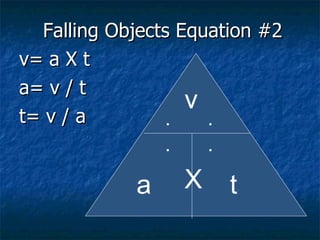
Air resistance is the force exerted by air on a moving object, acting in the opposite direction of the object's motion. The larger the surface area of an object, the greater the air resistance, which is why leaves fall more slowly than acorns of similar mass. As an object falls through air, air resistance increases until it balances the force of gravity, at which point the object reaches its terminal velocity and stops accelerating further downward.







