The document provides information about Western Europe, including:
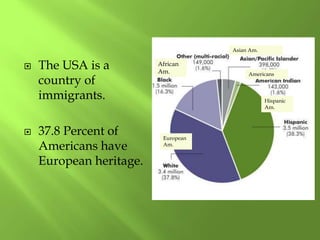
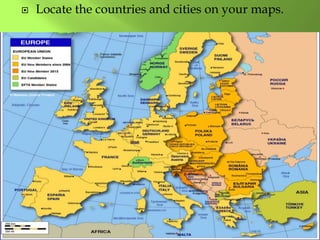
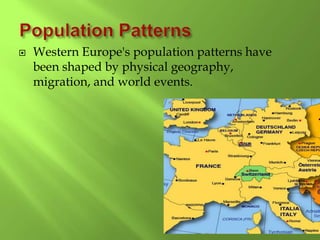
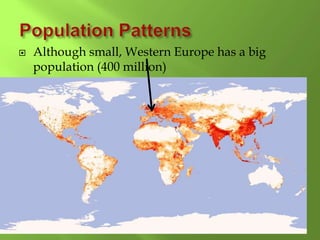
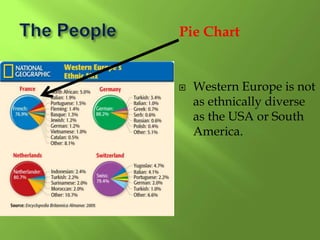
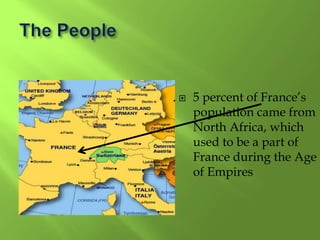
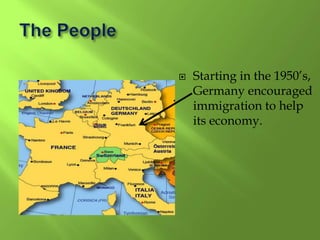
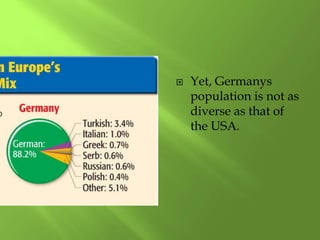
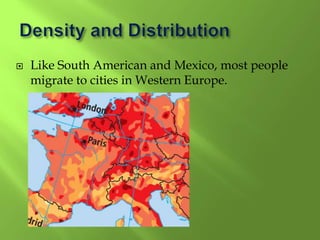
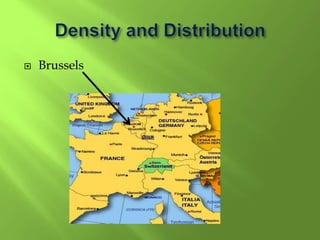
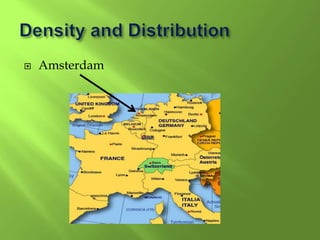
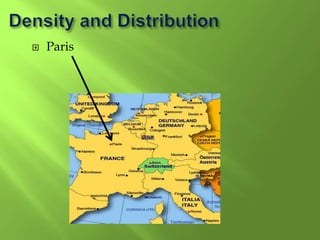
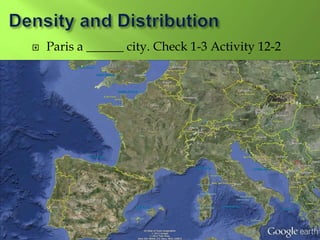
1) Western Europe's population patterns have been shaped by physical geography, migration, and world events. Major cities like Paris, Berlin, and Brussels are discussed.
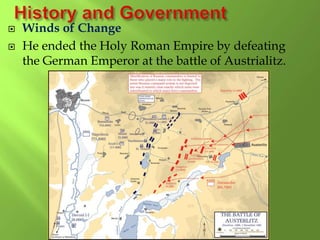
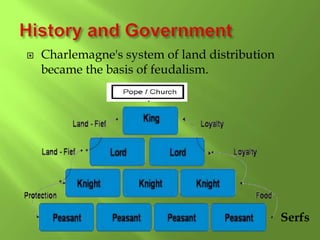
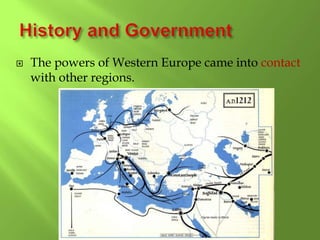
2) The region has a long history, from the Roman Empire to the Renaissance and periods like the Middle Ages and Reformation that influenced religion. Key figures that impacted the region are mentioned like Charlemagne and Martin Luther.
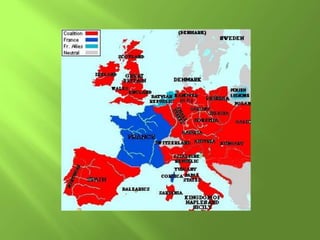
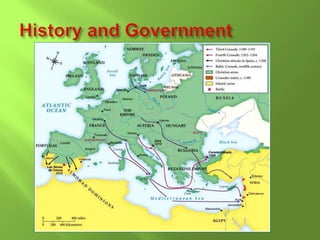
3) Major economic and political changes occurred like the French Revolution, which overthrew the monarchy and established a republic, influencing the growth of nationalism.






































































































![ Protestant Reformation, [a] a movement against
what the Protestants considered to be errors in
the Roman Catholic Church. It is one of the
major divisions of Christianity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/19-150907182810-lva1-app6892/85/19-western-europe-119-320.jpg)
































![TheRoyal FamilyAttempts
to Flee
June, 1791
Helped by the Swedish Count Hans Axel von
Fusen [Marie Antoinette’s lover].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/19-150907182810-lva1-app6892/85/19-western-europe-152-320.jpg)