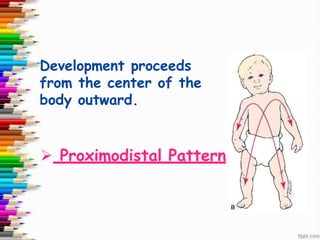
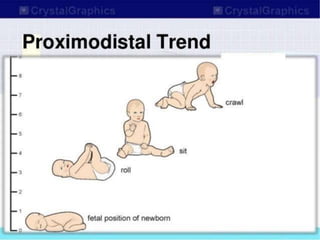
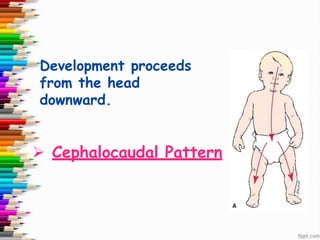
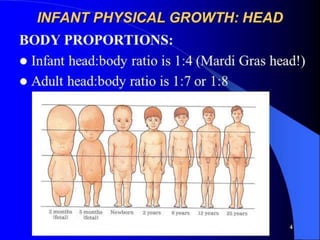
This document discusses human development and provides definitions, principles, and approaches. It defines human development as the pattern of growth from conception through the lifespan, including physical, cognitive, and socio-emotional changes. Major principles outlined are that development proceeds from the center of the body outward and from the head downward, and that the rate and outcomes of development vary between individuals. The two approaches to development discussed are the traditional perspective, which views development as extensive in childhood but minimal in adulthood, and the lifespan approach, which views development as ongoing throughout life.